Mountain Range Separating Europe And Asia
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 7 min read
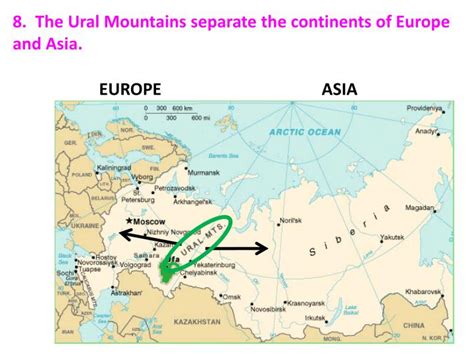
Table of Contents
The Ural Mountains: A Geographical Divide Between Europe and Asia
The Ural Mountains, a seemingly unassuming range stretching over 1,500 miles (2,400 kilometers) from the Arctic Ocean to the steppes of Kazakhstan, mark a significant geographical boundary: the traditional dividing line between Europe and Asia. While this division is more of a historical and cultural convention than a strictly defined geological one, the Urals hold a unique position in the world's geography, representing a fascinating blend of natural history, cultural significance, and geopolitical importance. This exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of the Ural Mountains, examining their geological formation, ecological diversity, historical impact, and contemporary significance.
Geological Formation: A Tapestry of Time and Tectonic Shifts
The Ural Mountains are ancient, their formation dating back to the Paleozoic Era, specifically the late Paleozoic period around 300-250 million years ago. Unlike the towering Himalayas or the Andes, which are the product of relatively recent plate collisions, the Urals are the remnants of a much older mountain-building process. Their creation involved the collision of the East European and Siberian cratons – ancient continental landmasses. This continental collision, a titanic event in Earth's history, resulted in immense pressure and folding of the Earth's crust, generating a range of mountains that initially reached significantly greater heights than they do today.
Millions of years of erosion and weathering have significantly reduced their elevation. The highest peak, Mount Narodnaya, only reaches 6,217 feet (1,895 meters) above sea level, illustrating the relentless forces of nature sculpting the landscape over vast spans of time. While seemingly modest in height compared to other mountain ranges globally, the Urals' extent and geological complexity are noteworthy. The range is characterized by a diverse array of rock formations, including metamorphic, igneous, and sedimentary rocks, reflecting the intense geological processes that shaped them. These diverse rock formations, in turn, support a remarkable variety of ecosystems.
Mineral Wealth: A Legacy of Geological Processes
The collision of continents that formed the Urals also led to the creation of vast mineral deposits. The range is renowned for its rich reserves of various minerals, including iron ore, copper, nickel, platinum, chromium, and coal. These resources have played a pivotal role in the economic and industrial development of Russia, with mining activity shaping the region's history and demographics for centuries. The discovery and exploitation of these mineral deposits have attracted human settlements and spurred technological advancements, further weaving the Ural Mountains into the fabric of human civilization. The historical and ongoing economic significance of the Urals cannot be overstated; its mineral wealth continues to be a vital component of Russia's economy.
Ecological Diversity: From Tundra to Steppes
The Ural Mountains' longitudinal stretch across diverse latitudes results in a remarkable variation in ecosystems. The northern regions are characterized by tundra, a stark landscape of low-lying vegetation, permafrost, and harsh climatic conditions. Moving southward, the landscape transitions into taiga, a vast boreal forest dominated by coniferous trees like spruce, fir, and pine. This taiga constitutes a significant portion of the range’s ecological character, harboring a rich biodiversity of fauna including wolves, bears, lynx, and numerous avian species. Further south, the taiga gives way to mixed forests, eventually transitioning into steppe grasslands towards the southern end of the range. This ecological gradient reflects the influence of both latitude and altitude on the distribution of plant and animal life, making the Ural Mountains a compelling study for ecologists and biogeographers.
Wildlife and Conservation: Protecting a Unique Heritage
The diverse ecosystems within the Ural Mountains support a unique assemblage of plant and animal species. Many of these species are endemic, meaning they are found nowhere else on Earth, highlighting the range’s importance for biodiversity conservation. However, the region has faced environmental challenges, including historical overexploitation of natural resources and the impacts of industrialization. Efforts towards conservation are ongoing, with the establishment of national parks and protected areas designed to safeguard the region’s rich biodiversity and maintain its ecological integrity. The future conservation of the Ural Mountains requires a balanced approach that integrates economic development with environmental protection to ensure the sustainability of its unique natural resources.
Historical and Cultural Significance: A Crossroads of Civilizations
The Ural Mountains have served as a significant geographical feature shaping human history and culture for millennia. Their role as a natural barrier influenced migration patterns, trade routes, and the development of distinct cultures on either side of the divide. The region has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires and kingdoms, serving as both a conduit for cultural exchange and a boundary between distinct spheres of influence. The presence of numerous ancient settlements and archaeological sites attests to the long history of human habitation within and around the Urals.
The Ural Mountains and the Russian Empire: A Pivotal Role
The Ural Mountains held particular significance for the Russian Empire and its successor, the Russian Federation. The region's mineral wealth fueled industrial growth, and its strategic location facilitated communication and control over vast territories. The Urals functioned as a crucial link between European Russia and its vast Asian territories, playing a central role in the expansion and consolidation of the Russian Empire's power. Numerous industrial cities developed along the range, transforming it from a relatively sparsely populated region into a hub of industrial activity. This industrialization, while having fostered economic growth, also introduced environmental challenges requiring careful management and regulation.
Geopolitical Significance: A Borderland of Continents
The Ural Mountains' designation as the boundary between Europe and Asia is a convention, rather than a rigidly defined geological or political frontier. The line itself is somewhat arbitrary, traversing a geographical transition zone, blurring the sharp division that maps might suggest. Nonetheless, the historical and cultural significance attributed to the Urals as a demarcation line persists. This perceived border has influenced political boundaries, trade routes, and cultural interactions throughout history. The region's geopolitical importance continues, given its role as a conduit between Eastern Europe and Asia.
Challenges and Opportunities in the 21st Century
The Ural Mountains face various challenges and opportunities in the 21st century. Sustainable resource management is crucial to balance economic development with environmental protection. Efforts to diversify the economy, reduce dependence on resource extraction, and promote sustainable tourism are gaining traction. The region's strategic location along key transportation routes continues to be significant, especially given its potential role in facilitating trade and economic cooperation between Europe and Asia. Managing environmental challenges, such as pollution from industrial activities and mitigating the effects of climate change, remains a major priority. The successful navigation of these challenges will determine the Ural Mountains' future, balancing economic development with environmental sustainability and cultural preservation.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Enduring Landscape
The Ural Mountains, though not imposing in their height, possess remarkable geological, ecological, and historical significance. Their formation, resulting from the collision of ancient continents, produced a rich tapestry of rock formations and mineral deposits. The range's longitudinal spread across a diverse array of latitudes yields a significant variation in ecosystems, from the frigid tundra to the fertile steppes. The Urals have played a vital role in shaping the history and culture of the region, influencing migration patterns, trade routes, and the rise and fall of empires. Furthermore, the designation of the Ural Mountains as the boundary between Europe and Asia underscores their ongoing geopolitical significance. Understanding the Ural Mountains requires a multi-faceted approach, acknowledging the interplay between geological processes, ecological dynamics, and human history. Managing the challenges and seizing the opportunities of the 21st century will ensure that the Ural Mountains continue to serve as a dynamic and enduring landscape for generations to come. The region’s preservation, its sustainable economic development, and its cultural heritage require careful attention and a holistic strategy ensuring both environmental and social well-being. The legacy of the Urals is not just one of geology and geography; it's a rich tapestry woven from the threads of time, human endeavour, and the enduring power of nature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
45 Is 60 Of What Number
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is Larger Mg Or Mcg
Mar 17, 2025
-
0 3 To The Power Of 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 5 Percent Of 200
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The 5 Difference Between Photosynthesis And Respiration
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Mountain Range Separating Europe And Asia . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
