How Many Meters Is One Light Year
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 4 min read
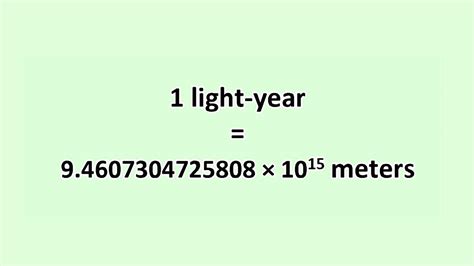
Table of Contents
How Many Meters is One Light Year? Unraveling the Immense Scale of Cosmic Distances
The universe is vast, a breathtaking expanse filled with stars, galaxies, and mysteries yet to be uncovered. Understanding the sheer scale of this cosmic ocean requires grappling with astronomical distances, and one of the most common units used to measure these distances is the light-year. But how many meters are actually in a single light-year? Let's delve into the fascinating calculation and explore the implications of this immense unit of measurement.
Understanding the Light-Year: A Measure of Distance, Not Time
Before we jump into the conversion, it's crucial to clarify a common misconception: a light-year measures distance, not time. It represents the distance light travels in one Earth year. This means it's a measure of how far light, traveling at an incredible speed, can journey within the span of 365.25 days.
The Speed of Light: The Foundation of Our Calculation
The speed of light (c) is a fundamental constant in physics. It's approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (m/s). This incredibly high speed is the foundation upon which the light-year is defined.
The Calculation: From Seconds to Meters in a Year
To determine the number of meters in a light-year, we need to perform a series of conversions:
-
Seconds in a Year: First, we need to calculate the total number of seconds in a year. There are 60 seconds in a minute, 60 minutes in an hour, 24 hours in a day, and approximately 365.25 days in a year (to account for leap years). Therefore:
60 seconds/minute * 60 minutes/hour * 24 hours/day * 365.25 days/year ≈ 31,557,600 seconds/year
-
Meters in a Light-Year: Now, we multiply the speed of light (in meters per second) by the number of seconds in a year:
299,792,458 m/s * 31,557,600 s/year ≈ 9,460,730,472,580,800 meters
Therefore, one light-year is approximately 9.461 x 10<sup>15</sup> meters. This is an incredibly large number, highlighting the vast distances involved in astronomy.
Visualizing the Immensity: Comparing Light-Years to Familiar Distances
To truly grasp the enormity of a light-year, let's compare it to distances we're more familiar with:
-
The Earth's Circumference: The Earth's circumference is approximately 40,075 kilometers (40,075,000 meters). A light-year is over 236 million times longer than Earth's circumference!
-
The Distance to the Moon: The average distance to the Moon is about 384,400 kilometers (384,400,000 meters). A light-year is over 24.6 million times farther than the distance to the Moon.
-
The Distance to the Sun: The average distance to the Sun (one astronomical unit or AU) is approximately 149.6 million kilometers (1.496 x 10<sup>11</sup> meters). A light-year is about 63,241 times farther than the distance to the Sun.
These comparisons demonstrate the incredible scale of a light-year and why it's necessary to use such a large unit to measure distances in space.
The Light-Year in Astronomy: Measuring the Cosmos
The light-year is an indispensable tool for astronomers. It helps them describe and understand the vast distances between celestial objects. Consider these examples:
-
Distances to Nearby Stars: The closest star to our Sun, Proxima Centauri, is approximately 4.24 light-years away. This means it takes light from Proxima Centauri 4.24 years to reach Earth.
-
Distances to Galaxies: Galaxies are enormous collections of stars, gas, and dust. The Andromeda Galaxy, the closest major galaxy to our Milky Way, is about 2.537 million light-years away.
-
The Observable Universe: The observable universe, the portion of the universe we can currently see, has a diameter of approximately 93 billion light-years. This is a truly mind-boggling distance.
Beyond the Light-Year: Other Units of Astronomical Distance
While the light-year is a commonly used unit, astronomers also utilize other units for measuring cosmic distances, depending on the scale:
-
Astronomical Unit (AU): Used primarily for distances within our solar system. One AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun.
-
Parsec (pc): A unit used for measuring distances to stars and galaxies. One parsec is approximately 3.26 light-years.
-
Kiloparsec (kpc): Equal to 1000 parsecs.
-
Megaparsec (Mpc): Equal to 1 million parsecs.
Conclusion: Embracing the Immensity of Space
Understanding the vastness of the universe is a humbling experience. The conversion of a light-year to meters – approximately 9.461 x 10<sup>15</sup> meters – underscores the incredible scale of cosmic distances. While the number itself might seem abstract, comparing it to familiar distances helps bring home the immensity of space and the challenges and wonders astronomers face as they explore this breathtaking expanse. The light-year, along with other astronomical units, provides essential tools for navigating and comprehending the universe's awe-inspiring dimensions. The exploration continues, and with each new discovery, our understanding of the cosmos deepens, driven by our ongoing efforts to measure and interpret the distances between celestial wonders.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
As We Move From Point A To Point D
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is Benzene A Pure Substance Or Mixture
Mar 23, 2025
-
Prove Square Root Of 5 Is Irrational
Mar 23, 2025
-
A Compound Contains Only Carbon Hydrogen And Oxygen
Mar 23, 2025
-
The Highest Barrier That A Projectile Can Clear Is
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Meters Is One Light Year . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
