In What Way Are Energy And Nutrients Similar
News Leon
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
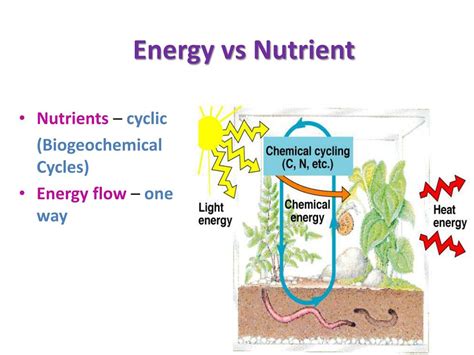
Table of Contents
In What Ways Are Energy and Nutrients Similar? A Deep Dive into Biological Processes
The human body, a marvel of biological engineering, requires a constant influx of energy and nutrients to function optimally. While seemingly distinct, energy and nutrients share surprising similarities in their roles and mechanisms within our biological systems. Understanding these parallels is crucial for comprehending human physiology, nutrition, and overall health. This article delves into the fascinating similarities between energy and nutrients, exploring their interconnectedness at a molecular level and their impact on various bodily functions.
The Fundamental Roles: Fueling Life's Processes
Both energy and nutrients serve as fundamental building blocks and operational fuels for life's processes. Energy, primarily derived from the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, powers cellular activities, enabling everything from muscle contraction and nerve impulse transmission to organ function and maintaining body temperature. Nutrients, encompassing vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and water, provide the essential raw materials for building and repairing tissues, synthesizing hormones and enzymes, and regulating various metabolic pathways.
The Interplay: Nutrients as Energy Sources
The similarity between energy and nutrients becomes apparent when we consider that many nutrients directly contribute to energy production. Carbohydrates, for instance, are the body's preferred energy source, rapidly broken down into glucose, which fuels cellular respiration. Fats, while providing long-term energy storage, are also metabolized to generate significant amounts of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of cells. Proteins, though primarily structural components, can also be catabolized for energy during periods of starvation or intense physical exertion.
The Dependence: Energy for Nutrient Utilization
Conversely, the utilization of nutrients is heavily dependent on the availability of energy. The absorption, transport, metabolism, and storage of nutrients all require energy expenditure. Active transport mechanisms, for example, move nutrients across cell membranes against their concentration gradients, a process that demands ATP. The synthesis of complex molecules from simpler nutrient components, such as protein synthesis from amino acids, is also an energy-intensive undertaking. Without sufficient energy, the body's ability to efficiently process and utilize nutrients is severely compromised.
Macro and Micronutrients: Building Blocks and Metabolic Regulators
The similarities between energy and nutrients are further illuminated by considering the distinct roles of macronutrients and micronutrients.
Macronutrients: Energy and Structure
Macronutrients—carbohydrates, fats, and proteins—provide both energy and structural components for the body. Carbohydrates serve as the primary and readily available source of energy. Fats are crucial for energy storage, hormone production, and cell membrane structure. Proteins form the building blocks of tissues, enzymes, and hormones, while also contributing to energy production in times of need.
Micronutrients: Metabolic Catalysts and Regulators
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are essential for various metabolic processes, including energy production and nutrient utilization. Vitamins act as coenzymes, assisting enzymes in catalyzing metabolic reactions, including those involved in energy metabolism. Minerals play diverse roles, such as acting as components of enzymes, regulating fluid balance, and participating in nerve impulse transmission, all of which are indirectly or directly linked to energy production and utilization. For example, iron is crucial for hemoglobin function, essential for oxygen transport, which is fundamentally necessary for cellular respiration and energy production.
Cellular Respiration: The Converging Point
Cellular respiration, the process by which cells generate energy from nutrients, represents a powerful convergence point highlighting the similarities between energy and nutrients. This intricate process involves a series of biochemical reactions that break down nutrients, primarily glucose, to produce ATP. The efficiency of cellular respiration directly depends on the availability and quality of both energy-yielding nutrients and micronutrients that act as catalysts in the process. Deficiencies in essential nutrients can significantly impair cellular respiration, resulting in decreased energy production and various metabolic disorders.
Homeostasis: The Balanced Act
The body strives to maintain a delicate balance, or homeostasis, in its energy and nutrient levels. This intricate equilibrium is achieved through complex regulatory mechanisms involving hormones, enzymes, and feedback loops. Both energy and nutrients are closely monitored and adjusted to meet the body's immediate and long-term needs. For example, insulin, a hormone released in response to elevated blood glucose levels, facilitates glucose uptake by cells, providing energy while also regulating blood sugar levels.
The Consequences of Imbalance: Malnutrition and Metabolic Disorders
Imbalances in either energy or nutrient intake can lead to significant health consequences. Energy imbalance, characterized by either excessive caloric intake (leading to obesity) or insufficient caloric intake (resulting in underweight and malnutrition), disrupts metabolic processes and can contribute to a range of health problems. Nutrient deficiencies, caused by inadequate intake or impaired absorption of essential vitamins and minerals, can impair various bodily functions, leading to conditions like anemia, rickets, and scurvy. These deficiencies can also indirectly impact energy production and overall health. Metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and metabolic syndrome, often stem from complex interactions between energy intake, nutrient metabolism, and hormonal regulation.
The Significance of a Balanced Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet that provides both adequate energy and a complete spectrum of essential nutrients is crucial for optimal health and well-being. This requires consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources, and healthy fats. A balanced dietary approach not only ensures adequate energy levels to fuel daily activities but also provides the building blocks and regulatory factors necessary for optimal cellular function, tissue repair, and overall metabolic homeostasis.
Conclusion: An Intertwined Relationship
In conclusion, while energy and nutrients might initially appear as separate entities, their roles and mechanisms within the body are deeply interconnected. Nutrients serve as the raw materials for energy production, while energy is essential for nutrient utilization and metabolic processes. Both are crucial for maintaining homeostasis, and imbalances in either can lead to significant health consequences. Understanding the remarkable similarities between energy and nutrients provides a deeper appreciation for the complex interplay of biological processes that sustain life and emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet for optimal health. This intricate relationship highlights the fundamental truth that energy and nutrients are not just separate entities, but rather two sides of the same coin—essential components working in concert to maintain the intricate machinery of the human body. Further research into the intricate interplay between energy metabolism and nutrient utilization is essential to develop better strategies for preventing and treating diet-related diseases and improving overall health outcomes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Mega In Scientific Notation
Apr 02, 2025
-
Is Lead Sulphate Soluble In Water
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Seconds Is 2 Years
Apr 02, 2025
-
Electric Field For Infinite Line Of Charge
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Are The Prime Factors Of 252
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In What Way Are Energy And Nutrients Similar . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
