How Many Bonds Can Beryllium Form
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
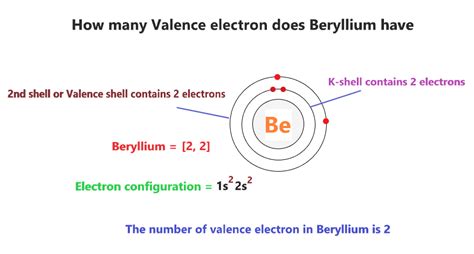
Table of Contents
How Many Bonds Can Beryllium Form? Exploring the Chemistry of an Exception to the Octet Rule
Beryllium, the fascinating element residing at the top of Group 2 in the periodic table, presents a unique case study in chemical bonding. While the octet rule, suggesting atoms strive to achieve a full outer shell of eight electrons, serves as a useful guideline for many elements, beryllium frequently defies this rule, leading to intriguing bonding behaviours. Understanding how many bonds beryllium can form requires delving into its electronic configuration, its tendency to violate the octet rule, and the various factors influencing its bonding preferences.
The Electronic Configuration and Bonding Capacity
Beryllium possesses an electronic configuration of 1s²2s². This implies that it has two valence electrons in its outermost shell. According to the simplistic application of the octet rule, one might expect beryllium to form only two bonds, losing its two valence electrons to achieve a stable, empty outer shell. However, the reality is considerably more nuanced.
While two-coordination is indeed common for beryllium, exhibiting a linear geometry, the element frequently forms compounds where it displays a higher coordination number. This discrepancy stems from the relatively high electronegativity of beryllium and the relatively small size of its atom. This smaller size permits it to have a higher coordination number without excessive steric hindrance. This means more atoms can coordinate to it. The fact that it doesn't easily conform to the octet rule means that it has the flexibility to explore other coordination options.
Beyond the Octet Rule: Factors Influencing Beryllium's Bonding
Several factors contribute to beryllium's ability to form more than two bonds and to not follow the octet rule. Let's explore them in detail:
1. High Charge Density:
Beryllium's small size and +2 charge lead to a high charge density. This attracts electrons strongly from ligands (atoms or molecules bonded to the central beryllium atom). This strong attraction can compensate for the energetic cost of exceeding the octet rule and allow for formation of more bonds.
2. 2p Orbital Participation:
Although beryllium's 2p orbitals are higher in energy than its 2s orbital, they can still participate in bonding, especially when coordinated to highly electronegative ligands. This participation increases the number of bonds possible beyond the two predicted from just the 2s electrons. These orbitals are sufficiently close in energy to the 2s orbital that the energy penalty is sufficiently low to permit bonding.
3. Polarization Effects:
The high charge density of beryllium leads to polarization effects on the ligands bonded to it. This polarization can further stabilize structures with higher coordination numbers. The polarization affects the distribution of electron density within the molecule and can enhance stability of these arrangements.
4. Ligand Effects:
The nature of the ligands surrounding the beryllium atom significantly influences the number of bonds it forms. Highly electronegative ligands, such as fluorine or oxygen, are particularly effective at stabilizing higher coordination numbers by accepting electron density from the beryllium.
5. Steric Factors:
While steric hindrance might be expected to limit the coordination number around a small atom like beryllium, the small size itself paradoxically allows for increased coordination. Bulky ligands may hinder higher coordination numbers, resulting in lower coordination numbers such as two. In contrast, smaller ligands offer fewer steric impediments and enable higher coordination.
Examples of Beryllium's Diverse Bonding
Beryllium exhibits a surprising range of coordination numbers, highlighting its capacity to surpass the simple expectation of two bonds. Let's consider some representative examples:
1. Two-coordinate Beryllium:
Linear BeX₂ molecules (X = halogen) are classic examples of two-coordinate beryllium compounds. Here, beryllium uses its two valence electrons to form two single bonds.
2. Three-coordinate Beryllium:
While less common than two-coordinate structures, three-coordinate beryllium complexes are known. These typically involve electron-donating ligands that can stabilize the higher coordination number. For example, some beryllium complexes with highly electronegative ligands display three-coordination.
3. Four-coordinate Beryllium:
Four-coordinate beryllium is quite prevalent, and such compounds are generally more stable due to a more even distribution of electron density surrounding the Be atom. Examples include tetrahedral beryllium complexes with oxygen-containing ligands or highly electronegative halogen ligands. The presence of a high electronegativity ligand facilitates the higher coordination.
4. Higher Coordination Numbers:
While less frequently encountered, instances of beryllium exhibiting coordination numbers of five and even six have been documented, predominantly in solid-state structures. This high coordination is typically observed when beryllium is bound to multiple small electronegative atoms or when these atoms are effectively bridging adjacent beryllium atoms, providing additional electron density.
Implications and Significance
The flexible bonding behavior of beryllium has significant implications across various fields:
- Material Science: Understanding beryllium's bonding capabilities is crucial for designing novel materials with specific properties. The element's unique bonding characteristics contribute to the exceptional properties of certain beryllium alloys.
- Inorganic Chemistry: Beryllium's ability to violate the octet rule expands our understanding of chemical bonding principles and challenges the limitations of simple models. This challenges us to explore the nuances of bonding beyond basic theories.
- Catalysis: Beryllium compounds have been explored in the context of catalysis, with their bonding features impacting their catalytic activity. The varying coordination numbers directly affect the catalytic applications.
Conclusion: The Complex Bonding World of Beryllium
In summary, while a simplistic view of beryllium's electronic configuration might suggest a maximum of two bonds, its actual bonding behavior is far more complex and multifaceted. The high charge density, the involvement of 2p orbitals, polarization effects, ligand characteristics, and steric factors all combine to allow beryllium to achieve coordination numbers beyond two, often defying the octet rule. Understanding this intricate bonding behavior is essential for unlocking the potential of this unique element in materials science, inorganic chemistry, and beyond. The reality is that beryllium demonstrates a remarkable versatility in bonding, showcasing the complexities and exceptions that exist even within the foundational rules of chemistry. This makes beryllium a particularly intriguing element for continued research and study. Its ability to exceed coordination number two highlights how crucial it is to consider the unique characteristics of each atom when studying chemical bonding. Further research into this area promises to reveal more about the rich and nuanced chemistry of this fascinating element. Further, a deeper understanding could lead to new advancements in material science and catalysis. The variable coordination numbers of beryllium underscore the need for sophisticated theoretical models in explaining and predicting its bonding behaviour. Continued study of this element will surely reveal further complexities and expand our understanding of chemical bonding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Derived Unit
Mar 22, 2025
-
Acceleration Is Always In The Direction
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes A Hormone
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is A Hydrogen Bond Stronger Than A Covalent Bond
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Equation
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Bonds Can Beryllium Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
