How Many Valence Electrons Does Tellurium Have
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
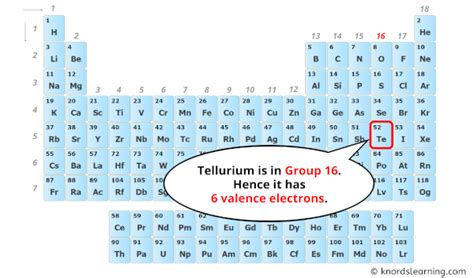
Table of Contents
- How Many Valence Electrons Does Tellurium Have
- Table of Contents
- How Many Valence Electrons Does Tellurium Have? A Deep Dive into its Electronic Structure and Chemical Properties
- Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Behavior
- Tellurium's Position in the Periodic Table: A Clue to its Valence Electrons
- Diving Deeper: Tellurium's Electronic Configuration
- The Significance of Six Valence Electrons: Chemical Implications
- Tellurium's Diverse Compounds: A Reflection of its Valence Electrons
- 1. Tellurides: Ionic Compounds
- 2. Tellurium Oxides: Covalent Compounds
- 3. Organotellurium Compounds: Carbon-Tellurium Bonds
- 4. Tellurium Halides: Covalent Bonds with Halogens
- Applications of Tellurium: Leveraging its Properties
- Conclusion: Valence Electrons – The Foundation of Tellurium's Chemistry
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Many Valence Electrons Does Tellurium Have? A Deep Dive into its Electronic Structure and Chemical Properties
Tellurium, a metalloid element residing in Group 16 of the periodic table, exhibits fascinating chemical properties largely dictated by its valence electrons. Understanding the number of valence electrons is crucial to comprehending its reactivity, bonding behavior, and the diverse compounds it forms. This in-depth exploration will delve into the electronic structure of tellurium, definitively answer the question of its valence electron count, and explore its implications.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Behavior
Before focusing specifically on tellurium, let's establish a firm understanding of valence electrons. These are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom, also known as the valence shell. They are the electrons most involved in chemical bonding and reactions. The number of valence electrons dictates an element's chemical properties, determining its reactivity, the types of bonds it can form (ionic, covalent, metallic), and the number of bonds it can create. The periodic table's organization reflects this, with elements in the same group (column) possessing the same number of valence electrons and therefore sharing similar chemical behavior.
Tellurium's Position in the Periodic Table: A Clue to its Valence Electrons
Tellurium (Te) is found in Group 16 (also known as the chalcogens or oxygen family) of the periodic table. This group is characterized by elements having six valence electrons. This crucial piece of information provides a direct answer to our initial question: Tellurium has six valence electrons.
Diving Deeper: Tellurium's Electronic Configuration
To fully understand the "why" behind the six valence electrons, we need to examine tellurium's electronic configuration. The electronic configuration describes how electrons are distributed among the various energy levels and orbitals within an atom. Tellurium's electronic configuration is [Kr] 4d<sup>10</sup> 5s<sup>2</sup> 5p<sup>4</sup>.
Let's break this down:
- [Kr]: This represents the core electrons, equivalent to the electronic configuration of krypton (a noble gas). These core electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus and generally do not participate in chemical bonding.
- 4d<sup>10</sup>: These are ten electrons in the 4d subshell. While these are not valence electrons (they're in a lower energy level), they do influence tellurium's overall properties, contributing to its metallic character.
- 5s<sup>2</sup>: Two electrons in the 5s subshell. These are valence electrons.
- 5p<sup>4</sup>: Four electrons in the 5p subshell. These are also valence electrons.
Adding the electrons from the 5s and 5p subshells (2 + 4 = 6), we confirm that tellurium possesses six valence electrons.
The Significance of Six Valence Electrons: Chemical Implications
The presence of six valence electrons significantly influences tellurium's chemical behavior. Elements strive to achieve a stable electron configuration, often resembling that of a noble gas (eight valence electrons – the octet rule). Tellurium can achieve this stability in several ways:
- Gaining two electrons: Tellurium can gain two electrons to form the Te<sup>2-</sup> anion, achieving a stable octet. This is common in ionic compounds where tellurium interacts with highly electropositive metals.
- Sharing electrons: Tellurium can share its valence electrons through covalent bonding to achieve a stable octet. This is prevalent in its many covalent compounds, where it forms bonds with other nonmetals. It can form single, double, and even some less common multiple bonds.
- Metallic Bonding: Because of its metalloid nature, tellurium can also participate in metallic bonding within its elemental form. In this case, valence electrons are delocalized throughout a lattice of tellurium atoms, contributing to its conductivity.
Tellurium's Diverse Compounds: A Reflection of its Valence Electrons
The versatility of tellurium's bonding behavior is evident in the wide array of compounds it forms. These include:
1. Tellurides: Ionic Compounds
Tellurides are binary compounds formed between tellurium and a more electropositive element, often a metal. In these compounds, tellurium typically accepts two electrons to form the Te<sup>2-</sup> anion, achieving a stable octet. Examples include zinc telluride (ZnTe) and lead telluride (PbTe), both used in semiconductor applications.
2. Tellurium Oxides: Covalent Compounds
Tellurium forms several oxides, the most common being tellurium dioxide (TeO<sub>2</sub>) and tellurium trioxide (TeO<sub>3</sub>). These compounds involve covalent bonding between tellurium and oxygen atoms, showcasing tellurium's ability to share its electrons. The structures and properties of these oxides are complex and depend on the specific bonding arrangements.
3. Organotellurium Compounds: Carbon-Tellurium Bonds
Organotellurium compounds contain carbon-tellurium bonds. These are interesting compounds because they blend organic chemistry with the unique properties of tellurium. The synthesis and study of these compounds are important areas of research with potential applications in material science and medicine.
4. Tellurium Halides: Covalent Bonds with Halogens
Tellurium forms a range of halides, such as tellurium tetrachloride (TeCl<sub>4</sub>) and tellurium hexafluoride (TeF<sub>6</sub>). These compounds highlight tellurium's ability to form multiple bonds with halogens, showcasing its versatility in covalent bonding.
Applications of Tellurium: Leveraging its Properties
Tellurium's unique properties, stemming directly from its six valence electrons and resulting bonding capabilities, lead to a variety of applications. These include:
- Semiconductors: Tellurides such as cadmium telluride (CdTe) and lead telluride (PbTe) are used in solar cells and infrared detectors due to their semiconducting properties. The ability of tellurium to form both ionic and covalent bonds plays a crucial role in tailoring the electronic band structure for specific applications.
- Metallurgy: Tellurium is added to certain alloys to improve their machinability and other mechanical properties. Its ability to form alloys stems from its metalloid nature and the availability of its valence electrons for metallic bonding.
- Rubber Vulcanization: Small amounts of tellurium are used as a vulcanizing agent in rubber production, modifying its properties to enhance its strength and durability. This application highlights the role of covalent bonding in modifying the macroscopic properties of materials.
- Chemical Catalysts: Tellurium compounds are used as catalysts in several chemical processes. The variable oxidation states of tellurium and its ability to participate in redox reactions are crucial for its catalytic activity.
Conclusion: Valence Electrons – The Foundation of Tellurium's Chemistry
The number of valence electrons an element possesses is fundamental in understanding its chemical behavior and the properties of its compounds. Tellurium, with its six valence electrons, exemplifies this principle. Its ability to gain, share, or delocalize these electrons allows it to form a variety of compounds with diverse applications in various industries. The detailed analysis of tellurium's electronic configuration and its resulting chemical properties offers a valuable insight into the fascinating world of inorganic chemistry and the crucial role of valence electrons in shaping the behavior of elements. Further exploration of the various tellurium compounds and their applications continues to be an active area of research, revealing new possibilities and expanding our understanding of this remarkable metalloid element.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Reaction Of Ammonia With Sulphuric Acid
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Main Purpose Of Cellular Respiration Is To
Mar 18, 2025
-
Red And White Blood Cells In Fluid Matrix
Mar 18, 2025
-
Why Blood Is Considered A Connective Tissue
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Much Is 1 4 Of A Gallon
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Does Tellurium Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
