In Guinea Pigs The Allele For Short Hair Is Dominant
News Leon
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
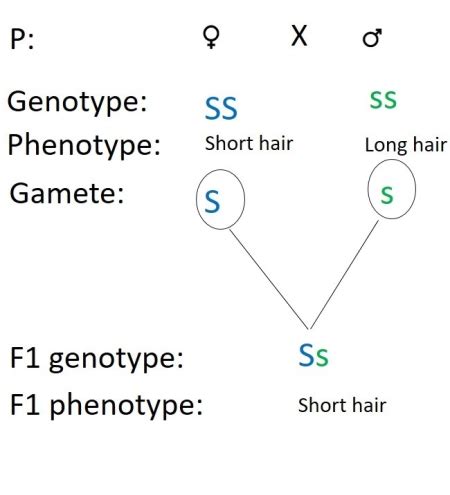
Table of Contents
In Guinea Pigs, the Allele for Short Hair is Dominant: A Deep Dive into Genetics
Guinea pigs, with their charming personalities and diverse coat types, are popular pets worldwide. Understanding their genetics, particularly the inheritance of coat characteristics, is fascinating and crucial for breeders aiming for specific traits. This article will delve into the genetics of guinea pig hair length, focusing on the dominance of the short-hair allele. We'll explore Mendelian inheritance, discuss the various coat types beyond simple short and long hair, and consider the implications for breeding programs.
Mendelian Inheritance and Guinea Pig Hair Length
The inheritance of short and long hair in guinea pigs follows a classic Mendelian pattern. This means a single gene, with two alleles (alternative forms of the gene), dictates hair length. The allele for short hair (S) is dominant, meaning it masks the expression of the recessive allele for long hair (s).
Homozygous and Heterozygous Genotypes:
- Homozygous dominant (SS): Guinea pigs with two copies of the dominant S allele exhibit short hair.
- Heterozygous (Ss): Guinea pigs with one dominant (S) and one recessive (s) allele also display short hair because the dominant allele masks the recessive allele.
- Homozygous recessive (ss): Only guinea pigs with two copies of the recessive s allele exhibit long hair.
Punnett Squares and Predicting Offspring:
Punnett squares are useful tools for visualizing the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from different parental combinations. Let's examine a few crosses:
1. Cross between two homozygous short-haired guinea pigs (SS x SS):
| S | S | |
|---|---|---|
| S | SS | SS |
| S | SS | SS |
All offspring (100%) will be homozygous dominant (SS) and have short hair.
2. Cross between a homozygous short-haired and a homozygous long-haired guinea pig (SS x ss):
| S | S | |
|---|---|---|
| s | Ss | Ss |
| s | Ss | Ss |
All offspring (100%) will be heterozygous (Ss) and have short hair. This generation is called the F1 generation.
3. Cross between two heterozygous short-haired guinea pigs (Ss x Ss):
| S | s | |
|---|---|---|
| S | SS | Ss |
| s | Ss | ss |
This cross produces a phenotypic ratio of 3:1 (short hair:long hair) and a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1 (SS:Ss:ss). 75% of the offspring will have short hair, and 25% will have long hair. This is a classic example of Mendelian inheritance.
Beyond Short and Long: The Complexity of Guinea Pig Coat Types
While the short/long hair distinction simplifies the explanation, guinea pig coat genetics are far more nuanced. Many genes interact to determine the final coat type, including those affecting:
- Hair texture: Beyond length, hair can be smooth, rough (rosette), or wiry.
- Hair density: Some guinea pigs have denser coats than others.
- Coat patterns: Many genes influence coat colour and patterns, such as agouti, self, and various spotting patterns.
These genes don't necessarily follow simple Mendelian inheritance. Some exhibit incomplete dominance (where heterozygotes show an intermediate phenotype), while others may display codominance (where both alleles are fully expressed). Epistasis, where one gene affects the expression of another, also plays a significant role.
Interaction of Genes: An Example
Imagine a scenario where a gene for hair texture (e.g., smooth vs. rough) interacts with the hair length gene. A guinea pig could be homozygous recessive for long hair (ss) but homozygous dominant for smooth hair (RR), resulting in a long-haired, smooth-coated guinea pig. The interaction of multiple genes creates a vast array of coat types observed in guinea pigs.
Implications for Breeding Programs
Understanding the genetics of guinea pig coat types is vital for breeders aiming to maintain or develop specific traits. Careful selection of breeding pairs, based on knowledge of their genotypes (ideally determined through pedigree analysis and/or genetic testing, though genetic testing isn't readily available for all traits), is key to achieving desired outcomes.
Selective Breeding and Desired Traits:
Breeders can use Punnett squares and their understanding of Mendelian inheritance and other genetic principles to predict the likelihood of producing offspring with specific coat types. This allows them to:
- Maintain purebred lines: Breeders of recognized guinea pig breeds strive to maintain the consistent phenotypic characteristics within their lines by carefully selecting mating pairs with known genotypes.
- Develop new breeds or coat types: Through careful cross-breeding and selection, new coat types and variations can emerge.
- Avoid undesirable traits: By understanding the inheritance of recessive traits that might be undesirable (e.g., genetic diseases), breeders can make informed choices to minimize the risk of passing on these traits.
Challenges and Considerations:
Even with a deep understanding of guinea pig genetics, breeding for specific traits presents challenges:
- Incomplete penetrance and expressivity: Some genes may not always be expressed, or their expression may vary in intensity between individuals, even with the same genotype. This makes predicting outcomes less precise.
- Limited genetic testing: While genetic testing is becoming more common in animal breeding, it's not universally available for all guinea pig coat characteristics.
- Ethical considerations: Breeders must prioritize the health and welfare of their animals. Overemphasis on specific traits can lead to health problems if related genes also affect the animal’s health.
Conclusion: The Fascinating World of Guinea Pig Genetics
The seemingly simple inheritance pattern of short and long hair in guinea pigs opens a door to a much more complex and fascinating world of genetic interactions. Understanding the basic principles of Mendelian inheritance provides a foundation for comprehending the broader spectrum of coat types and patterns observed in these captivating animals. This knowledge is essential for responsible breeding practices, ensuring the health and well-being of guinea pigs while allowing breeders to achieve their desired results. Further research into the specific genes responsible for various coat characteristics will continue to unravel the intricacies of guinea pig genetics, leading to a deeper appreciation for these beloved pets.
Further Exploration:
- Investigate the genetics of specific guinea pig coat colours and patterns: Explore resources like breed standards and scientific publications to learn more about the genes responsible for colour and pattern variations.
- Research the role of epistasis in guinea pig coat genetics: Understand how the interaction of multiple genes can affect the final coat phenotype.
- Explore the ethical implications of selective breeding: Consider the potential for health problems and the responsible use of breeding practices.
By exploring these areas, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the fascinating world of guinea pig genetics and contribute to the responsible stewardship of these beloved animals.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
K2 Cr2 O7 H2 S O4
Apr 06, 2025
-
Why The Electric Field Inside A Conductor Is Zero
Apr 06, 2025
-
Chromatin Consists Of Dna And Protein
Apr 06, 2025
-
Fill In The Blanks With The Correct Interrogative Words
Apr 06, 2025
-
3x Y 2 6x 2y 4
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In Guinea Pigs The Allele For Short Hair Is Dominant . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
