Sodium Hydroxide And Sulfuric Acid Balanced Equation
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
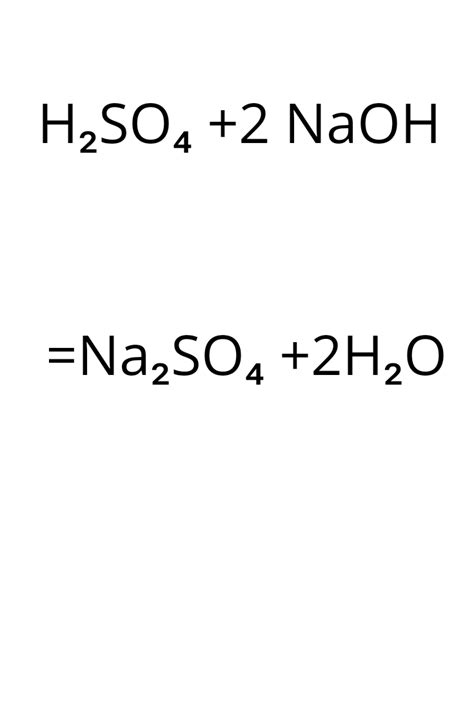
Table of Contents
Sodium Hydroxide and Sulfuric Acid: A Balanced Equation and Beyond
The reaction between sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a strong base, and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), a strong acid, is a classic example of a neutralization reaction. Understanding this reaction, from its balanced chemical equation to its practical applications and safety considerations, is crucial for anyone working with chemicals, especially in chemistry, engineering, and related fields. This article delves deep into this fundamental chemical process, exploring its intricacies and providing a comprehensive understanding.
The Balanced Chemical Equation
The reaction between sodium hydroxide and sulfuric acid produces sodium sulfate (Na₂SO₄) and water (H₂O). The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2NaOH(aq) + H₂SO₄(aq) → Na₂SO₄(aq) + 2H₂O(l)
This equation signifies that two moles of sodium hydroxide react with one mole of sulfuric acid to yield one mole of sodium sulfate and two moles of water. The (aq) indicates that the reactants and product are aqueous solutions (dissolved in water), and (l) denotes liquid water. The crucial aspect here is the stoichiometric ratio – the precise numerical relationship between reactants and products, which dictates the quantitative aspects of the reaction.
Understanding the Reaction Mechanism
This neutralization reaction is essentially a double displacement reaction, also known as a double replacement reaction. The hydrogen ions (H⁺) from the sulfuric acid react with the hydroxide ions (OH⁻) from the sodium hydroxide to form water. The sodium ions (Na⁺) and sulfate ions (SO₄²⁻) then combine to form sodium sulfate, a soluble salt.
This process involves the transfer of protons (H⁺) from the acid to the base, ultimately leading to the formation of a neutral solution (assuming the acid and base are completely neutralized). The pH of the resulting solution will depend on the relative amounts of acid and base used. If equal molar amounts react completely, the resulting solution will be neutral with a pH of 7.
Stoichiometric Calculations and Applications
The balanced equation is crucial for performing stoichiometric calculations. These calculations allow us to determine the amounts of reactants required or products formed in a given reaction. For example, if we know the amount of sulfuric acid used, we can calculate the amount of sodium hydroxide needed for complete neutralization, or vice-versa.
This knowledge has vast applications:
-
Titrations: Acid-base titrations are routinely performed to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base. By carefully adding a known concentration of one reactant (e.g., NaOH) to a known volume of the other (e.g., H₂SO₄), until the equivalence point is reached (neutral pH), we can calculate the concentration of the unknown. The balanced equation is essential for accurate calculations in these titrations.
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes involve neutralization reactions. For example, wastewater treatment plants often use sodium hydroxide to neutralize acidic waste streams before discharging them. The balanced equation helps engineers determine the exact amount of base needed for effective neutralization.
-
Chemical Synthesis: The neutralization reaction can be used in the synthesis of certain salts. By carefully controlling the reaction conditions, sodium sulfate, a common chemical with various industrial applications (detergents, paper manufacturing, etc.), can be produced with high purity.
-
Understanding pH Changes: The balanced equation, coupled with understanding molarity and stoichiometry, allows us to predict how the pH of a solution will change when a strong acid and a strong base are mixed. This is essential in controlling the pH of solutions for various applications, ranging from chemical reactions to biological processes.
Safety Precautions and Handling
Both sodium hydroxide and sulfuric acid are highly corrosive chemicals that require careful handling. Direct contact with skin or eyes can cause severe burns. Inhalation of their fumes can also be harmful. Therefore, it's crucial to observe the following safety precautions:
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety goggles, gloves, and a lab coat, when handling these chemicals.
-
Ventilation: Conduct experiments in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to minimize exposure to harmful fumes.
-
Dilution: Always add acid to water, never water to acid, when diluting sulfuric acid. This prevents splashing and minimizes the risk of burns.
-
Neutralization: In case of spills, immediately neutralize the spill with a suitable neutralizing agent. For sulfuric acid spills, a base like sodium bicarbonate can be used, while for sodium hydroxide spills, a weak acid like acetic acid is suitable.
-
Emergency Procedures: Have a thorough understanding of emergency procedures and know where to locate safety equipment like eyewash stations and safety showers.
The Role of Concentration and Reaction Rate
The rate at which the reaction proceeds is influenced by several factors:
-
Concentration: Higher concentrations of both reactants lead to faster reaction rates. This is because there are more reactant molecules available to collide and react.
-
Temperature: Increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the molecules, leading to more frequent and energetic collisions and thus a faster reaction rate.
-
Presence of Catalysts: Although rare in this specific reaction, a catalyst can increase the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed.
Applications of Sodium Sulfate (Na₂SO₄)
The sodium sulfate produced in this reaction has a wide range of industrial applications:
-
Detergent Industry: Sodium sulfate is used as a filler in detergents to improve their flowability and prevent caking.
-
Paper Manufacturing: It's used in the kraft pulping process in paper manufacturing.
-
Textile Industry: Sodium sulfate is used as a dyeing auxiliary in textile processing.
-
Medicine: It's used as a laxative.
-
Glass Manufacturing: It's employed in the manufacturing of certain types of glass.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts
The reaction between sodium hydroxide and sulfuric acid, while seemingly simple, offers opportunities to explore more advanced chemical concepts:
-
Thermodynamics: The reaction's enthalpy change (ΔH) can be determined experimentally or calculated using standard enthalpy of formation data. This gives insights into the reaction's energy changes and spontaneity.
-
Kinetics: The rate law for the reaction can be determined experimentally by measuring the rate of reaction at varying concentrations and temperatures.
-
Equilibrium: While this is a straightforward neutralization, the concept of equilibrium can be applied to understand the relative amounts of reactants and products at different stages of the reaction.
-
Electrochemistry: This reaction can be studied electrochemically by using appropriate electrodes to measure the potential changes during the reaction.
Conclusion
The reaction between sodium hydroxide and sulfuric acid is a fundamental chemical process with significant practical implications. Understanding the balanced chemical equation, stoichiometry, safety precautions, and applications of this reaction is essential for students and professionals in various scientific and industrial fields. Furthermore, exploring the reaction's more advanced aspects provides a deeper understanding of chemical principles and their applications in diverse contexts. This comprehensive overview highlights the importance of a thorough understanding of this seemingly simple yet profoundly significant chemical reaction. By mastering this reaction, a foundation for tackling more complex chemical problems is established, paving the way for further exploration and innovation in the field of chemistry and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Capacitance Is Required To Store An Energy Of
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Major Product Of The Following Reaction Sequence
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Lightyears Is The Sun
Mar 14, 2025
-
Convert Timestamp To Date Time Python
Mar 14, 2025
-
Difference Between A Monologue And A Soliloquy
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sodium Hydroxide And Sulfuric Acid Balanced Equation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
