Possesses Both The A And B Antigens
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
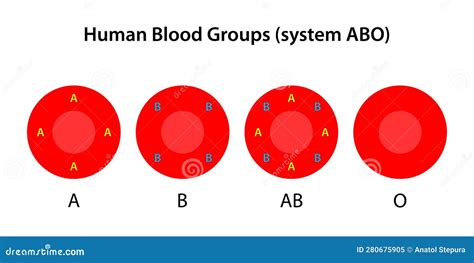
Table of Contents
Possessing Both A and B Antigens: Understanding the AB Blood Type
The human blood group system is a complex tapestry of antigens and antibodies, a critical aspect of our biology with significant implications for blood transfusions and overall health. One of the most fascinating and important aspects of this system is the AB blood type, characterized by the presence of both A and B antigens on the surface of red blood cells. This article delves into the intricacies of the AB blood type, exploring its genetics, prevalence, implications for blood transfusions, potential health risks, and its unique position within the broader blood group system.
The Genetics of AB Blood Type
The inheritance of blood type is determined by the combination of alleles (alternative forms of a gene) inherited from each parent. These alleles, designated as IA, IB, and i, determine the presence or absence of A and B antigens.
- IA: Codes for the production of A antigen.
- IB: Codes for the production of B antigen.
- i: Codes for the production of neither A nor B antigen (resulting in the O blood type).
The AB blood type arises from the inheritance of one IA allele and one IB allele, one from each parent. Because IA and IB are codominant alleles, meaning both are expressed equally, individuals with the AB blood type express both A and B antigens on their red blood cells. This contrasts with the homozygous IAIA or heterozygous IAi genotypes that result in blood type A, and the homozygous IBIB or heterozygous IBi genotypes that result in blood type B. The ii genotype results in blood type O, lacking both A and B antigens.
Understanding Codominance
Codominance is a key concept in understanding the AB blood type. Unlike incomplete dominance where the phenotype is a blend of the two alleles, in codominance, both alleles are fully expressed. Therefore, an individual with the AB blood type exhibits the characteristics of both A and B antigens without any blending or intermediate expression. This is reflected in the presence of both A and B antigens on the red blood cell surface.
Prevalence of AB Blood Type
The frequency of the AB blood type varies across different populations globally. It is generally less common than blood types A, B, or O. For example, it is relatively more common in certain parts of Asia and less frequent in many African and Native American populations. This variation reflects the complex interplay of historical migrations, genetic drift, and evolutionary pressures influencing allele frequencies within various populations. These variations highlight the fascinating genetic diversity inherent in the human population.
AB Blood Type and Blood Transfusions
The AB blood type holds a unique position in the context of blood transfusions. Individuals with AB blood type are often referred to as "universal recipients." This is because their plasma does not contain antibodies against either A or B antigens. Therefore, they can receive blood transfusions from individuals with blood types A, B, AB, and O, without triggering a potentially life-threatening immune response. However, this "universal recipient" status is a simplification, and careful blood typing and cross-matching are still essential before any transfusion to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Understanding Antibody Presence
While AB individuals lack A and B antibodies in their plasma, they do possess other antibodies against different blood group systems. Therefore, careful compatibility testing, beyond just A and B antigens, is crucial for safe transfusions. The absence of anti-A and anti-B antibodies in AB individuals is the primary reason for their designation as universal recipients, but it does not negate the need for meticulous pre-transfusion screening.
Potential Health Risks and Considerations for Individuals with AB Blood Type
While the AB blood type itself doesn't directly cause specific diseases, some studies suggest potential correlations between AB blood type and certain health conditions. However, these correlations are often complex and influenced by numerous other genetic and environmental factors. It is important to avoid drawing simplistic conclusions about health risks solely based on blood type.
Potential Associations (Require Further Research)
Several studies have explored potential links between AB blood type and a slightly increased risk of certain cardiovascular diseases and other conditions. These findings are often preliminary and require further investigation to confirm the causal relationship and understand the underlying mechanisms. It's crucial to remember that these are statistical associations, and the presence of AB blood type is not a deterministic factor for developing these conditions.
Importance of a Holistic Approach
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management, remains paramount for overall health, irrespective of blood type. The AB blood type is just one piece of a much larger puzzle, and focusing on healthy habits is far more impactful than solely focusing on blood type as a predictor of health outcomes.
AB Blood Type and Other Blood Group Systems
The ABO blood group system is only one of many blood group systems. Beyond the A and B antigens, there are numerous other antigens present on red blood cells, each contributing to the overall complexity of blood typing and transfusion compatibility. These systems, such as the Rh system (positive or negative), are equally important to consider during blood transfusions. A complete blood type profile encompasses the ABO system and other systems to ensure compatibility.
Rh Factor and its Importance
The Rh factor is a crucial component of blood typing and transfusions. It is independent of the ABO system. Individuals are either Rh positive (possessing the Rh D antigen) or Rh negative (lacking the Rh D antigen). Rh incompatibility, especially between an Rh-negative mother and an Rh-positive fetus, can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn. Understanding both the ABO and Rh blood types is critical for safe blood transfusions and managing pregnancy-related complications.
Conclusion: The Significance of AB Blood Type
The AB blood type, with its unique characteristic of possessing both A and B antigens, offers a fascinating insight into the complexities of human genetics and blood group systems. While it does not directly cause specific diseases, understanding its genetic basis, prevalence, implications for blood transfusions, and potential associations with certain health conditions is crucial. This knowledge emphasizes the importance of careful blood typing and cross-matching procedures for safe transfusions and promotes a more holistic understanding of health and well-being. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the potential links between AB blood type and specific health outcomes, but the current understanding highlights the significant role of this blood type within the broader context of human biology. Remember, while blood type is an important factor to consider, it's just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to overall health and well-being. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle remains the most crucial aspect for preventing and managing health conditions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Has The Largest Inertia
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Components Of Nucleotides
Mar 20, 2025
-
Is Fluorine A Cation Or Anion
Mar 20, 2025
-
Find The Matrix A Such That
Mar 20, 2025
-
A Group Of Tissues That Work Together
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Possesses Both The A And B Antigens . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
