Is Supporting Combustion A Physical Or Chemical Property
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
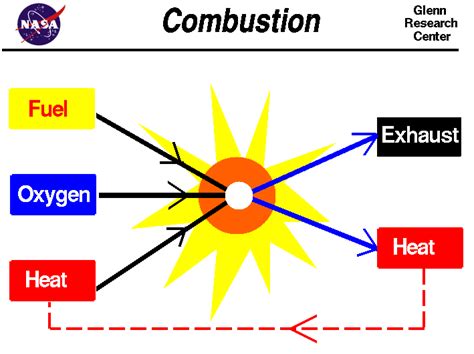
Table of Contents
- Is Supporting Combustion A Physical Or Chemical Property
- Table of Contents
- Is Supporting Combustion a Physical or Chemical Property? A Deep Dive
- Understanding Physical and Chemical Properties
- Physical Properties
- Chemical Properties
- Combustion: A Chemical Process
- Supporting Combustion: A Chemical Property
- Differentiating Physical Changes from Chemical Changes Related to Combustion
- Practical Examples
- Conclusion: Supporting Combustion is a Chemical Property
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Is Supporting Combustion a Physical or Chemical Property? A Deep Dive
The question of whether supporting combustion is a physical or chemical property often arises in chemistry discussions. It's a nuanced question that requires a thorough understanding of both physical and chemical properties, and the intricate processes involved in combustion itself. This article will delve deep into this topic, exploring the definitions, differentiating characteristics, and ultimately providing a conclusive answer.
Understanding Physical and Chemical Properties
Before diving into the specifics of combustion, let's solidify our understanding of the fundamental difference between physical and chemical properties.
Physical Properties
Physical properties are characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the substance's chemical composition. These properties describe the substance's inherent nature without altering its molecular structure. Examples include:
- Color: The visual appearance of a substance.
- Density: Mass per unit volume.
- Melting point: The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
- Boiling point: The temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas.
- Solubility: The ability to dissolve in a solvent.
- Odor: The smell of a substance.
- Hardness: Resistance to scratching or indentation.
- Malleability: Ability to be hammered into thin sheets.
- Ductility: Ability to be drawn into wires.
These properties can be observed and measured without altering the fundamental chemical makeup of the substance. A change in state (solid, liquid, gas) is still considered a physical change because the molecules themselves remain unchanged.
Chemical Properties
Chemical properties, on the other hand, describe how a substance reacts with other substances or transforms into a new substance. Observing a chemical property requires a chemical change, which alters the molecular structure. Examples include:
- Flammability: The ability to burn in the presence of oxygen.
- Reactivity with acids: How a substance reacts when exposed to acids.
- Toxicity: The ability to cause harm to living organisms.
- Corrosion resistance: The ability to withstand degradation from chemical reactions.
- Oxidation state: The degree of oxidation of an atom in a compound.
These properties inherently involve chemical reactions, resulting in the formation of new substances with different properties. The original substance is fundamentally transformed.
Combustion: A Chemical Process
Combustion is a rapid chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant, usually oxygen, that produces heat and light. It's an exothermic reaction, meaning it releases energy in the form of heat. The process involves the breaking and forming of chemical bonds, resulting in the formation of new compounds, primarily carbon dioxide and water in the case of hydrocarbons.
Key Characteristics of Combustion:
- Exothermic: Releases heat.
- Rapid: Occurs quickly.
- Involves oxidation: The fuel is oxidized (loses electrons).
- Produces new substances: The reactants are transformed into different products.
The process is fundamentally a chemical transformation, not a mere physical change. The molecules involved are rearranged, forming new chemical bonds and releasing energy. Observing the ability of a substance to support combustion requires initiating a chemical reaction, thus necessitating a chemical change.
Supporting Combustion: A Chemical Property
Now, let's directly address the central question: Is supporting combustion a physical or chemical property?
The answer is definitively chemical.
A substance's ability to support combustion refers to its capacity to act as an oxidant, typically providing the oxygen necessary for the combustion process. This process involves a chemical reaction, where oxygen atoms combine with the fuel molecules, forming new compounds. This interaction fundamentally alters the chemical composition of both the fuel and the oxidant.
Consider oxygen itself. Oxygen's ability to support combustion isn't a simple observation like its color or density; it's its capacity to participate in a chemical reaction with a fuel, leading to a transformation of matter and energy. The interaction between oxygen and a combustible material results in new products (e.g., carbon dioxide, water, and potentially other oxides), making it a chemical property.
Furthermore, other substances can support combustion even in the absence of free oxygen. For instance, fluorine and chlorine are strong oxidizing agents that can support combustion reactions, demonstrating that the ability to support combustion isn't solely tied to oxygen but to the fundamental capacity to participate in a chemical oxidation reaction.
Differentiating Physical Changes from Chemical Changes Related to Combustion
It's crucial to differentiate between physical changes that might accompany combustion and the underlying chemical process.
For example, the expansion of gases during combustion, or the production of flames (which involves the emission of light), are physical manifestations of the underlying chemical reaction. The increase in temperature is a physical change, as it affects the kinetic energy of molecules, but doesn't alter their fundamental chemical structure. However, these physical changes are direct consequences of the primary chemical reaction of combustion, confirming its chemical nature. You cannot observe the supporting of combustion without observing a chemical change.
Practical Examples
Let's illustrate with some examples:
-
Oxygen: Oxygen readily reacts with fuels (e.g., wood, gasoline) during combustion, resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide and water. This is a chemical change, and oxygen's capacity to facilitate this is a chemical property.
-
Chlorine: Chlorine gas, although not as commonly associated with combustion as oxygen, can support the combustion of certain metals, like sodium. This reaction forms sodium chloride and releases energy, confirming chlorine's role as a chemical oxidant and its chemical property of supporting combustion.
-
Fluorine: Fluorine is the most reactive element and a potent oxidizing agent. It can support combustion even more vigorously than oxygen. This again illustrates that the ability to support combustion is a characteristic linked to chemical reactivity.
Conclusion: Supporting Combustion is a Chemical Property
In conclusion, the ability of a substance to support combustion is unequivocally a chemical property. It's not simply a matter of observation but involves a chemical reaction—the oxidation of a fuel—that leads to a fundamental transformation of matter and the release of energy. The physical manifestations of combustion, like heat and light, are byproducts of this central chemical process. Understanding this distinction is essential for a comprehensive grasp of combustion and the fundamental principles of chemistry. The ability to support combustion is intrinsically tied to the chemical reactivity of the substance and its capacity to participate in an oxidation-reduction reaction, making it a crucial chemical characteristic.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Moles Of Solute Per Liter Of Solution
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Oxidation Number Of Sulfur In So42
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Angular Position Of A Point On A Rotating Wheel
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Electron Transport Chain Occurs In The
Mar 20, 2025
-
Person Who Looks On The Dark Side
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Supporting Combustion A Physical Or Chemical Property . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
