Inside The Chloroplasts Chlorophyll Is Found In The
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
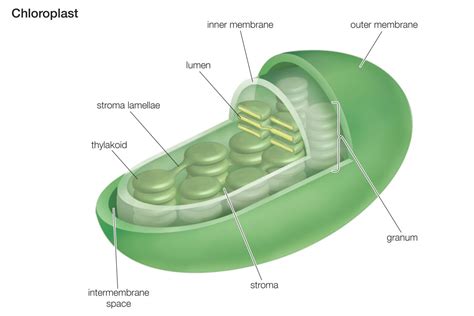
Table of Contents
Inside the Chloroplast: Chlorophyll's Role in Photosynthesis
Chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for the vibrant hues of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, resides within specialized organelles called chloroplasts. Understanding the intricacies of chloroplast structure and the precise location of chlorophyll within it is crucial to comprehending the complex process of photosynthesis, the foundation of most life on Earth. This article delves deep into the chloroplast's internal architecture, exploring where chlorophyll is found and how its strategic positioning facilitates its vital role in capturing light energy.
The Chloroplast: A Photosynthetic Powerhouse
Chloroplasts are double-membrane-bound organelles found in plant and algal cells. These miniature powerhouses are the sites of photosynthesis, the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Their structure is highly organized, reflecting the complex series of reactions required for this crucial process.
The Double Membrane System
The chloroplast is enclosed by a double membrane: the outer membrane and the inner membrane. The outer membrane acts as a selective barrier, regulating the passage of molecules into and out of the chloroplast. The inner membrane, on the other hand, is more specialized, playing a key role in transporting molecules involved in photosynthesis and maintaining the internal environment of the chloroplast. Between these two membranes lies the intermembrane space, a narrow region that plays a role in regulating the passage of ions and molecules.
The Stroma: The Chloroplast's Cytoplasm
Inside the inner membrane lies the stroma, a fluid-filled space analogous to the cytoplasm of a cell. The stroma is a dynamic environment containing various enzymes, ribosomes, DNA, and thylakoids—the site where chlorophyll resides. It’s here that the dark reactions of photosynthesis, also known as the Calvin cycle, take place. These reactions use the ATP and NADPH generated during the light-dependent reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
Thylakoids: The Light-Harvesting Machines
Within the stroma are intricate membranous structures called thylakoids. These flattened, sac-like structures are stacked into columns called grana (singular: granum). The thylakoid membrane is crucial because it's where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur. This is where chlorophyll and other pigments are embedded, forming the photosystems.
Chlorophyll's Location: Embedded in the Thylakoid Membrane
The answer to the question "Inside the chloroplast, chlorophyll is found in the..." is unequivocally the thylakoid membrane. More specifically, chlorophyll molecules are integral components of photosystem I (PSI) and photosystem II (PSII), large protein complexes embedded within this membrane.
Photosystems: Antenna Complexes and Reaction Centers
Photosystems are not simply collections of chlorophyll; they are highly organized structures consisting of:
-
Antenna Complexes: These complexes consist of hundreds of chlorophyll molecules and other pigments like carotenoids and phycobilins. These pigments act as an antenna, absorbing light energy from a broad range of wavelengths and efficiently funneling it to the reaction center. The chlorophyll molecules in the antenna complex are mainly chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b, with minor variations in structure affecting the wavelengths they absorb most effectively.
-
Reaction Centers: At the heart of each photosystem is the reaction center, a specialized chlorophyll a molecule (P680 in PSII and P700 in PSI). This chlorophyll molecule is uniquely positioned to initiate the electron transfer chain, the core process of converting light energy into chemical energy. When the reaction center absorbs light energy, an electron is excited to a higher energy level, initiating a series of electron transfers that ultimately lead to the production of ATP and NADPH.
Chlorophyll a vs. Chlorophyll b: A Functional Division of Labor
While both chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b are integral parts of the antenna complexes, they have slightly different absorption spectra. Chlorophyll a primarily absorbs red and blue light, while chlorophyll b absorbs blue and orange light. This subtle difference in absorption allows the photosystems to capture a wider range of the visible light spectrum, maximizing the efficiency of light energy harvesting.
The Importance of Chlorophyll's Location
The strategic positioning of chlorophyll within the thylakoid membrane is critical for the efficiency of photosynthesis. The tightly packed arrangement of chlorophyll molecules in the photosystems ensures efficient energy transfer from the antenna complexes to the reaction centers. The thylakoid membrane also provides a compartmentalized environment, separating the light-dependent reactions from the stroma where the light-independent reactions occur. This separation ensures the efficient and regulated flow of energy and molecules during photosynthesis.
Beyond Chlorophyll: Other Pigments in the Thylakoid Membrane
While chlorophyll is the dominant pigment, other pigments play a supporting role in photosynthesis:
-
Carotenoids: These pigments absorb light in the blue-green region of the spectrum and protect chlorophyll from photodamage by absorbing excessive light energy. They act as antioxidants, preventing the formation of harmful reactive oxygen species.
-
Phycobilins: Found primarily in cyanobacteria and red algae, phycobilins are accessory pigments that absorb light in the green-yellow region, extending the range of wavelengths used in photosynthesis.
The Role of the Thylakoid Lumen
The space inside the thylakoid sac is called the thylakoid lumen. The lumen plays a crucial role in maintaining the proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane, which is essential for ATP synthesis. The light-dependent reactions pump protons into the lumen, creating a higher concentration of protons compared to the stroma. This proton gradient drives ATP synthase, an enzyme embedded in the thylakoid membrane that produces ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Factors Affecting Chlorophyll Content and Photosynthesis
Several factors can influence the amount of chlorophyll present in the chloroplast and thus impact the rate of photosynthesis:
-
Light intensity: High light intensity can lead to photoinhibition, damaging chlorophyll and reducing photosynthetic efficiency.
-
Nutrient availability: The availability of nutrients, particularly nitrogen and magnesium, is essential for chlorophyll synthesis. Nutrient deficiencies can result in reduced chlorophyll levels and lower photosynthetic rates.
-
Temperature: Extreme temperatures can denature chlorophyll and other photosynthetic proteins, impacting the efficiency of light capture and energy conversion.
-
Water availability: Water stress can negatively affect photosynthesis, leading to reduced chlorophyll content and stomatal closure, limiting carbon dioxide uptake.
Conclusion: Chlorophyll – The Heart of Photosynthetic Energy Conversion
In summary, chlorophyll's location within the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast is central to its function in photosynthesis. Its strategic organization within photosystems, coupled with the support of accessory pigments, allows plants, algae, and cyanobacteria to efficiently capture and convert light energy into the chemical energy that sustains life on Earth. Understanding the intricate details of chloroplast structure and the precise role of chlorophyll within it remains a key area of research, with potential implications for improving crop yields and developing sustainable energy solutions. Further research continues to unravel the complexities of this remarkable process and its critical role in the global ecosystem.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Pints In 1 Lb
Mar 14, 2025
-
Reflexive And Transitive But Not Symmetric
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Percent Of 90 Is 120
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Chambers Does The Heart Of An Amphibian Have
Mar 14, 2025
-
Is Boiling Water Chemical Or Physical Change
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Inside The Chloroplasts Chlorophyll Is Found In The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
