Is Sr Oh 2 An Acid Or Base
News Leon
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
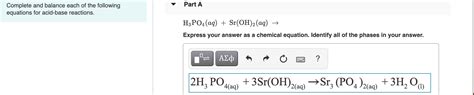
Table of Contents
Is Sr(OH)₂ an Acid or a Base? Understanding Strontium Hydroxide
Determining whether a compound is an acid or a base is fundamental in chemistry. This article delves into the properties of strontium hydroxide, Sr(OH)₂, clarifying its nature and exploring its behavior in aqueous solutions. We'll examine its chemical structure, its reaction with water, and its implications in various chemical processes. We’ll also explore related concepts to provide a comprehensive understanding.
Understanding Acids and Bases
Before diving into the specifics of Sr(OH)₂, let's establish a strong foundation in acid-base chemistry. Several theories define acids and bases, but the most relevant for our discussion are the Arrhenius and Brønsted-Lowry theories.
Arrhenius Theory
The Arrhenius theory defines an acid as a substance that produces hydrogen ions (H⁺) when dissolved in water, and a base as a substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH⁻) when dissolved in water. This theory, while simple, provides a good starting point for understanding many common acids and bases.
Brønsted-Lowry Theory
The Brønsted-Lowry theory offers a broader perspective. It defines an acid as a proton (H⁺) donor and a base as a proton acceptor. This theory expands the definition to include substances that don't necessarily contain OH⁻ but can still act as bases by accepting a proton.
Strontium Hydroxide: A Strong Base
Sr(OH)₂, strontium hydroxide, unequivocally falls into the category of strong bases. This classification stems from its behavior in water.
Dissociation in Water
When strontium hydroxide dissolves in water, it undergoes complete dissociation, meaning it breaks apart almost entirely into its constituent ions: strontium cations (Sr²⁺) and hydroxide anions (OH⁻). This complete dissociation is a hallmark of strong bases. The reaction can be represented as follows:
Sr(OH)₂(s) → Sr²⁺(aq) + 2OH⁻(aq)
The presence of a significant concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in the solution is what makes Sr(OH)₂ a base according to both the Arrhenius and Brønsted-Lowry theories. The high concentration of OH⁻ ions leads to a high pH, typically greater than 7.
pH and pOH
The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution. A pH of 7 is neutral. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic, while those with a pH greater than 7 are basic (or alkaline). The pOH scale is related to the pH scale and is calculated as pOH = 14 - pH. A low pOH indicates a high concentration of hydroxide ions, characteristic of strong bases like Sr(OH)₂.
Properties of Strontium Hydroxide
Understanding the properties of Sr(OH)₂ helps in comprehending its behavior as a strong base.
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Sr(OH)₂ is typically a white, crystalline powder.
- Solubility: While considered a strong base, its solubility in water is relatively low compared to other strong bases like sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- Melting Point: Strontium hydroxide has a relatively high melting point.
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity with Acids: Sr(OH)₂ readily reacts with acids in a neutralization reaction, producing salt and water. For example, its reaction with hydrochloric acid (HCl) is: Sr(OH)₂(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → SrCl₂(aq) + 2H₂O(l)
- Reactivity with Carbon Dioxide: Strontium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide (CO₂) in the air, forming strontium carbonate (SrCO₃): Sr(OH)₂(aq) + CO₂(g) → SrCO₃(s) + H₂O(l) This reaction is often used to remove CO₂ from gases.
Applications of Strontium Hydroxide
The strong basic nature of Sr(OH)₂ makes it useful in various applications:
- Sugar Refining: Sr(OH)₂ is used in the refining of beet sugar to remove impurities. Its strong basicity helps in the process of separating and removing unwanted substances.
- Manufacturing of Other Strontium Compounds: It serves as a precursor in the synthesis of other strontium compounds, which have diverse uses in various industries.
- Specialty Chemicals: Sr(OH)₂ finds use in various niche applications within the chemical industry, often leveraging its strong base properties.
Comparing Sr(OH)₂ with Other Bases
It's helpful to compare Sr(OH)₂ with other common bases to understand its relative strength and properties:
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
NaOH, also known as caustic soda or lye, is a much stronger base than Sr(OH)₂ in terms of solubility. NaOH is highly soluble in water, leading to a significantly higher concentration of OH⁻ ions in solution for the same molar quantity.
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH)
Similar to NaOH, KOH is a highly soluble strong base with a high concentration of OH⁻ ions in solution. Both NaOH and KOH are commonly used in industrial applications where high basicity is required.
Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂)
Ca(OH)₂, also known as slaked lime, is a less soluble strong base compared to Sr(OH)₂. It is still a strong base, but its lower solubility limits the concentration of OH⁻ ions in solution.
Safety Precautions
Working with Sr(OH)₂, like any strong base, requires careful attention to safety precautions:
- Eye Protection: Always wear appropriate eye protection, as contact with Sr(OH)₂ can cause severe irritation or damage to the eyes.
- Skin Protection: Wear gloves to prevent skin contact, as it can cause burns and irritation.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation when working with Sr(OH)₂, as it can produce irritating dust.
- Disposal: Dispose of Sr(OH)₂ according to local regulations and guidelines for hazardous waste.
Conclusion
Strontium hydroxide, Sr(OH)₂, is definitively a strong base. Its complete dissociation in water, resulting in a high concentration of hydroxide ions, confirms this classification according to both the Arrhenius and Brønsted-Lowry theories. Its properties and reactivity make it useful in various industrial applications, particularly those requiring a strong alkaline environment. However, safe handling procedures are essential due to its corrosive nature. Understanding its chemical behavior and taking appropriate safety precautions are crucial for anyone working with this compound. Remember always to consult relevant safety data sheets (SDS) before handling any chemical substance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Bar Magnet Is Placed In A Uniform Magnetic Field
Apr 05, 2025
-
Balance Equation Naoh H2so4 Na2so4 H2o
Apr 05, 2025
-
Non Metal Liquid At Room Temp
Apr 05, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Pollution
Apr 05, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not Characteristic Of Metals
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Sr Oh 2 An Acid Or Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
