Number Of Valence Electrons In Magnesium
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
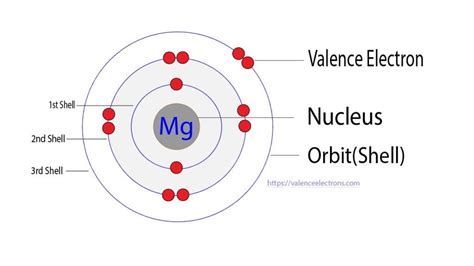
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into Magnesium: Unveiling the Secrets of its Valence Electrons
Magnesium, a silvery-white alkaline earth metal, plays a crucial role in various biological and industrial processes. Understanding its electronic structure, particularly the number of valence electrons, is key to comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. This in-depth exploration will unravel the intricacies of magnesium's valence electrons, examining its electronic configuration, bonding characteristics, and its significance in diverse applications.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Reactivity
Before delving into magnesium's specifics, let's establish a foundational understanding of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom's electron shell. These electrons are the primary players in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it can form. The number of valence electrons dictates the atom's capacity to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, typically resembling a noble gas. This stability is often achieved by having a full outermost shell, a principle explained by the octet rule.
Magnesium's Electronic Configuration: A Closer Look
Magnesium (Mg), with an atomic number of 12, possesses 12 electrons. To understand its valence electrons, we must examine its electronic configuration. Using the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule, we arrive at the following electronic configuration: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s².
This configuration reveals the distribution of electrons across different energy levels (shells) and sub-levels (orbitals). The first shell (n=1) contains two electrons in the 1s orbital. The second shell (n=2) holds eight electrons, with two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbitals. Finally, the third shell (n=3) contains the remaining two electrons in the 3s orbital.
Identifying Magnesium's Valence Electrons
Since valence electrons are the outermost electrons, we identify them as those residing in the highest principal energy level (the outermost shell). In magnesium's case, the outermost shell is the third shell (n=3), which contains two electrons in the 3s orbital. Therefore, magnesium possesses two valence electrons.
Magnesium's Chemical Behavior: Driven by its Valence Electrons
Magnesium's two valence electrons are the driving force behind its chemical behavior. Because it's easier for magnesium to lose these two electrons than to gain six more to complete its octet, it readily forms cations (positively charged ions) with a +2 charge. This tendency to lose electrons makes magnesium a highly reactive metal.
Ionic Bonding: Magnesium's Preferred Bonding Mechanism
Magnesium's reactivity is evident in its formation of ionic bonds. When magnesium reacts with a non-metal, such as chlorine, it loses its two valence electrons to chlorine atoms. Each chlorine atom gains one electron, achieving a stable octet. The resulting ions, Mg²⁺ and Cl⁻, are held together by electrostatic attraction, forming the ionic compound magnesium chloride (MgCl₂).
This ionic bonding mechanism is crucial in many of magnesium's applications, as it contributes to the formation of various stable compounds with crucial properties.
Other Bonding Interactions: A Secondary Role
While ionic bonding is magnesium's dominant bonding mechanism, it can also participate in other bonding interactions to a lesser extent. For instance, magnesium can form metallic bonds with other magnesium atoms, contributing to its metallic properties such as conductivity and malleability. While these bonds involve the valence electrons, their contribution is secondary to the ionic bonding behavior that dominates magnesium's chemical interactions.
Significance of Magnesium's Two Valence Electrons in Diverse Applications
Magnesium's two valence electrons are directly responsible for its various applications across diverse fields:
1. Metallurgy and Alloys: Lightweight and Strong
The low density of magnesium, coupled with its relatively high strength, makes it invaluable in the production of lightweight alloys. These alloys are extensively used in the automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics industries. The presence of two valence electrons allows magnesium to readily form alloys with other metals, tailoring the properties of the final material. These alloys combine strength and lightness, leading to improved fuel efficiency in vehicles and lighter, more durable electronic devices.
2. Biological Importance: A Vital Nutrient
Magnesium is an essential mineral for human health. It plays a crucial role in numerous enzymatic reactions, muscle function, nerve transmission, and maintaining healthy bones. The two valence electrons influence magnesium's ability to interact with biological molecules and participate in these vital processes. Magnesium's presence in chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants essential for photosynthesis, also highlights its crucial role in the biosphere. Its ability to readily participate in electron transfer reactions is a key aspect of its biological functionality.
3. Chemical Industry: Versatile Reactant
Magnesium's reactivity, driven by its two valence electrons, makes it a valuable reagent in various chemical processes. It is used as a reducing agent in the production of other metals, as well as in organic synthesis, where it participates in Grignard reactions. This reactivity stems directly from its willingness to readily donate its two valence electrons.
4. Pyrotechnics: A Bright and Brilliant Element
Magnesium's ability to burn with an intensely bright white flame is utilized extensively in pyrotechnics. The combustion of magnesium involves its valence electrons being involved in redox reactions, leading to the release of significant energy in the form of light and heat. This characteristic makes it an important component of flares, fireworks, and other pyrotechnic devices.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts
The number of valence electrons in magnesium provides a foundational understanding of its chemical behavior. However, a deeper dive reveals more sophisticated aspects:
Effective Nuclear Charge and Shielding Effect
The effective nuclear charge experienced by magnesium's valence electrons is relatively low due to the shielding effect of the inner electrons. This lower effective nuclear charge contributes to magnesium's tendency to lose its valence electrons relatively easily.
Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity
Magnesium's relatively low first and second ionization energies reflect the ease with which it loses its two valence electrons. Its electron affinity is relatively low, indicating that it doesn't readily gain electrons.
Atomic Radius and Metallic Character
Magnesium's atomic radius is relatively small, contributing to its high density and metallic character. The two valence electrons contribute to the metallic bonding that governs its physical properties.
Conclusion: The Significance of Magnesium's Two Valence Electrons
In conclusion, the two valence electrons in magnesium are not merely a numerical fact; they are the cornerstone of magnesium's chemical reactivity, bonding behavior, and its diverse applications. Understanding the number and role of these electrons is crucial to appreciating magnesium's significance in various fields, from lightweight alloys to biological systems. The detailed analysis presented in this article demonstrates the importance of relating basic electronic configuration to the complex behavior and applications of an element like magnesium. Its two valence electrons are the key to unlocking its properties and potential. Further research and exploration into magnesium's chemistry will continue to reveal its importance and uncover new potential applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Steroid Hormone
Mar 24, 2025
-
The Layer Of Gases Surrounding Earth Is The
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is 3 Percent Of 18
Mar 24, 2025
-
In Triangle Abc The Measure Of Angle B Is 90
Mar 24, 2025
-
Write The Iupac Name Of The Compound Shown
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Number Of Valence Electrons In Magnesium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
