Mountain Range Separating Europe From Asia
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
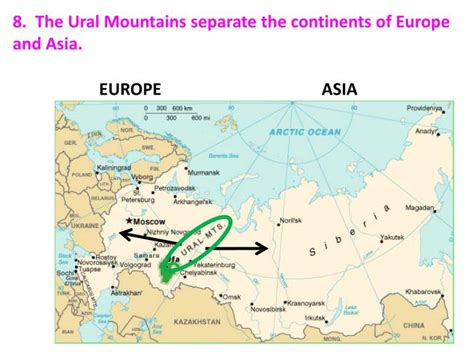
Table of Contents
The Ural Mountains: Dividing Europe and Asia – A Natural Boundary and Cultural Crossroads
The Ural Mountains, a seemingly unassuming range stretching over 2,500 kilometers (1,550 miles) from the Arctic Ocean to the vast steppes of Kazakhstan, stand as a significant geographical feature. More than just a mountain range, the Urals represent a complex geological, ecological, and historical boundary, traditionally marking the continental divide between Europe and Asia. While the precise demarcation remains a subject of debate among geographers, the Urals' unique characteristics and historical significance solidify its role in shaping the landscapes and cultures of both continents.
A Geological Tapestry Woven Over Millions of Years
The formation of the Ural Mountains is a testament to the powerful forces of plate tectonics. Unlike the dramatic, jagged peaks of younger mountain ranges formed by recent tectonic collisions, the Urals are a considerably older range. Their creation began around 300 million years ago during the Paleozoic Era, the result of a collision between the East European Craton and the Siberian Craton. This monumental event crumpled and folded layers of ancient rocks, creating the mountain range we see today.
The Uralian Orogeny: A Defining Moment
The collision, known as the Uralian Orogeny, was a protracted process lasting tens of millions of years. This tectonic upheaval resulted in the formation of diverse rock formations, including igneous rocks like granite and basalt, metamorphic rocks like schist and gneiss, and sedimentary rocks deposited over millions of years. This geological diversity contributes to the varied landscapes and mineral wealth of the Urals. The range is rich in mineral deposits, including iron ore, copper, nickel, platinum, gold, and diamonds, which have historically played a significant role in the region's economic development.
Erosion's Gentle Hand: Shaping the Landscape
Millions of years of erosion have shaped the Ural Mountains into their current form. While lacking the towering peaks of the Himalayas or the Alps, the Urals offer a range of stunning landscapes. Gentle slopes and rolling hills characterize much of the range, particularly in the southern sections. However, the northern Urals boast more dramatic peaks, deep valleys carved by glaciers, and rugged terrain, influenced by ice ages. This interplay of geological processes and weathering contributes to the region's biodiversity.
Biodiversity Hotspots: A Rich Ecosystem in a Unique Setting
The Ural Mountains are home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, adapted to the varying climates and elevations. The taiga, or boreal forest, dominates the northern parts of the range, characterized by coniferous trees like spruce, fir, and pine. As one moves south, the taiga gradually transitions into mixed forests, featuring deciduous trees like birch and aspen, interspersed with coniferous species. Steppe grasslands stretch across the southern foothills, providing a stark contrast to the forested slopes above.
Wildlife of the Urals: A Tapestry of Life
The Urals' varied ecosystems support a rich array of wildlife. Large mammals like brown bears, wolves, lynx, elk, and wild boar roam the forests. Smaller mammals such as foxes, badgers, and various species of rodents are also common. A variety of bird species, including owls, eagles, and numerous migratory birds, inhabit the forests and mountains. The rivers and lakes teeming with fish such as pike, perch, and trout provide crucial food sources and support aquatic ecosystems.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting the Uralian Heritage
Recognizing the importance of preserving the Urals' unique biodiversity, several national parks and reserves have been established. These protected areas safeguard vital habitats and help maintain the ecological integrity of the mountain range. However, pressures such as logging, mining, and industrial activities continue to pose threats to the region's natural environment, highlighting the ongoing need for effective conservation measures.
The Urals as a Cultural and Historical Divide: A Blurred Line
The Ural Mountains have served as a significant geographical and cultural boundary, influencing the historical development and cultural identities of both Europe and Asia. However, the line separating the two continents is not a clear-cut division; rather, it's a zone of transition where cultural influences have blended over centuries.
A Shifting Boundary: Defining Europe and Asia
The exact location of the boundary between Europe and Asia is not universally agreed upon. While many geographers use the Ural Mountains as the primary marker, other features like the Ural River, the Emba River, and the Kuma-Manych Depression are also considered. This ambiguity reflects the complexities of defining continental boundaries, which often blend seamlessly.
Historical Crossroads: Migration and Cultural Exchange
The Ural Mountains have served as a corridor for migration and cultural exchange throughout history. Nomadic peoples such as the Scythians and various Turkic groups migrated through the Urals, shaping the cultural landscape of both continents. The region's rich mineral deposits attracted settlers and traders, leading to the development of numerous towns and cities along the mountain range.
The Influence of the Soviet Era: A Period of Industrialization
The Soviet era witnessed significant industrial development in the Ural region. Vast reserves of minerals and resources fueled rapid industrial growth, transforming the landscape and shaping the lives of the people who inhabited the region. This period also influenced cultural exchange and the blending of different traditions within the broader Soviet context.
The Ural Mountains Today: Economic Significance and Tourism
The Ural Mountains continue to play a vital economic role, owing to their rich mineral resources. Mining remains a significant industry, contributing to the region's economy. The region also supports other industries, including forestry, metalworking, and energy production. However, the transition to a more sustainable and diversified economy is crucial for ensuring long-term economic growth.
Ecotourism and Adventure: Exploring the Urals
In recent years, the Ural Mountains have gained recognition as a destination for ecotourism and adventure tourism. Hiking, climbing, skiing, and exploring the region's diverse landscapes are popular activities. The stunning natural beauty, coupled with the region's rich history and culture, offers a unique blend of experiences for visitors.
Sustainable Development: Balancing Economic Growth and Environmental Protection
Balancing economic growth with environmental protection is a crucial challenge facing the Ural region. Sustainable development practices, including responsible mining, eco-tourism initiatives, and investments in renewable energy sources, are essential for ensuring the long-term health of the environment and the well-being of the region's inhabitants. The preservation of biodiversity hotspots and the reduction of environmental pollution are key priorities.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Natural Wonder and Human Endeavor
The Ural Mountains stand as a testament to the power of geological forces, shaping landscapes, influencing biodiversity, and acting as a historical and cultural crossroads between Europe and Asia. Their rich mineral resources have fueled economic development, while their diverse ecosystems support a wealth of plant and animal life. The blurred line dividing continents highlights the complex interplay of geography, culture, and history. As the region moves forward, striking a balance between sustainable development and environmental conservation is vital to preserving the legacy of the Urals for future generations. The mountains, once a natural barrier, now serve as a unique and captivating region for exploration, research, and economic opportunity. The future of the Urals depends on mindful stewardship and a forward-looking approach to balancing the needs of people with the preservation of its natural beauty.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Boiling Water Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 17, 2025
-
45 Is 60 Of What Number
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is Larger Mg Or Mcg
Mar 17, 2025
-
0 3 To The Power Of 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 5 Percent Of 200
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Mountain Range Separating Europe From Asia . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
