How Many H Bonds Between A And T
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
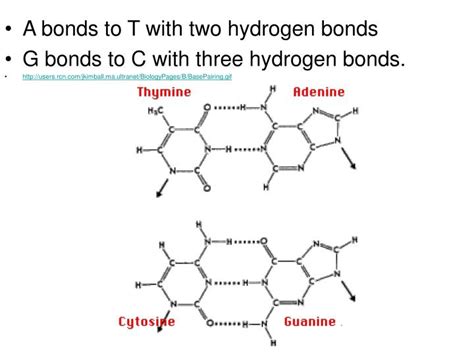
Table of Contents
How Many Hydrogen Bonds Between A and T? Understanding Adenine-Thymine Base Pairing
The question of how many hydrogen bonds exist between adenine (A) and thymine (T) is fundamental to understanding the structure and function of DNA. This seemingly simple question opens the door to a deeper exploration of molecular biology, highlighting the precise interactions that underpin life itself. This article will delve into the specifics of A-T base pairing, exploring the number of hydrogen bonds, the forces involved, and the broader implications for DNA structure and function.
The Foundation of DNA: Base Pairing
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the blueprint of life, carrying the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. Its structure, a double helix elegantly described by Watson and Crick, relies heavily on the specific interactions between its constituent bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). These bases are organized into nucleotides, which are then linked together to form the two polynucleotide strands that compose the DNA double helix.
The stability and specificity of the DNA double helix are crucially dependent on the hydrogen bonds formed between complementary bases on opposing strands. This base pairing follows Chargaff's rules, which state that in any DNA molecule, the amount of adenine (A) equals the amount of thymine (T), and the amount of guanine (G) equals the amount of cytosine (C). This 1:1 ratio is a direct consequence of the specific hydrogen bonding patterns between the bases.
A-T Base Pairing: Two Hydrogen Bonds
The fundamental answer to the question, "How many hydrogen bonds between A and T?" is two. Adenine and thymine form a base pair held together by two hydrogen bonds. These bonds are not covalent bonds; they are weaker electrostatic interactions between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom (such as oxygen or nitrogen) and another electronegative atom.
Let's break down the specific hydrogen bonds:
- Bond 1: A hydrogen atom attached to a nitrogen atom (N) on adenine forms a hydrogen bond with an oxygen atom (O) on thymine.
- Bond 2: A hydrogen atom attached to a nitrogen atom (N) on thymine forms a hydrogen bond with a nitrogen atom (N) on adenine.
These two hydrogen bonds, while individually weaker than covalent bonds, collectively provide sufficient stability to maintain the DNA double helix structure under physiological conditions. The precise geometry of these bonds, including the bond lengths and angles, is crucial for the proper stacking of base pairs and the overall stability of the double helix.
The Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in DNA Structure and Function
The two hydrogen bonds between A and T are not just a structural curiosity; they play several critical roles in DNA's function:
-
Specificity of Base Pairing: The specific number and geometry of hydrogen bonds ensure the precise pairing of A with T and G with C. This precise pairing is essential for accurate DNA replication and transcription, which are fundamental processes for maintaining genetic information and expressing genes.
-
Stability of the Double Helix: While individual hydrogen bonds are relatively weak, the cumulative effect of numerous hydrogen bonds along the length of the DNA molecule provides substantial stability to the double helix structure. This stability protects the genetic information from damage and ensures its accurate transmission across generations.
-
Ease of Strand Separation: The relatively weak nature of hydrogen bonds allows for the easy separation of the two DNA strands during processes such as DNA replication and transcription. Enzymes facilitate this process, breaking the hydrogen bonds in a controlled manner to allow access to the genetic information.
-
DNA Packaging: The interactions between base pairs, including hydrogen bonds, contribute to the overall three-dimensional structure of DNA. This structure is further compacted into chromatin fibers, enabling the efficient packaging of the vast amount of genetic information within the confines of a cell nucleus.
Comparing A-T and G-C Base Pairing
While A-T pairs are held together by two hydrogen bonds, guanine (G) and cytosine (C) form base pairs held together by three hydrogen bonds. This difference in the number of hydrogen bonds has implications for the stability of the DNA double helix:
-
G-C Base Pairs are Stronger: The three hydrogen bonds in G-C base pairs make them inherently stronger and more resistant to denaturation (strand separation) compared to A-T base pairs.
-
GC Content and DNA Stability: Regions of DNA with a high GC content are generally more stable than regions with a high AT content. This has implications for the melting temperature (Tm) of DNA, which is the temperature at which the two strands separate. Higher GC content results in a higher Tm.
-
Implications for Gene Regulation: The differing stability of A-T and G-C base pairs can play a role in gene regulation. For example, regions of DNA with a lower GC content may be more easily unwound and transcribed than regions with a higher GC content.
Beyond the Basics: Factors Influencing Hydrogen Bond Strength
The strength of hydrogen bonds between A and T, and indeed between any base pairs, isn't solely determined by the number of bonds. Several other factors also play a role:
-
Environmental Conditions: Factors like temperature, pH, and ionic strength of the surrounding solution significantly influence hydrogen bond stability. Higher temperatures weaken hydrogen bonds, making DNA denaturation more likely.
-
Base Stacking Interactions: Besides hydrogen bonding, the base pairs in DNA also interact through stacking interactions—hydrophobic forces between adjacent bases. These interactions contribute significantly to the overall stability of the DNA double helix.
-
Solvent Effects: The water molecules surrounding the DNA molecule can also influence hydrogen bond strength through interactions with the bases and the surrounding phosphate backbone.
-
Presence of Ions: The presence of ions in the solution can shield the electrostatic interactions involved in hydrogen bonding, affecting their strength.
Errors in Base Pairing and their Consequences
Although the hydrogen bonding system ensures high fidelity in DNA replication, errors can occasionally occur. Incorrect base pairing can lead to mutations, which can have varying effects on the organism. The cell has various mechanisms to repair these errors, but some mutations can persist and lead to significant consequences, including genetic diseases or cancer. The relatively weak nature of hydrogen bonds, while beneficial for processes like DNA replication and transcription, also makes them susceptible to such errors.
Conclusion: The Significance of Two Hydrogen Bonds
In conclusion, the answer to "how many hydrogen bonds between A and T?" is definitively two. These two hydrogen bonds, though individually weak, collectively contribute significantly to the stability and functionality of the DNA double helix. Understanding the precise nature of these bonds, their interactions with other forces within the DNA molecule, and their influence on DNA structure and function is fundamental to comprehending the complex machinery of life. The seemingly simple two hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine are, in essence, a cornerstone of the intricate blueprint of life itself. Further research continues to unravel the subtleties of these interactions and their impact on various biological processes, emphasizing the enduring importance of this seemingly straightforward question.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Floating Ice Block Is Pushed Through A Displacement
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Event Had An Enormous Effect On Us Workplace Safety
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Formula For Magnesium Acetate
Mar 19, 2025
-
Converse Of Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Distance Between Adjacent Crests Is Called
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many H Bonds Between A And T . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
