Is Supports Combustion A Physical Property
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
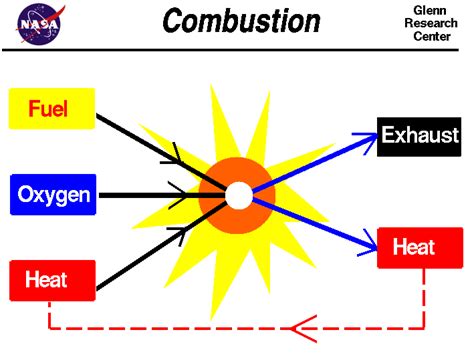
Table of Contents
Is Supporting Combustion a Physical Property? Delving into the Nature of Chemical and Physical Changes
The question of whether supporting combustion is a physical or chemical property often sparks debate. Understanding the distinction between physical and chemical properties is crucial for correctly classifying this characteristic. This comprehensive article will explore the nature of combustion, delve into the definitions of physical and chemical properties, and definitively answer whether supporting combustion is a physical property. We will also examine related concepts and provide illustrative examples.
Understanding Combustion: A Chemical Reaction
Combustion, at its core, is a rapid chemical reaction between a substance (the fuel) and an oxidant (usually oxygen), producing heat and light. This process involves the breaking and forming of chemical bonds, resulting in the creation of entirely new substances. The products of combustion often include carbon dioxide, water, and other oxides, depending on the nature of the fuel. Crucially, this transformation is irreversible; you can't easily revert the products back to the original fuel and oxygen.
Key Characteristics of Combustion:
- Exothermic Reaction: Combustion releases a significant amount of energy in the form of heat, making it an exothermic process.
- Rapid Oxidation: The reaction occurs swiftly, often characterized by flames or glowing embers.
- Chemical Change: The fundamental chemical structure of the reactants (fuel and oxygen) changes, producing new substances.
- Irreversible: The products of combustion cannot be easily converted back into the original reactants.
Defining Physical and Chemical Properties
To determine whether supporting combustion is a physical or chemical property, we need clear definitions:
Physical Properties:
Physical properties describe the characteristics of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing its chemical composition. These properties can often be reversed. Examples include:
- Color: The visual appearance of a substance.
- Density: The mass per unit volume.
- Melting Point: The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
- Boiling Point: The temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas.
- Solubility: The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent.
- Conductivity: The ability of a substance to conduct electricity or heat.
- Hardness: Resistance to scratching or indentation.
- Odor: The smell of a substance.
Chemical Properties:
Chemical properties describe how a substance reacts with other substances or its ability to undergo a chemical change. These properties involve changes in chemical composition. Examples include:
- Flammability: The ability of a substance to burn in the presence of oxygen.
- Reactivity with acids: How a substance reacts when exposed to an acid.
- Toxicity: The degree to which a substance is poisonous.
- Corrosion Resistance: The ability of a substance to withstand chemical attack.
Why Supporting Combustion is a Chemical Property
The ability of a substance to support combustion is inherently linked to its chemical reactivity with the fuel undergoing combustion. Substances that support combustion, such as oxygen, act as oxidants, directly participating in the chemical reaction. Oxygen doesn't merely facilitate the burning process; it's a fundamental reactant, forming chemical bonds with the fuel molecules.
The process of combustion involves the oxidation of the fuel, a chemical change that fundamentally alters the molecular structure of the fuel. The oxidant, in this case oxygen, undergoes a chemical transformation as well, becoming incorporated into the products of combustion (e.g., water, carbon dioxide). Therefore, the ability to support combustion is a direct reflection of a substance's chemical reactivity.
Examples Illustrating the Chemical Nature of Supporting Combustion:
- Oxygen (O2): Oxygen is the most common supporter of combustion. Its reaction with a fuel like methane (CH4) produces carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), demonstrating a clear chemical transformation.
- Chlorine (Cl2): While less common than oxygen, chlorine can support combustion with certain fuels, producing different chemical products. This again demonstrates a chemical reaction rather than a physical interaction.
- Fluorine (F2): Fluorine is a highly reactive element that vigorously supports combustion, even with materials typically considered non-flammable. This is another clear example of a chemical interaction.
Distinguishing Between Supporting Combustion and Physical Properties that Influence Combustion
It's crucial to differentiate between a substance's ability to support combustion (a chemical property) and physical properties that influence the rate or intensity of combustion. For example:
- Surface Area: A finely divided fuel will burn more rapidly than a large, solid chunk of the same material due to increased surface area for oxygen contact. This is a physical property affecting reaction kinetics, not the chemical nature of supporting combustion itself.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures can initiate and accelerate combustion. This is a physical property affecting reaction rate, not the chemical nature of combustion itself.
- Pressure: Increased pressure can increase the concentration of reactants, influencing combustion rate. Again, a physical property impacting reaction kinetics, not the chemical aspect of supporting combustion.
These physical properties affect the rate and efficiency of combustion, but they don't change the fundamental fact that combustion is a chemical reaction requiring an oxidant (like oxygen). The ability of a substance to act as an oxidant and participate in the chemical reaction of combustion remains a chemical property.
Conclusion: A Definitive Answer
Supporting combustion is unequivocally a chemical property. It is intrinsically linked to the chemical reactivity of a substance, its ability to participate in a chemical reaction with a fuel, leading to the formation of new substances and the release of energy. While physical properties like surface area and temperature can influence the rate and intensity of combustion, the underlying ability to support combustion itself is a characteristic of a substance's chemical nature. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate scientific classification and analysis of chemical phenomena.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Intermolecular Forces Are Present In Ch4
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Man Was Murdered In His Office Riddle
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Coil Is Formed By Winding 250 Turns
Mar 28, 2025
-
A Rotating Fan Completes 1200 Revolutions
Mar 28, 2025
-
1 Meter Equals How Many Millimeters
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Supports Combustion A Physical Property . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
