How Many Electrons Does Nitrogen Have In Its Outer Shell
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
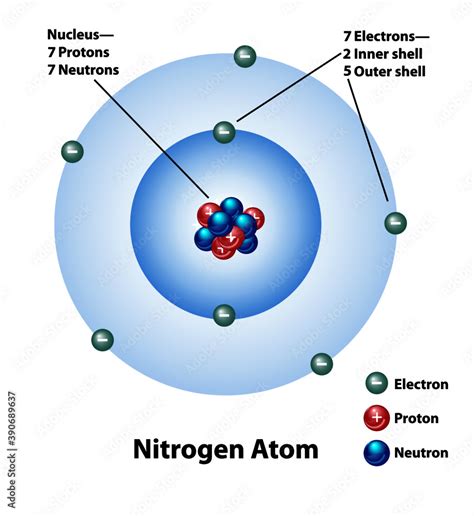
Table of Contents
How Many Electrons Does Nitrogen Have in Its Outer Shell? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Nitrogen, a crucial element for life as we know it, plays a pivotal role in various biological processes and industrial applications. Understanding its electronic structure, particularly the number of electrons in its outer shell (also known as the valence shell), is key to comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. This article delves into the fascinating world of nitrogen's atomic structure, explaining not only how many valence electrons it possesses but also the implications of this configuration for its properties and bonding characteristics.
Understanding Atomic Structure and Electron Shells
Before focusing on nitrogen specifically, let's establish a foundational understanding of atomic structure. Atoms are composed of a central nucleus containing protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral), surrounded by orbiting electrons (negatively charged). These electrons are arranged in distinct energy levels or shells, with each shell capable of holding a specific maximum number of electrons.
The arrangement of electrons within these shells dictates an atom's chemical properties. The outermost shell, called the valence shell, houses the valence electrons, which are directly involved in chemical bonding. The number of valence electrons an atom possesses largely determines its reactivity and the types of bonds it can form.
The Significance of Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the key players in chemical reactions. Atoms tend to react in ways that achieve a stable electron configuration, often a full outer shell. This stability is often achieved by gaining, losing, or sharing valence electrons with other atoms. This process is fundamental to the formation of chemical bonds – the forces that hold atoms together in molecules and compounds.
Nitrogen's Electron Configuration: Unveiling the Mystery
Nitrogen (N) has an atomic number of 7, meaning it possesses 7 protons and 7 electrons in a neutral atom. To understand the electron arrangement, we use the concept of electron shells and subshells. Electrons fill shells and subshells according to specific rules based on energy levels and the Pauli Exclusion Principle (which states that no two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers).
The electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s²2s²2p³. Let's break this down:
- 1s²: The first shell (n=1) contains the 's' subshell, which can hold a maximum of two electrons. Nitrogen has two electrons in this innermost shell.
- 2s²: The second shell (n=2) also contains an 's' subshell, capable of holding two electrons. Nitrogen fills this subshell completely.
- 2p³: The second shell also contains a 'p' subshell, which can hold up to six electrons (distributed across three orbitals, px, py, and pz). Nitrogen has three electrons in its 2p subshell.
The Answer: Nitrogen's Valence Electrons
From the electron configuration (1s²2s²2p³), we can clearly see that nitrogen has five valence electrons. These are the electrons in the outermost shell (n=2), which includes both the 2s and 2p subshells. These five valence electrons are responsible for nitrogen's chemical reactivity and its ability to form a variety of chemical bonds.
Chemical Bonding and Nitrogen's Valence Electrons
The presence of five valence electrons significantly influences nitrogen's bonding behavior. To achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in its outer shell), nitrogen readily forms covalent bonds, sharing electrons with other atoms. This tendency explains its presence in numerous molecules and compounds crucial for life and various industrial processes.
Examples of Nitrogen's Bonding:
- Ammonia (NH₃): Nitrogen shares three electrons with three hydrogen atoms, forming three covalent bonds and achieving a stable octet.
- Nitrogen gas (N₂): Two nitrogen atoms share three pairs of electrons, forming a strong triple bond (a very stable structure) to fulfill their octet requirement. This triple bond explains the relative inertness of nitrogen gas in its elemental form.
- Nitric oxide (NO): A more complex example showing nitrogen's ability to form bonds with varying bond orders, resulting in molecules with unpaired electrons (radicals) and exhibiting unique reactivity.
Nitrogen's Role in Biological Systems and Industrial Applications
Nitrogen's unique electronic configuration and its ability to form stable covalent bonds are directly linked to its vital roles in biology and industry.
Biological Significance:
- Amino acids and proteins: Nitrogen is a fundamental component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, which are essential for countless biological processes.
- Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA): Nitrogen is also crucial for the structure of nucleic acids, the carriers of genetic information.
- Nitrogen cycle: The nitrogen cycle, involving the conversion of nitrogen between various forms (e.g., atmospheric nitrogen, ammonia, nitrates), is essential for maintaining the balance of life on Earth, with nitrogen-fixing bacteria playing a key role in converting atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms for plants and other organisms.
Industrial Applications:
- Fertilizers: Nitrogen-containing fertilizers are vital for enhancing crop yields and food production worldwide. The Haber-Bosch process, which converts atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, is a cornerstone of modern agriculture.
- Explosives: Certain nitrogen-containing compounds are used in the production of explosives, leveraging the energy released during the breakdown of nitrogen-oxygen bonds.
- Pharmaceuticals: Nitrogen is found in many pharmaceutical compounds, contributing to their biological activity and therapeutic properties.
Further Exploration of Nitrogen Chemistry
Understanding nitrogen's valence electrons is just the beginning of a deeper exploration into its rich chemistry. The study of nitrogen includes:
- Oxidation states: Nitrogen can exhibit various oxidation states, from -3 (as in ammonia) to +5 (as in nitric acid), showcasing its versatile bonding capabilities.
- Coordination chemistry: Nitrogen can act as a ligand, forming coordinate bonds with metal ions, playing a critical role in various catalytic processes and the synthesis of coordination complexes.
- Nitrogen isotopes: The existence of different isotopes of nitrogen (¹⁴N and ¹⁵N) provides valuable tools for studying various biological and geochemical processes.
Conclusion: The Significance of Five Valence Electrons
In conclusion, nitrogen possesses five valence electrons, a key factor determining its chemical behavior and its critical roles in biological systems and various industrial applications. This seemingly simple number underpins the complexity of nitrogen chemistry, highlighting the profound impact of atomic structure on the properties and functions of this essential element. Further investigation into nitrogen's fascinating properties continues to reveal new insights into its diverse roles in our world. The understanding of its valence electron configuration serves as a foundational principle in comprehending its behavior and importance across numerous scientific disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Value Of Log Subscript 27 Baseline 9
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Chromosomes In Liver Cells
Apr 01, 2025
-
All Of The Following Refer To Mitosis Except
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Temperatures Is The Coldest
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Short Term Unsecured Promissory Note Issued By A Company Is
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Electrons Does Nitrogen Have In Its Outer Shell . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
