Is Dry Ice An Element Compound Or Mixture
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
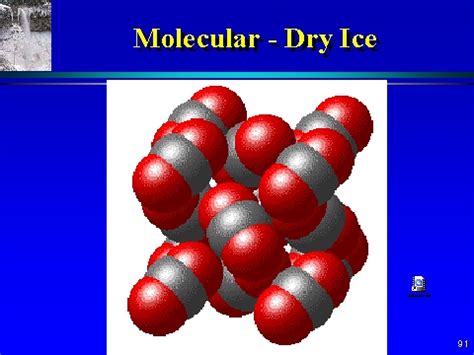
Table of Contents
Is Dry Ice an Element, Compound, or Mixture? Understanding the Nature of Solid Carbon Dioxide
Dry ice, a substance often associated with spooky Halloween effects and theatrical fog, is more than just a visually appealing material. Understanding its true nature – whether it's an element, compound, or mixture – requires delving into the fundamental concepts of chemistry. This article will thoroughly explore the composition of dry ice, definitively classifying it and explaining the differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures. We'll also touch upon its properties and various applications, further solidifying your understanding.
What is Dry Ice?
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide (CO₂). Unlike regular ice (water ice), which melts into liquid water at 0°C (32°F), dry ice sublimates – meaning it transitions directly from a solid to a gas at -78.5°C (-109.3°F) at standard atmospheric pressure. This unique property is what gives it its name and makes it so useful in various applications.
Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures: A Quick Review
Before we classify dry ice, let's refresh our understanding of the fundamental concepts of elements, compounds, and mixtures:
Elements: The Building Blocks
Elements are pure substances consisting of only one type of atom. They cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Examples include oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and carbon (C). These are listed on the periodic table and represent the fundamental building blocks of all matter. Each element is defined by its atomic number – the number of protons in its nucleus.
Compounds: Combining Elements
Compounds are pure substances formed when two or more different elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio. These elements are bonded together, forming a new substance with unique properties different from its constituent elements. Water (H₂O), for example, is a compound formed from the combination of hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The properties of water are distinctly different from those of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The chemical formula for a compound represents the precise ratio of the elements involved.
Mixtures: A Combination of Substances
Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances (elements or compounds) that are not chemically bonded. They can be physically separated into their components. Mixtures retain the properties of their constituent parts, unlike compounds. There are two main types of mixtures: homogeneous (uniform composition throughout) and heterogeneous (non-uniform composition). Air, saltwater, and granite are examples of mixtures.
Classifying Dry Ice: Compound or Mixture?
Now, armed with this knowledge, let's address the central question: Is dry ice an element, compound, or mixture? The answer is clear: dry ice is a compound.
Dry ice is entirely composed of carbon dioxide (CO₂), which itself is a compound. Each molecule of carbon dioxide consists of one carbon atom (C) chemically bonded to two oxygen atoms (O). This chemical bond is a strong covalent bond, holding the atoms together in a fixed ratio. The properties of dry ice (its sublimation point, its density, its lack of odor in its solid form) are distinctly different from the properties of elemental carbon and oxygen. Therefore, it cannot be classified as an element or a mixture.
Why it's not a mixture: A mixture implies that the components are not chemically bonded. Dry ice is a pure substance – you can't separate it into carbon and oxygen by physical means like filtration or distillation. The carbon and oxygen atoms are inextricably linked by chemical bonds.
Why it's not an element: Dry ice contains two different elements, carbon and oxygen, chemically bonded together. Elements by definition consist of only one type of atom.
Properties and Applications of Dry Ice
Dry ice's unique properties make it invaluable in various applications:
Sublimation: The Key Property
The sublimation of dry ice, its transition directly from solid to gas without an intervening liquid phase, is a key property behind many of its applications. This eliminates the mess and inconvenience associated with melting ice.
Cooling Agent: A Superior Alternative
Dry ice is an effective cooling agent because of its extremely low sublimation temperature. It's used extensively in the transportation and storage of perishable goods, including:
- Food and Beverages: Maintaining the cold chain for frozen foods, ice cream, and other temperature-sensitive products during transport.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring the stability and potency of medications requiring refrigeration.
- Biological Samples: Preserving the integrity of tissue samples, blood, and other biological materials.
Industrial Applications
Dry ice's industrial applications are numerous and diverse, including:
- Cleaning: Dry ice blasting is a non-abrasive cleaning method used to remove contaminants from surfaces without damaging the underlying material. This is often used in industries ranging from food processing to manufacturing.
- Manufacturing: Controlled cooling in various industrial processes.
- Agriculture: In controlled freezing processes.
Other Notable Applications
- Special Effects: Its dramatic sublimation creates a visually striking fog effect in theatrical productions, concerts, and haunted houses.
- Refrigeration: While not widely used for household refrigeration due to safety concerns, it plays a crucial role in industrial and scientific refrigeration systems.
Safety Precautions When Handling Dry Ice
Dry ice is a powerful coolant and should be handled with caution. Direct contact can cause frostbite. Never consume dry ice, and ensure adequate ventilation when using it in confined spaces as the carbon dioxide gas can displace oxygen and lead to asphyxiation.
Conclusion
In summary, dry ice is definitively a compound, specifically the solid form of carbon dioxide (CO₂). It's not an element because it comprises two different elements chemically bonded. It's not a mixture because its components are chemically bound and inseparable through physical means. Understanding this fundamental classification is crucial to appreciating its unique properties and diverse applications. From food preservation to industrial cleaning and theatrical special effects, dry ice continues to play a significant role in various aspects of modern life. Remembering the importance of safety measures while working with this powerful coolant is paramount to ensure both personal and environmental well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Co2 Are Produced In The Krebs Cycle
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 1 4
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Single Celled Organism Is Called
Mar 26, 2025
-
Anything That Has Mass And Takes Up Space Is Called
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Protons And Electrons In Magnesium
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Dry Ice An Element Compound Or Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
