How Many Bonds Does Boron Form
News Leon
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
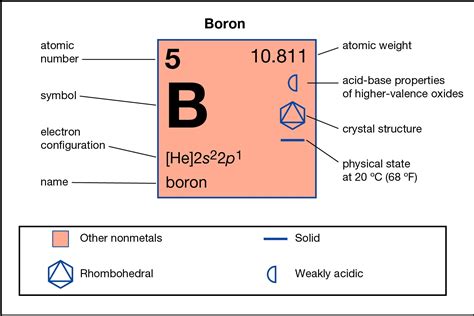
Table of Contents
How Many Bonds Does Boron Form? Exploring the Unusual Bonding Behavior of Boron
Boron, the fifth element on the periodic table, presents a fascinating case study in chemical bonding. Unlike its neighbors carbon and aluminum, boron doesn't consistently follow the octet rule, leading to a diverse range of bonding behaviors and structural complexities. This article delves deep into the intricacies of boron bonding, exploring why it forms the number of bonds it does and the consequences of this unique behavior.
The Octet Rule and its Exceptions: Boron's Dilemma
The octet rule, a cornerstone of basic chemistry, suggests that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable configuration of eight valence electrons. This stable configuration resembles that of a noble gas. However, boron, with only three valence electrons, cannot achieve an octet simply by forming covalent bonds. This limitation forces boron to exhibit unconventional bonding patterns.
Understanding Boron's Valence Electrons
Boron's electron configuration is 1s²2s²2p¹. This implies that it has three valence electrons available for bonding. According to the octet rule, it would need five more electrons to achieve stability. This presents a challenge, leading boron to explore strategies beyond the strict adherence to the octet rule.
The Prevalence of Three-Center Two-Electron Bonds
One of the most significant characteristics of boron chemistry is its propensity to form three-center two-electron (3c-2e) bonds. These bonds involve three atoms sharing two electrons, effectively bridging the gap between boron atoms and achieving a more stable arrangement. This unique bonding motif is crucial in understanding many boron compounds' structures and properties.
Examples of 3c-2e Bonding in Boron Compounds
The classic example of 3c-2e bonding in boron is found in diborane (B₂H₆). In diborane, two boron atoms are linked by two 3c-2e bonds, often described as "banana bonds" due to their curved shape. These bonds supplement the four regular two-center two-electron (2c-2e) bonds between boron and hydrogen atoms. The formation of these 3c-2e bonds allows each boron atom to achieve a semblance of stability, although it falls short of a complete octet.
Implications of 3c-2e Bonds on Boron's Bonding Capacity
The presence of 3c-2e bonds fundamentally alters boron's bonding behavior. While it may appear that boron only forms three "conventional" covalent bonds (as in BH₃), the inclusion of 3c-2e bonds expands its effective bonding capacity. Diborane, for instance, effectively demonstrates boron's ability to participate in a greater number of bonding interactions than initially suggested by its three valence electrons.
Boron's Bonding Capacity: Beyond Three Bonds
While the prevalent view suggests boron forms three bonds, a more nuanced understanding reveals a more complex picture. The actual number of bonds formed depends heavily on the surrounding atoms and the specific molecular structure.
Factors Influencing Boron's Bonding
Several factors significantly influence the number of bonds boron forms:
- Electronegativity of the bonded atoms: The electronegativity difference between boron and the atom it is bonded to can influence bond strength and stability. Highly electronegative atoms can pull electron density away from boron, impacting its overall bonding behavior.
- Steric factors: The size and spatial arrangement of neighboring atoms can influence the formation of 3c-2e bonds or other unconventional bonding modes. Steric hindrance can prevent the formation of certain bonds, restricting boron's bonding capacity.
- The presence of electron-donating ligands: Electron-donating ligands, such as ammonia or amines, can interact with boron atoms, modifying their electronic environment and influencing bonding behavior. These interactions can lead to an increase in the number of effective bonds involving boron.
Higher Coordination Numbers in Boron Compounds
Beyond the typical three-bond scenario, boron can exhibit higher coordination numbers in certain compounds. This indicates that boron can form more than three bonds, although not necessarily through conventional covalent bonding.
Examples of Higher Coordination Numbers
In some borate structures, for instance, boron atoms can be surrounded by four or even five oxygen atoms. In these cases, the bonding involves a combination of covalent and ionic interactions, leading to a higher coordination number. These structures highlight that the simple "three-bond" notion is an oversimplification in understanding the true extent of boron's bonding versatility.
Boron Clusters: A World of Complex Bonding
Boron's tendency to form clusters is a testament to its unique bonding behavior. These clusters feature intricate networks of boron atoms bonded together in various arrangements, often incorporating 3c-2e bonds and other unconventional bonding modes.
The Structure and Bonding in Boron Clusters
The stability of boron clusters is attributed to the delocalization of electrons across the cluster framework. This delocalization enhances the overall stability of the structure. The bonding in these clusters is often described using concepts from molecular orbital theory, revealing a complex interplay of bonding and antibonding interactions. These clusters represent a significant challenge and a fascinating area of ongoing research in chemistry.
Applications Leveraging Boron's Unique Bonding
The unusual bonding properties of boron have led to a wide range of applications in various fields:
- Materials Science: Boron compounds, particularly boron nitride and boron carbide, are known for their exceptional hardness and high thermal stability, making them valuable materials in high-temperature applications and protective coatings.
- Medicine: Boron-containing compounds have shown promise in boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT), a type of cancer treatment. The unique nuclear properties of boron are exploited in this method.
- Catalysis: Boron compounds act as catalysts in various chemical reactions, often due to their Lewis acidity. Their ability to accept electron pairs makes them effective catalysts in organic synthesis.
Conclusion: The Versatile World of Boron Bonding
In conclusion, while boron typically displays three covalent bonds, a more accurate description recognizes its tendency to form 3c-2e bonds, participate in higher coordination numbers, and create complex clusters. Its bonding behavior is far from simple, relying on a combination of covalent, ionic, and delocalized bonding interactions. This versatility makes boron a crucial element in various chemical compounds and materials, influencing their properties and applications in diverse fields. Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of boron's bonding, promising new insights and applications in the future. The seemingly simple question of "how many bonds does boron form?" leads us down a fascinating rabbit hole of sophisticated chemical bonding and intriguing structural possibilities.
Further Exploration: Delving Deeper into Boron Chemistry
This article has provided a foundational understanding of boron's bonding. To deepen your knowledge, further research into these topics is recommended:
- Advanced Bonding Theories: Explore the application of molecular orbital theory and density functional theory to boron compounds to gain a deeper understanding of the electronic structure and bonding.
- Boron Cluster Chemistry: Investigate the diverse structures and bonding patterns observed in boron clusters and their implications for materials science.
- Boron-containing polymers and materials: Research the synthesis and properties of polymers and materials containing boron, understanding their unique characteristics derived from the boron's bonding behavior.
- Computational Chemistry studies of boron compounds: Access and analyze computational studies that provide detailed information on the electron distribution and bond properties in boron compounds.
By delving deeper into these topics, you can gain a much more comprehensive appreciation for the multifaceted and fascinating world of boron chemistry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
3 Cards Same From 52 Probability
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Cell Organelle Is Found Only In Plant Cell
Mar 16, 2025
-
The Summer Of The White Horse
Mar 16, 2025
-
How To Separate Water And Gasoline
Mar 16, 2025
-
Is Wool A Conductor Or Insulator
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Bonds Does Boron Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
