Is Paper Burning A Chemical Change
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
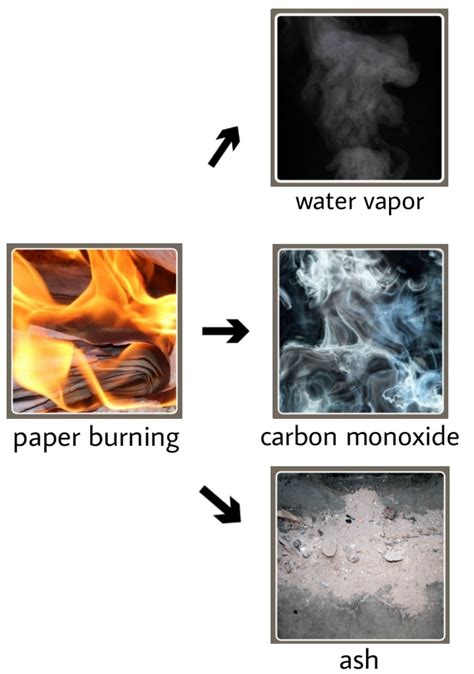
Table of Contents
Is Burning Paper a Chemical Change? A Deep Dive into Combustion
Burning paper is a quintessential example of a chemical change, a transformation that alters the fundamental composition of a substance. While seemingly simple, the process is remarkably complex, involving numerous chemical reactions and the release of significant energy. Understanding why burning paper represents a chemical change requires delving into the nature of chemical reactions, the properties of paper, and the process of combustion itself.
Understanding Chemical vs. Physical Changes
Before exploring the specifics of burning paper, it's crucial to define the difference between chemical and physical changes.
Physical Changes
A physical change alters the form or appearance of a substance but doesn't change its chemical composition. Examples include melting ice, dissolving sugar in water, or tearing paper. In each case, the substance remains fundamentally the same; its molecules haven't undergone any rearrangement. These changes are often reversible. For instance, you can refreeze melted ice, and while you can't perfectly reassemble torn paper, the basic cellulose fibers remain intact.
Chemical Changes
A chemical change, also known as a chemical reaction, involves the rearrangement of atoms and molecules, resulting in the formation of new substances with different properties. These changes are often irreversible, meaning you cannot easily restore the original substances. Examples include rusting iron, baking a cake, or, as we'll explore extensively, burning paper. The chemical bonds within the original substances are broken, and new bonds are formed, leading to fundamentally different compounds.
The Composition of Paper: A Complex Mixture
Paper, despite its seemingly simple nature, is a complex mixture of materials. The primary component is cellulose, a long-chain polymer of glucose molecules. Cellulose fibers are interwoven to create the structure of the paper. However, paper also contains various additives, including:
- Lignin: A complex polymer that adds strength and rigidity to paper.
- Hemicellulose: Another polymer found in plant cell walls, contributing to the paper's overall structure.
- Fillers: Such as calcium carbonate, which enhance the paper's opacity and smoothness.
- Sizing agents: These reduce the paper's absorbency and improve its printing properties.
These additives contribute to the overall chemical composition of the paper, influencing how it reacts during combustion.
The Combustion of Paper: A Chemical Reaction in Action
Burning paper is a classic example of combustion, a rapid chemical reaction between a substance and an oxidant, typically oxygen, producing heat and light. This process is exothermic, meaning it releases energy in the form of heat and light.
The Chemical Equation (Simplified)
While the complete chemical equation for burning paper is extremely complex due to the presence of numerous components, a simplified representation can illustrate the core process:
(C6H10O5)n + O2 → CO2 + H2O + Energy
This equation represents the combustion of cellulose (C6H10O5)n, where 'n' represents the number of repeating glucose units. When cellulose reacts with oxygen (O2), it produces carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and energy in the form of heat and light.
Stages of Combustion
The burning of paper occurs in stages, each involving distinct chemical reactions:
-
Ignition: This is the initial stage where the paper is heated to its ignition temperature. The heat energy overcomes the activation energy required to initiate the chemical reaction.
-
Pyrolysis: As the paper heats, it undergoes pyrolysis, a thermal decomposition process where large molecules break down into smaller volatile compounds. This stage produces flammable gases, such as methane, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide.
-
Flaming Combustion: The flammable gases released during pyrolysis react with oxygen in the air, producing a flame. This is the most visually striking part of the burning process.
-
Glowing Combustion: After the flammable gases are consumed, the remaining char (mostly carbon) continues to burn, producing a glowing ember. This is a slower process than flaming combustion.
-
Ash Formation: Eventually, the burning process concludes, leaving behind ash, which is primarily composed of inorganic compounds from the paper's additives.
Evidence of Chemical Change
Several key observations confirm that burning paper is a chemical change:
-
Irreversibility: You cannot simply put the ashes back together to reconstruct the original paper. The cellulose molecules have been broken down into entirely different substances.
-
Formation of New Substances: The combustion process produces entirely new substances, carbon dioxide, water vapor, and ash, differing significantly from the original cellulose and other components of the paper. Their chemical and physical properties are drastically different.
-
Energy Release: The release of significant heat and light energy is a hallmark of chemical reactions, especially exothermic ones.
-
Color Change: The change in color from white or off-white to black ash is another visual indication of a chemical transformation.
-
Gas Production: The release of gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor, which are easily detectable, also supports the conclusion that a chemical reaction has occurred.
Factors Affecting Paper Combustion
Several factors can influence the rate and efficiency of paper combustion:
-
Oxygen Availability: Sufficient oxygen is crucial for complete combustion. Restricting oxygen supply can lead to incomplete combustion, producing carbon monoxide, a toxic gas.
-
Temperature: Higher temperatures generally accelerate the rate of combustion.
-
Paper Composition: The type of paper, its density, and the presence of various additives can affect how readily it burns. For instance, papers with higher lignin content may burn more readily.
-
Surface Area: Increasing the surface area of the paper, such as by crumpling it, can accelerate combustion by increasing contact with oxygen.
Beyond Burning Paper: The Broader Significance of Combustion
Understanding the combustion of paper provides a foundational understanding of combustion processes more generally. Combustion plays a vital role in various applications, from generating electricity in power plants to powering internal combustion engines. It is a fundamental chemical process with far-reaching consequences and applications. The knowledge gained from studying paper combustion can be extrapolated to comprehend other forms of combustion, contributing to advancements in various fields like energy production and environmental science.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
It's important to address some common misconceptions about burning paper:
-
"It's just a physical change because you can still see the ash." While ash remains, it represents the residue of chemical transformations. The original cellulose is gone, and new compounds are formed.
-
"The paper is just decomposing." While pyrolysis, a form of decomposition, is part of the process, it's not the whole story. Combustion involves a rapid reaction with oxygen, fundamentally changing the chemical composition.
Conclusion: The Unmistakable Chemical Transformation
The process of burning paper is unequivocally a chemical change. The transformation is irreversible, produces new substances, releases significant energy, and involves a complex series of chemical reactions. Understanding this seemingly simple process offers insight into the fundamental principles of chemistry, combustion, and the dynamic interactions between matter and energy. The evidence overwhelmingly points to a chemical change, making it a prime example for illustrating this crucial concept in chemistry and beyond. From the microscopic rearrangement of atoms to the macroscopic release of heat and light, burning paper serves as a compelling demonstration of the powerful forces at play in the chemical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Advantage Of Having Four Chambered Heart
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Device Provides Electrical Energy To Run An Electric Circuit
Mar 23, 2025
-
Select The Statement That Best Describes Homeostasis
Mar 23, 2025
-
Calculate The Molecular Mass Of Co2
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Alkenes Is The Most Stable
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Paper Burning A Chemical Change . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
