Mass Of An Electron In Amu
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
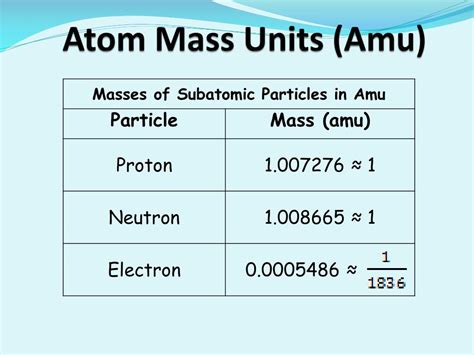
Table of Contents
The Mass of an Electron in AMU: A Deep Dive
The electron, a fundamental subatomic particle, plays a crucial role in the structure of atoms and the behavior of matter. Understanding its properties, particularly its mass, is fundamental to grasping many concepts in physics and chemistry. This article delves into the mass of an electron, expressed in atomic mass units (amu), exploring its measurement, significance, and applications. We'll also examine the related concepts of atomic mass, molar mass, and the implications of the electron's mass in various scientific fields.
What is an Atomic Mass Unit (amu)?
Before diving into the electron's mass, let's clarify the unit of measurement: the atomic mass unit (amu), also known as the dalton (Da). The amu is a standard unit used to express the mass of atoms and molecules. Historically, it was defined as 1/16 the mass of an oxygen-16 atom. However, the modern definition, adopted by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), is more precise: one atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This means one amu is approximately 1.66054 × 10⁻²⁷ kilograms. Using this standardized definition ensures consistent and accurate measurements across scientific disciplines.
Determining the Mass of an Electron
Accurately determining the mass of an electron presented a significant challenge to early scientists. Unlike larger particles, the electron's small mass makes direct measurement incredibly difficult. Several methods have been employed over time, leading to progressively more precise values.
Early Experiments and Millikan's Oil Drop Experiment
Early experiments focused on studying the behavior of electrons in electric and magnetic fields. The groundbreaking work of Robert Millikan with his famous oil drop experiment played a crucial role. While primarily designed to determine the elementary charge of the electron (e), Millikan's experiment also provided crucial data that contributed to the estimation of the electron's mass. By observing the motion of charged oil droplets under the influence of gravity and electric fields, Millikan could deduce the charge-to-mass ratio (e/m) of the electron.
Combining Charge-to-Mass Ratio with Elementary Charge
Once the elementary charge (e) was accurately determined, scientists could calculate the electron's mass (m) using the known charge-to-mass ratio: m = e / (e/m). This approach, combined with advancements in experimental techniques, progressively refined the estimate of the electron's mass.
Modern Techniques and Precise Measurement
Modern techniques utilize sophisticated methods, such as mass spectrometry and advanced particle accelerators, to achieve extremely high precision in measuring the electron's mass. These methods leverage the interaction of electrons with electromagnetic fields and other particles to derive its mass with remarkable accuracy.
The Mass of an Electron in AMU
The accepted value for the mass of an electron is approximately 5.48579909070 × 10⁻⁴ amu. This incredibly small mass highlights the electron's relatively insignificant contribution to the overall mass of an atom, especially when compared to the mass of protons and neutrons within the atom's nucleus.
Comparing Electron Mass to Proton and Neutron Mass
To appreciate the scale of the electron's mass, consider comparing it to the masses of protons and neutrons:
- Proton mass: Approximately 1.007276 amu
- Neutron mass: Approximately 1.008665 amu
The electron's mass is roughly 1/1836 the mass of a proton and approximately 1/1839 the mass of a neutron. This significant mass difference explains why the mass of an atom is primarily determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
Significance of Electron Mass in Atomic and Molecular Physics
The electron's mass, although small, has profound implications in various scientific fields:
Atomic Structure and Isotopes
The negligible mass of electrons means that the atomic mass number (A) of an atom is essentially determined by the sum of its protons and neutrons. This is crucial in understanding the concept of isotopes, which are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but differing numbers of neutrons, thus having different atomic masses. The slight mass difference due to different neutron numbers is far more significant than the electron's mass contribution.
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Properties
While the electron's mass is small, its charge and orbital behavior are crucial for chemical bonding. Electrons involved in covalent and ionic bonds influence the strength and nature of chemical bonds, ultimately determining the properties of molecules and compounds. The mass of the electrons involved doesn't directly influence bond strength but indirectly plays a role in the overall dynamics of electron interactions.
Spectroscopy and Quantum Mechanics
Electron mass is essential in various spectroscopic techniques and quantum mechanical calculations. The energy levels and transitions of electrons within an atom are directly influenced by their mass, which dictates their behavior in electromagnetic fields and their interaction with photons. Accurate calculations of atomic and molecular spectra rely on precisely knowing the mass of the electron.
Nuclear Physics and Particle Physics
While the electron's mass might seem negligible compared to nuclear particles, it plays a role in certain nuclear processes and particle physics phenomena. For instance, understanding electron capture (a type of radioactive decay) requires considering the electron's mass and interaction with the nucleus. Furthermore, the electron's mass is part of the broader context of particle physics and its role in the Standard Model of particle physics.
Applications and Further Exploration
Understanding the electron's mass is critical in numerous applications:
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry techniques heavily rely on the precise mass-to-charge ratio of ions, including those involving electrons. Accurate determination of electron mass is essential for calibrating and interpreting mass spectrometry data, which is vital in various fields, including proteomics, metabolomics, and forensic science.
Materials Science and Nanotechnology
The properties of materials depend strongly on the electronic structure and interactions within the material. A precise understanding of the electron's mass is essential for modeling and predicting the behavior of materials at the atomic and molecular levels, which has significant implications in materials science and nanotechnology.
Astrophysics and Cosmology
Even the seemingly insignificant mass of the electron plays a role in astrophysical and cosmological processes. In stellar nucleosynthesis and the evolution of stars, electron pressure and electron-proton interactions are vital factors that influence the stability and lifetime of stars.
Conclusion
The mass of an electron, though minuscule compared to protons and neutrons, is a fundamental constant with far-reaching consequences in various scientific fields. From the structure of atoms to the behavior of materials and the evolution of stars, understanding this seemingly insignificant mass is essential for a deeper understanding of the universe around us. The ongoing refinement of measurement techniques will continue to improve the accuracy of the electron's mass, providing a more robust foundation for scientific understanding and advancement. The journey to precisely determining this value showcases the ingenuity and perseverance of scientists in their relentless quest to unlock the secrets of the universe at its most fundamental level. Further research into the properties of the electron and its interactions with other particles will undoubtedly contribute to even more significant scientific breakthroughs in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Periodic Table Group Contains Only Metals
Mar 24, 2025
-
A Flat Surface That Extends Infinitely In All Directions
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Function Of Political Parties
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Are The 4 Types Of Possession
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Intellectual Property
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Mass Of An Electron In Amu . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
