In The Figure The Battery Has A Potential Difference Of
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
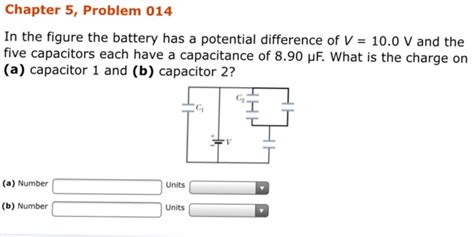
Table of Contents
- In The Figure The Battery Has A Potential Difference Of
- Table of Contents
- Decoding the Circuit: Understanding Potential Difference in a Battery
- What is Potential Difference (Voltage)?
- The Battery: The Source of Potential Difference
- Measuring Potential Difference
- Potential Difference and Circuit Components
- Series and Parallel Circuits: Implications on Potential Difference
- Potential Difference and Circuit Troubleshooting
- Advanced Concepts: Kirchhoff's Voltage Law and Voltage Dividers
- Conclusion: The Significance of Potential Difference
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Decoding the Circuit: Understanding Potential Difference in a Battery
Understanding circuits is fundamental to grasping electricity. A core concept within circuit analysis is the potential difference, often referred to as voltage, across components. This article delves deep into the meaning of potential difference, particularly when focusing on the battery within a circuit, explaining its role, measurement, and implications for circuit behavior. We'll explore various scenarios and provide practical examples to solidify your understanding.
What is Potential Difference (Voltage)?
Potential difference, measured in volts (V), is the work done per unit charge in moving a charge between two points in an electric circuit. Think of it as the electrical pressure that pushes electrons through the circuit. A higher potential difference means a greater "push," resulting in a stronger current flow. This difference in electrical potential arises from a separation of charges; one point has a surplus of electrons (negative potential), while the other has a deficit (positive potential). The battery is the device that creates and maintains this separation of charges.
Analogy Time: Imagine a water tank elevated above the ground. The difference in height between the water level in the tank and the ground represents the potential difference. The higher the tank, the greater the potential energy of the water, and the faster it will flow when a valve is opened. Similarly, a higher potential difference in a circuit leads to a greater flow of electrons (current).
The Battery: The Source of Potential Difference
In the context of a circuit, the battery is the primary source of potential difference. It's an electrochemical device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. This conversion process creates an electric field, driving electrons through the external circuit. The positive terminal (anode) has a deficiency of electrons, while the negative terminal (cathode) has an excess. This difference in electron density creates the potential difference across the battery's terminals.
Key Battery Characteristics:
- Voltage Rating: This is the potential difference between the battery's terminals when no current is flowing (open circuit). It's often written on the battery itself (e.g., 1.5V, 9V, 12V).
- Internal Resistance: No battery is perfect; they possess internal resistance, which opposes the flow of current. This resistance causes a voltage drop within the battery itself, meaning the actual voltage available to the external circuit is slightly less than the rated voltage.
- Capacity: Measured in Ampere-hours (Ah) or milliampere-hours (mAh), it represents the total charge the battery can supply before becoming depleted. A higher capacity means longer operating time.
Measuring Potential Difference
Potential difference is measured using a voltmeter. A voltmeter is a high-resistance device that is connected in parallel across the component (in this case, the battery or a specific part of the circuit) whose voltage we want to measure. The voltmeter measures the potential difference between the two points where it's connected without significantly affecting the circuit's operation.
Important Note: Always ensure the voltmeter is connected correctly with its positive terminal to the higher potential point and its negative terminal to the lower potential point. Connecting it incorrectly can damage the meter or the circuit.
Potential Difference and Circuit Components
The potential difference across a battery isn't solely its rated voltage. When current flows through a circuit, the potential difference across the battery terminals changes due to the internal resistance. Let's consider a simple circuit:
- A Battery: Let's assume it has a voltage rating of 9V and an internal resistance (r) of 1 ohm.
- A Resistor: Let's say it has a resistance (R) of 10 ohms.
Using Ohm's Law (V = IR), where V is the potential difference, I is the current, and R is the resistance, we can analyze the circuit:
-
Total Resistance: The total resistance (R<sub>T</sub>) in the circuit is the sum of the internal resistance of the battery and the external resistor: R<sub>T</sub> = r + R = 1Ω + 10Ω = 11Ω.
-
Current (I): Using Ohm's Law and the total resistance, we can calculate the current flowing through the circuit: I = V / R<sub>T</sub> = 9V / 11Ω ≈ 0.82A.
-
Voltage across the Resistor: The voltage (V<sub>R</sub>) across the resistor can be found using Ohm's Law again: V<sub>R</sub> = IR = 0.82A * 10Ω ≈ 8.2V.
-
Voltage across the Internal Resistance: The voltage drop (V<sub>r</sub>) across the battery's internal resistance is: V<sub>r</sub> = Ir = 0.82A * 1Ω ≈ 0.82V.
Analysis: Notice that the voltage across the resistor (8.2V) is less than the battery's rated voltage (9V). This 0.82V difference is the voltage drop across the battery's internal resistance. The terminal voltage of the battery (the voltage measured across its terminals) is 8.2V, not 9V, when current is flowing. This exemplifies how internal resistance affects the potential difference available to the external circuit.
Series and Parallel Circuits: Implications on Potential Difference
The way batteries are connected in a circuit significantly impacts the overall potential difference.
Series Connection: When batteries are connected in series, their voltages add up. For example, two 1.5V batteries connected in series produce a total potential difference of 3V. The positive terminal of one battery is connected to the negative terminal of the next, creating a cumulative voltage.
Parallel Connection: When batteries are connected in parallel, the potential difference remains the same as that of a single battery. However, the total capacity increases. This is useful for increasing the operating time of a circuit but doesn't increase the voltage.
Potential Difference and Circuit Troubleshooting
Understanding potential difference is crucial for troubleshooting circuits. A significant drop in voltage across a component might indicate a fault, such as a short circuit or a damaged component. Measuring the potential difference across different points in a circuit helps pinpoint the location of the problem.
Advanced Concepts: Kirchhoff's Voltage Law and Voltage Dividers
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL): This fundamental law states that the sum of the potential differences around any closed loop in a circuit is zero. This is a powerful tool for analyzing complex circuits with multiple loops and components.
Voltage Dividers: This is a simple circuit configuration used to obtain a specific voltage from a higher voltage source. By connecting resistors in series, a portion of the input voltage is dropped across each resistor, creating a lower output voltage. The ratio of the resistances determines the output voltage.
Conclusion: The Significance of Potential Difference
The potential difference across a battery is a crucial parameter in understanding circuit behavior. It's not merely a fixed value but is dynamically influenced by factors like internal resistance and the configuration of the circuit. Mastering the concept of potential difference and its relationship with other circuit parameters, such as current and resistance, is essential for anyone working with electrical circuits, from simple household appliances to sophisticated electronic systems. By understanding these concepts, you can effectively design, analyze, and troubleshoot a wide range of electrical circuits. Remember that practice and careful experimentation are key to truly grasping these fundamental principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Migration Is True
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Homogeneous Mixture Of Two Or More Substances Is A
Mar 26, 2025
-
In Which Stage Of Meiosis Crossing Over Occurs
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Lymphoid Organ
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Reason For Doing A Test Cross
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In The Figure The Battery Has A Potential Difference Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
