How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does Octagon Have
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
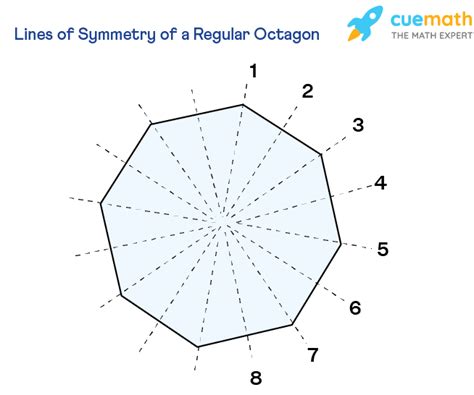
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does an Octagon Have? A Comprehensive Guide
Symmetry, a captivating concept in geometry, refers to the balanced distribution of a shape's parts around a central point or axis. Understanding lines of symmetry is crucial in various fields, from art and design to engineering and mathematics. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of octagons and their lines of symmetry, providing a detailed explanation suitable for students, educators, and anyone curious about geometrical properties.
Understanding Symmetry and Lines of Symmetry
Before diving into the specific case of octagons, let's establish a firm grasp on the fundamental concepts of symmetry and lines of symmetry.
Symmetry in geometry implies that a shape can be folded along a line (or rotated around a point) so that the two halves perfectly match. This means each corresponding point on one half of the shape has a matching point on the other half, equidistant from the line of symmetry (or point of rotational symmetry).
A line of symmetry (also called an axis of symmetry) is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves will perfectly overlap.
Exploring Regular and Irregular Octagons
Octagons, eight-sided polygons, can be categorized into two main types: regular and irregular. This distinction significantly impacts the number of lines of symmetry they possess.
A regular octagon has eight equal sides and eight equal angles (each measuring 135 degrees). It possesses a high degree of symmetry. An irregular octagon, on the other hand, has sides and angles of varying lengths and measures. Consequently, irregular octagons exhibit less symmetry.
Lines of Symmetry in a Regular Octagon
The beauty of a regular octagon lies in its numerous lines of symmetry. Let's systematically analyze how to identify them:
1. Lines of Symmetry Through Opposite Vertices:
A regular octagon possesses four lines of symmetry that pass directly through opposite vertices (corners). Imagine drawing a line from one corner to the corner directly opposite it. This line perfectly bisects the octagon into two mirror-image halves. Since there are four pairs of opposite vertices, there are four lines of symmetry of this type.
2. Lines of Symmetry Through Midpoints of Opposite Sides:
Besides the lines through vertices, a regular octagon also exhibits four lines of symmetry that connect the midpoints of opposite sides. Consider drawing a line connecting the midpoints of two sides that are parallel to each other. Again, this line divides the octagon into two perfectly symmetrical halves. There are four such pairs of parallel sides; therefore, there are four lines of symmetry of this type.
Total Lines of Symmetry in a Regular Octagon:
Combining the lines of symmetry through opposite vertices and the lines of symmetry through midpoints of opposite sides, we find that a regular octagon has a total of 4 + 4 = eight lines of symmetry.
Lines of Symmetry in an Irregular Octagon
The situation becomes considerably simpler (and less symmetrical) when dealing with irregular octagons. Because the sides and angles are unequal, the chances of finding a line that divides the shape into two perfectly mirrored halves are significantly reduced.
An irregular octagon might, depending on its specific shape, possess zero, one, or two lines of symmetry, or even rarely, more, but it will never possess eight. The existence and number of lines of symmetry in an irregular octagon is entirely dependent on the specific configuration of its sides and angles. It requires a careful inspection of the figure to determine the presence of any lines of symmetry. In most cases, irregular octagons will have either zero or a small number of lines of symmetry.
Visualizing Lines of Symmetry: Practical Exercises
To further solidify your understanding, consider engaging in some practical exercises:
-
Draw a regular octagon: Use a ruler and compass for accuracy. Then, carefully draw all eight lines of symmetry, alternating between those passing through opposite vertices and those passing through midpoints of opposite sides.
-
Draw several irregular octagons: Experiment with various shapes and sizes. See if you can identify any lines of symmetry. You’ll find that most irregular octagons possess very few or no lines of symmetry.
-
Use interactive geometry software: Many free online tools allow you to create and manipulate geometric shapes. This can provide a dynamic way to visualize lines of symmetry in both regular and irregular octagons. Experiment by dragging the vertices of an octagon and observe how the lines of symmetry change (or disappear).
Applications of Symmetry in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of symmetry, and the understanding of lines of symmetry in particular, finds wide-ranging applications in various fields:
-
Architecture and Design: Symmetrical designs are commonly employed in architecture to create visually appealing and balanced structures. From ancient temples to modern skyscrapers, symmetry plays a vital role in aesthetic design.
-
Art and Crafts: Artists and craftspeople utilize symmetry to create visually stunning and balanced compositions. Symmetrical patterns are prevalent in various forms of art, including painting, sculpture, and textile design.
-
Engineering: Symmetry considerations are crucial in engineering, particularly in designing structures and mechanisms. Symmetrical designs often lead to greater stability and efficiency.
-
Nature: Symmetry is prevalent throughout the natural world. From snowflakes to flowers to many animal species, symmetrical patterns are abundant. Understanding symmetry is essential in various scientific fields, including biology and crystallography.
Advanced Concepts: Rotational Symmetry
Beyond lines of symmetry, shapes can also possess rotational symmetry. Rotational symmetry refers to the ability of a shape to be rotated around a central point and still look identical. The order of rotational symmetry refers to the number of times the shape looks identical during a 360-degree rotation. A regular octagon possesses rotational symmetry of order 8, meaning it looks identical eight times during a 360-degree rotation. This is a further demonstration of the high degree of symmetry inherent in a regular octagon.
Conclusion: Mastering the Symmetry of Octagons
Understanding the lines of symmetry in octagons, whether regular or irregular, requires a systematic approach that combines theoretical knowledge with practical application. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the subject, emphasizing the key differences between regular and irregular octagons and illustrating the diverse applications of symmetry in various fields. By mastering these concepts, you'll enhance your geometrical understanding and appreciate the elegance and importance of symmetry in both mathematics and the wider world. Through practice and further exploration, you can deepen your understanding and appreciation for the fascinating world of geometry and symmetry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Are True About Natural Selection
Mar 17, 2025
-
Boiling Water Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 17, 2025
-
45 Is 60 Of What Number
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is Larger Mg Or Mcg
Mar 17, 2025
-
0 3 To The Power Of 3
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does Octagon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
