How Many Chambers Are In The Fish Heart
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
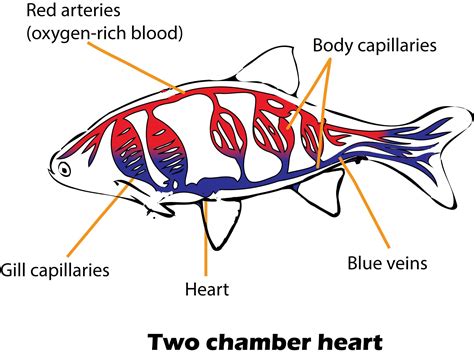
Table of Contents
How Many Chambers Does a Fish Heart Have? Exploring the Cardiovascular System of Fishes
The seemingly simple question, "How many chambers are in a fish heart?" opens a fascinating window into the diverse and intricate world of fish physiology. While the answer is generally two, a closer examination reveals complexities and variations within this seemingly straightforward anatomical feature. Understanding the fish heart's structure is crucial to appreciating its function, the evolution of cardiovascular systems, and the remarkable adaptations that allow fish to thrive in a vast array of aquatic environments. This article delves into the details of the fish heart, exploring its chambers, circulation pathways, and the evolutionary significance of its unique design.
The Two-Chambered Heart: A Closer Look
Unlike the complex four-chambered hearts of mammals and birds, fish possess a two-chambered heart. This simpler structure consists of:
- One atrium: This thin-walled chamber receives deoxygenated blood returning from the body. Think of it as a collecting chamber, preparing the blood for its journey to the next stage.
- One ventricle: This thick-walled chamber pumps the deoxygenated blood to the gills for oxygenation. This is the powerhouse of the fish heart, responsible for generating the pressure needed to propel the blood through the gills and subsequently throughout the body.
This seemingly rudimentary structure is incredibly efficient for its purpose. The single pathway ensures that all blood passes through the gills before circulating to the rest of the body. This single circuit circulatory system is a defining characteristic of fish cardiovascular systems.
The Circulatory Pathway: A Single Journey
The circulatory pathway in fish is a single, continuous loop, often referred to as a single circulation. This contrasts sharply with the double circulation found in mammals and birds, where blood passes through the heart twice in one complete circuit. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of the fish circulatory pathway:
- Deoxygenated blood: Blood depleted of oxygen returns from the body tissues to the atrium via the venous system. This system comprises a network of veins that converge on the heart.
- Atrium to ventricle: The atrium contracts, pushing the deoxygenated blood into the ventricle. This transfer is facilitated by the pressure difference between the two chambers.
- Ventricle to gills: The ventricle, with its powerful muscular walls, contracts forcefully, pumping the deoxygenated blood through the ventral aorta to the gills. The ventral aorta is a large artery that branches off into smaller arteries supplying the gill filaments.
- Gill oxygenation: Within the gills, the blood undergoes gas exchange. Oxygen diffuses from the water into the blood, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the water. This process is highly efficient due to the large surface area provided by the numerous gill filaments.
- Oxygenated blood to body: The now-oxygenated blood leaves the gills via the dorsal aorta, a large artery that distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. This system branches into a complex network of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries, ensuring that all tissues receive the oxygen they need.
- Return to the heart: After delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body's tissues, the deoxygenated blood returns to the heart via the venous system, completing the cycle.
Variations and Exceptions: Beyond the Two-Chambered Norm
While the two-chambered heart is the typical configuration, some exceptions and variations exist within the fish kingdom. These variations highlight the remarkable adaptability of cardiovascular systems to different environments and lifestyles.
- Lungfish: Lungfish, a group of freshwater fish possessing both gills and lungs, represent a fascinating evolutionary step. Their hearts show a partial separation within the atrium, suggesting a transition towards a more efficient circulatory system. Although still fundamentally two-chambered, this subtle modification hints at evolutionary pathways towards more complex cardiac structures.
- Embryonic Development: In some fish species, during embryonic development, the heart might exhibit temporary structural changes. This is a common evolutionary pattern; the developmental stages of an organism can often provide valuable clues to evolutionary history and relationships.
- Specialized Adaptations: Certain fish species inhabiting extreme environments (e.g., high altitudes or deep-sea trenches) might exhibit subtle modifications in their cardiovascular systems to cope with the specific challenges of their habitats. These modifications aren't necessarily reflected in the number of chambers but in the efficiency of blood flow and gas exchange.
Evolutionary Significance: A Stepping Stone to Complexity
The two-chambered heart of fish is not simply a primitive structure; it's a highly effective solution for a single circulatory system. It represents a crucial stage in the evolution of vertebrate cardiovascular systems. The evolution of more complex hearts with multiple chambers, such as those seen in amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, involved a series of adaptations to improve oxygen delivery efficiency and support higher metabolic rates. These adaptations included the separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood flows, which drastically improved the efficiency of oxygen transport.
The fish heart’s simplicity highlights the elegance of evolutionary design. Its structure reflects a balance between efficient oxygen delivery within the limitations of a single circulatory pathway and the metabolic demands of aquatic life.
The Importance of Understanding Fish Cardiovascular Systems
Understanding the fish heart's structure and function is crucial for several reasons:
- Conservation efforts: Knowledge of fish physiology is essential for effective conservation and management of fish populations. Understanding how environmental factors affect cardiovascular health can help inform strategies to mitigate the effects of pollution, climate change, and habitat loss.
- Aquaculture: Efficient aquaculture practices require an understanding of fish physiology to optimize growth, health, and reproductive success. Cardiovascular health is a critical factor in overall fish well-being.
- Fisheries Management: Understanding the physiological adaptations of fish to different environments is crucial for sustainable fisheries management.
- Medical Research: The study of fish cardiovascular systems contributes to broader biological and medical research. Fish models are used in studies of heart development, disease mechanisms, and drug discovery.
Conclusion: Simplicity and Efficiency
The answer to "How many chambers are in a fish heart?" is fundamentally two, an atrium and a ventricle. However, this simple structure belies the complexity and sophistication of the fish circulatory system. Its design reflects an evolutionary adaptation perfectly suited to the challenges and opportunities of aquatic life. The two-chambered heart, with its single circulatory pathway, ensures efficient oxygen delivery within the constraints of its environment. Further exploration of this seemingly simple organ reveals a fascinating story of adaptation, evolution, and the remarkable diversity of life in the world's oceans and freshwater ecosystems. The study of fish cardiovascular systems continues to offer valuable insights into biology, evolution, and the health of aquatic environments.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lines Of Symmetry On A Trapezoid
Mar 18, 2025
-
Two Same Words With Different Meanings
Mar 18, 2025
-
Select The Correct Statement About Equilibrium
Mar 18, 2025
-
Draw The Major Product Of The Following Reaction
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Chambers Are In The Fish Heart . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
