Is Air A Element Compound Or Mixture
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
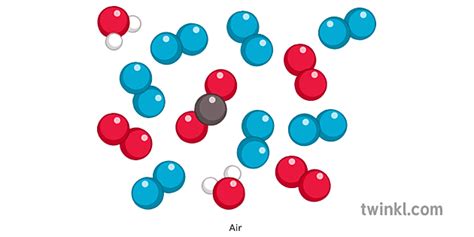
Table of Contents
Is Air an Element, Compound, or Mixture? A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Composition
The question of whether air is an element, compound, or mixture is a fundamental one in chemistry and atmospheric science. Understanding the answer requires delving into the definitions of these terms and exploring the intricate composition of the air we breathe. The short answer is that air is a mixture. However, to fully grasp this, let's examine the distinctions between elements, compounds, and mixtures and then apply this knowledge to the complex composition of Earth's atmosphere.
Understanding the Basic Chemical Classifications
Before we analyze the nature of air, let's clearly define the terms: element, compound, and mixture.
Elements: The Building Blocks of Matter
Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. They are the fundamental building blocks of all matter, each characterized by a unique atomic number (the number of protons in its nucleus). Examples of elements include oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), and iron (Fe). Elements are represented by chemical symbols, such as O for oxygen and N for nitrogen. These elements exist in various forms, including gases, liquids, and solids, depending on their properties and environmental conditions.
Compounds: Elements Bound Together
Compounds are substances formed when two or more different elements chemically combine in fixed proportions. These elements are held together by strong chemical bonds, resulting in a new substance with properties distinct from its constituent elements. For example, water (H₂O) is a compound formed from two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The properties of water are significantly different from the properties of hydrogen and oxygen in their elemental forms. Compounds have a defined chemical formula, such as H₂O for water or CO₂ for carbon dioxide. This formula represents the ratio of each element within the compound.
Mixtures: A Blend of Substances
Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. The components of a mixture retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical means, such as filtration, distillation, or evaporation. Unlike compounds, mixtures don't have a fixed composition; the proportions of the components can vary. Air, for instance, is a mixture of various gases, each retaining its individual properties. The relative amounts of these gases can vary depending on location and environmental factors.
The Composition of Air: A Detailed Examination
Now that we've established the differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures, let's analyze the composition of air to determine its classification. Air is primarily composed of:
-
Nitrogen (N₂): Approximately 78% of Earth's atmosphere is nitrogen gas. Nitrogen is a diatomic element, meaning two nitrogen atoms are bonded together. Although it is essential for life, it's generally inert in its gaseous form and doesn't readily react with other substances.
-
Oxygen (O₂): Oxygen makes up roughly 21% of the atmosphere. Also a diatomic element, oxygen is crucial for respiration in most living organisms. It is highly reactive and participates in many combustion and oxidation processes.
-
Argon (Ar): Argon is a noble gas, making up about 0.93% of the atmosphere. Noble gases are generally unreactive and exist as monatomic elements.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Carbon dioxide represents a small but critically important component of air, typically around 0.04%. Although present in small quantities, it plays a vital role in the Earth's climate system through the greenhouse effect. Carbon dioxide is a compound, formed from one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
-
Trace Gases: Besides these major components, air also contains trace amounts of other gases, such as neon (Ne), helium (He), methane (CH₄), krypton (Kr), hydrogen (H₂), and nitrous oxide (N₂O). These gases, while present in small concentrations, can have significant impacts on the environment and human health. Some of these, like methane, are compounds.
Why Air is a Mixture
The components of air are not chemically bonded together; they exist as individual molecules or atoms. This is the key reason why air is classified as a mixture. The proportions of these gases can vary depending on several factors including:
-
Altitude: The composition of air changes with altitude. The concentration of oxygen decreases with increasing altitude, while the proportion of some trace gases might increase.
-
Location: Air composition can vary depending on geographical location. Areas with high industrial activity might have higher concentrations of pollutants.
-
Time of Day: Variations in temperature and atmospheric circulation patterns can cause minor fluctuations in air composition throughout the day.
-
Season: Seasonal changes can affect air composition, for instance, increased pollen levels during spring.
The fact that these variations exist highlights the key characteristic of a mixture: variable composition. If air were a compound, its composition would be fixed and invariable.
Separating the Components of Air
Further evidence supporting the classification of air as a mixture is the ability to separate its components through physical means. Techniques such as fractional distillation can be used to isolate and purify the different gases present in air. This would not be possible if air were a compound, as compounds require chemical processes for separation.
The Importance of Understanding Air's Composition
Understanding that air is a mixture is crucial for various reasons:
-
Environmental Science: Accurate knowledge of air composition is critical for monitoring air quality, studying climate change, and developing strategies for pollution control. Tracking changes in the concentration of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide is vital for climate modelling and policy decisions.
-
Medicine and Health: The composition of air directly affects human health. Breathing air with insufficient oxygen or high levels of pollutants can have severe health consequences. Understanding the different components of air allows us to develop strategies for maintaining safe and healthy breathing environments.
-
Industrial Applications: Many industrial processes depend on the properties of the gases in air. For example, the nitrogen in air is used in various industrial processes, and oxygen is crucial for combustion and other chemical reactions.
-
Aerospace Engineering: The composition and properties of air at different altitudes are crucial factors in aerospace engineering, affecting aircraft design and flight performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, air is unequivocally a mixture, not an element or a compound. Its composition is variable, its components retain their individual properties, and these components can be separated by physical means. Understanding the detailed composition of air, including its major and minor components, is essential for various scientific disciplines, including environmental science, medicine, and industrial applications. The complexity of atmospheric composition and the critical roles of different gases highlight the importance of continued research and monitoring of our planet's atmosphere. This research is paramount to safeguarding both environmental health and human well-being for generations to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Show Me How To Do It
Mar 24, 2025
-
Sample Letter Of Request For Permission
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Are The Units Of Entropy
Mar 24, 2025
-
The Genetic Material Of Hiv Consists Of
Mar 24, 2025
-
In The Figure Two Particles Each With Mass M
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Air A Element Compound Or Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
