How Many Protons Does Xenon Have
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
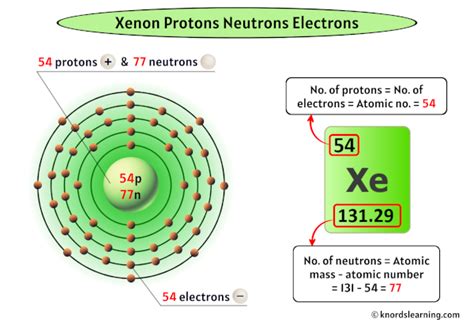
Table of Contents
How Many Protons Does Xenon Have? Exploring the Noble Gas and its Atomic Structure
Xenon, a fascinating element residing in Group 18 of the periodic table, is a noble gas known for its unique properties and applications. Understanding its atomic structure is key to appreciating its behavior and uses. A fundamental aspect of this understanding is knowing the number of protons it possesses. This article delves deep into the world of xenon, exploring its atomic structure, isotopic variations, and the significance of its proton count in determining its identity and properties.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before diving into the specifics of xenon, let's review the basic building blocks of an atom:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element's atomic number and determines its identity.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also residing in the nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge. The number of neutrons can vary within an element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The arrangement of these subatomic particles dictates an atom's chemical and physical properties. The number of protons is paramount; it's the atomic fingerprint that distinguishes one element from another.
Xenon's Atomic Number: The Key to its Identity
The atomic number of xenon is 54. This means that every xenon atom contains 54 protons in its nucleus. This is the defining characteristic of xenon, setting it apart from all other elements. No other element has 54 protons; therefore, any atom with 54 protons is, by definition, a xenon atom.
The Significance of the Atomic Number
The atomic number's significance extends beyond simple identification. It directly influences:
- Chemical behavior: The number of protons determines the number of electrons in a neutral atom, which dictates how the atom interacts with other atoms to form chemical bonds. Xenon's full outer electron shell (8 electrons) accounts for its inertness – its reluctance to form chemical compounds.
- Physical properties: Properties like melting point, boiling point, density, and reactivity are all influenced by the atomic structure, with the proton number playing a crucial role. Xenon's noble gas nature results in low boiling and melting points, making it a gas at room temperature.
- Isotopic variations: While the number of protons remains constant for a given element, the number of neutrons can vary. These variations create isotopes, which are atoms of the same element with different mass numbers (the total number of protons and neutrons).
Isotopes of Xenon: Variations in Neutron Count
Xenon has numerous stable isotopes, meaning isotopes that do not undergo radioactive decay. These isotopes differ in their neutron count but all share the same 54 protons. The most abundant isotopes include Xenon-129 (26%) and Xenon-132 (27%), with other isotopes like Xenon-131, Xenon-134, and Xenon-136 also present in significant quantities.
Understanding Isotopic Abundance
The percentages mentioned represent the natural isotopic abundance of xenon. This means that in a naturally occurring sample of xenon, approximately 26% of the atoms will be Xenon-129, 27% will be Xenon-132, and so on. These variations in isotopic abundance have implications for various scientific applications, including geochronology and atmospheric studies.
Applications of Xenon: Leveraging its Unique Properties
Xenon's unique properties stemming from its atomic structure, especially its inertness and its ability to absorb and emit light, have led to several important applications:
- Lighting: Xenon is used in high-intensity discharge lamps, such as those found in car headlights and some specialized photographic lighting. The gas's ability to emit bright light when excited by an electrical discharge makes it ideal for these applications.
- Medical Imaging: Xenon's isotopes have applications in medical imaging techniques like SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography). Radioactive isotopes of xenon can be used to track blood flow and assess organ function.
- Anesthesia: Xenon is a powerful anesthetic gas with several advantages over other anesthetic agents. Its use is growing in some medical settings, offering a potential alternative to commonly used anesthetics.
- Spacecraft Propulsion: Xenon's ion propulsion systems are used in some spacecraft. Its inert nature and high atomic mass are beneficial for generating thrust in these systems.
- Scientific Research: Xenon's chemical inertness and ability to form compounds under specific conditions make it a valuable tool in various scientific research endeavors.
The Role of Protons in Xenon's Applications
It's crucial to understand that all these applications rely directly or indirectly on xenon's atomic structure, particularly its 54 protons. The number of protons determines the electronic configuration and, consequently, xenon's chemical and physical properties, which are the foundation of its diverse uses.
Further Exploration: Beyond the Basics
The information presented above provides a solid foundation for understanding the number of protons in xenon and its significance. However, the topic extends beyond the scope of a simple answer. There are numerous avenues for further exploration, including:
- Advanced atomic theory: A deeper dive into quantum mechanics and atomic orbital theory can provide a more nuanced understanding of electron arrangement and chemical bonding in xenon.
- Nuclear physics: Studying the nuclear properties of xenon's isotopes, including their stability and radioactive decay pathways for unstable isotopes, provides insights into nuclear structure and decay processes.
- Chemical compounds of xenon: While generally inert, xenon can form compounds under specific conditions. Investigating these compounds reveals the complex interactions between xenon and other elements under extreme conditions.
- Analytical techniques for xenon analysis: Various techniques like mass spectrometry and gas chromatography are used to analyze the isotopic composition of xenon samples.
By exploring these areas, one gains a deeper appreciation of xenon's role in various scientific disciplines.
Conclusion: The Importance of Xenon's 54 Protons
In conclusion, xenon, with its characteristic 54 protons, holds a unique position in the periodic table. Its atomic number dictates its identity, chemical behavior, physical properties, and ultimately, its wide-ranging applications in various fields. Understanding the significance of this proton count is crucial for appreciating xenon's role in science, technology, and medicine. The exploration of xenon's atomic structure opens doors to a deeper understanding of the fundamental principles of chemistry and physics, highlighting the intricate relationship between an element's atomic composition and its macroscopic properties. The 54 protons in each xenon atom are the cornerstone of this fascinating element's identity and capabilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Python Check If A String Is A Number
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Length Of Line Segment Pq
Mar 19, 2025
-
Homologous Chromosomes Separate During Which Phase Of Meiosis
Mar 19, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between Mcg And Mg
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Type Of Symmetry Do Sponges Have
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Does Xenon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
