How Many Electrons Are In A Neutral Carbon-14 Atom
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
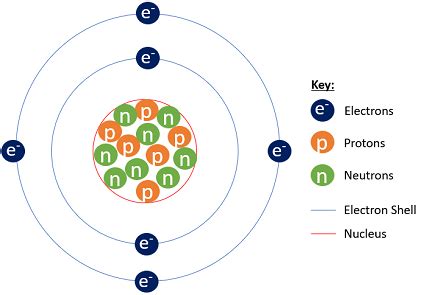
Table of Contents
How Many Electrons Are in a Neutral Carbon-14 Atom? Understanding Atomic Structure and Isotopes
The question of how many electrons are in a neutral carbon-14 atom is seemingly simple, yet it opens the door to a deeper understanding of atomic structure, isotopes, and the fundamental principles of chemistry. Let's delve into the answer and explore the related concepts in detail.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
To answer our central question, we must first grasp the basics of atomic structure. An atom consists of three fundamental subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; all carbon atoms, regardless of their isotope, have 6 protons.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also located in the atom's nucleus. The number of neutrons can vary within the same element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
Isotopes: Variations in Neutron Number
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in their number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties significantly. Carbon, for example, has several isotopes, the most common being carbon-12 (¹²C) and carbon-13 (¹³C), and the radioactive isotope carbon-14 (¹⁴C). The number after the element's name represents the mass number (A), which is the sum of protons and neutrons.
Carbon-14: A Radioactive Isotope
Carbon-14 (¹⁴C) is a radioactive isotope of carbon, meaning its nucleus is unstable and undergoes radioactive decay. This decay process involves the emission of particles, ultimately transforming the ¹⁴C atom into a different element. This radioactive decay is a crucial tool in radiocarbon dating, a technique used to determine the age of organic materials.
Determining the Number of Electrons in Carbon-14
Now, let's address the main question: how many electrons are in a neutral carbon-14 atom? Since the number of electrons in a neutral atom always equals the number of protons, and carbon always has 6 protons, a neutral carbon-14 atom has 6 electrons.
The extra neutrons in ¹⁴C (8 neutrons compared to 6 in ¹²C) do not affect the number of electrons. Neutrons contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge. The electron configuration remains the same as in other carbon isotopes; they occupy specific energy levels around the nucleus.
Electron Configuration and Energy Levels
Understanding electron configuration provides a more detailed picture of the atom's structure. Electrons occupy specific energy levels or shells around the nucleus. These shells have different capacities for electrons. The electron configuration of a neutral carbon atom, including ¹⁴C, is 1s²2s²2p².
- 1s²: Two electrons in the first energy level (n=1), which is closest to the nucleus.
- 2s²: Two electrons in the second energy level (n=2), the s subshell.
- 2p²: Two electrons in the second energy level (n=2), the p subshell.
This arrangement explains the atom's chemical behavior, as the outermost electrons (valence electrons) in the 2s and 2p subshells determine its reactivity.
Significance of Carbon-14 in Science and Technology
Carbon-14's radioactive nature has made it invaluable in several scientific fields:
1. Radiocarbon Dating:
This technique leverages the known decay rate of ¹⁴C to estimate the age of organic materials like artifacts, fossils, and ancient documents. The ratio of ¹⁴C to ¹²C in the sample is compared to the ratio in the atmosphere, enabling scientists to calculate the time elapsed since the organism died.
2. Archaeological and Anthropological Studies:
Radiocarbon dating has revolutionized archaeology and anthropology by providing precise dates for artifacts and fossils, allowing researchers to reconstruct past civilizations and understand evolutionary processes more accurately.
3. Geological Studies:
¹⁴C dating extends beyond the study of organic materials, finding applications in geological studies to date sediments, groundwater, and other geological formations.
4. Biomedical Research:
Carbon-14, due to its radioactive nature and its incorporation into biological molecules, plays a significant role in biomedical research. It's used as a tracer to study metabolic processes, drug interactions, and the fate of molecules within living organisms.
5. Environmental Science:
Understanding the distribution and levels of ¹⁴C in the environment can provide insights into various environmental processes, including carbon cycling, pollutant dispersal, and the impact of human activities.
Further Exploring Atomic Concepts
The understanding of atomic structure, isotopes, and the unique properties of carbon-14 extends to more complex concepts:
1. Nuclear Reactions and Decay:
The radioactive decay of ¹⁴C involves beta decay, where a neutron is converted into a proton, emitting an electron (beta particle) and an antineutrino. This process transforms ¹⁴C into nitrogen-14 (¹⁴N).
2. Nuclear Chemistry:
The study of nuclear chemistry delves into the properties and reactions of atomic nuclei, including the processes involved in nuclear fission and fusion.
3. Quantum Mechanics:
The behavior of electrons within an atom is described by the principles of quantum mechanics, where electrons are considered as both particles and waves, occupying specific orbitals with defined energy levels.
4. Mass Spectrometry:
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique used to identify and quantify isotopes in a sample. By measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of ions, mass spectrometry can accurately determine the isotopic composition of a sample, including the abundance of ¹⁴C.
Conclusion: A Fundamental Understanding
The simple question, "How many electrons are in a neutral carbon-14 atom?" has led us on a journey through the fascinating world of atomic structure, isotopes, and the unique properties of carbon-14. Understanding the number of electrons (6) in a neutral carbon-14 atom requires a grasp of fundamental principles, while also highlighting the significance of this radioactive isotope in diverse scientific disciplines. The knowledge gained provides a foundation for exploring more complex concepts in chemistry, physics, and related fields. The applications of ¹⁴C dating and its use as a tracer in various research areas emphasize the practical significance of understanding atomic structure at the most fundamental level.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Statement About Natural Selection Is True
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Chamber Of Heart Has Thickest Wall
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 1 2 Miles
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lines Of Symmetry On A Trapezoid
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Electrons Are In A Neutral Carbon-14 Atom . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
