How Do You Make Calcium Carbide
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
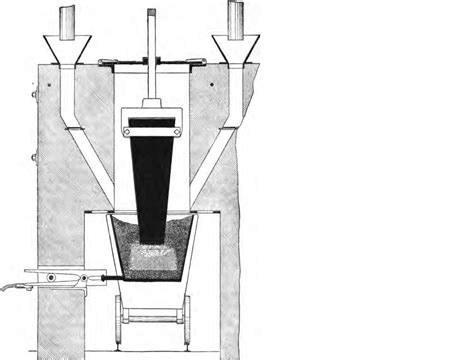
Table of Contents
How Do You Make Calcium Carbide? A Deep Dive into Production Methods
Calcium carbide (CaC₂), a crucial industrial chemical, is the cornerstone of numerous applications, from the production of acetylene gas to the synthesis of other valuable chemicals. Understanding its manufacturing process is key to appreciating its widespread importance. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate details of calcium carbide production, exploring the raw materials, the reaction mechanisms, and the various technological advancements that shape modern manufacturing processes.
The Chemistry Behind Calcium Carbide Production: A High-Temperature Affair
At its core, calcium carbide production hinges on a high-temperature reaction between calcium oxide (CaO), commonly known as quicklime, and carbon (C), typically in the form of coke or anthracite coal. This reaction, expressed as:
CaO + 3C → CaC₂ + CO
is highly endothermic, meaning it requires a significant input of heat to proceed. This explains the necessity of electric arc furnaces, the dominant technology in modern calcium carbide manufacturing. The reaction doesn't simply happen at high temperatures; it needs a specific environment to be efficient and yield a high-quality product.
Understanding the Reaction Dynamics
The reaction between calcium oxide and carbon is not a simple one-step process. Several intermediate reactions occur, and the overall kinetics are complex. The rate of reaction is heavily influenced by:
-
Temperature: The reaction's speed dramatically increases with temperature, necessitating the use of extremely high temperatures (typically around 2000°C or higher) within the electric arc furnace. This high temperature ensures a sufficient reaction rate and a high yield of calcium carbide.
-
Raw Material Purity: Impurities in the quicklime or carbon source can significantly hinder the reaction, reducing the yield and potentially degrading the quality of the final product. Therefore, careful selection and pre-treatment of raw materials are crucial.
-
Particle Size and Mixing: The optimal particle size of both calcium oxide and carbon influences the reaction rate. A well-mixed blend of finely ground raw materials ensures intimate contact and promotes efficient reaction kinetics.
-
Furnace Design and Operation: The design of the electric arc furnace and the precise control of operational parameters, such as voltage, current, and the feed rate of raw materials, significantly influence the reaction efficiency and product quality.
The Electric Arc Furnace: The Heart of Calcium Carbide Production
The electric arc furnace is the workhorse of calcium carbide manufacturing. This furnace employs a powerful electric arc to generate the extreme temperatures necessary for the reaction to occur. The process typically involves:
Raw Material Preparation: Purity and Particle Size Control
Before entering the furnace, both quicklime and carbon undergo rigorous preparation to ensure optimal reaction conditions. This involves:
-
Quicklime (CaO) Purification: The quicklime used is typically derived from high-quality limestone through a calcination process. Impurities like silica, alumina, and iron oxides are undesirable, as they can reduce the yield and contaminate the final product. Careful selection of limestone and stringent quality control during calcination are vital.
-
Carbon Source Selection and Processing: Coke or anthracite coal serves as the carbon source. The carbon source is ground to a specific particle size to optimize the reaction rate. Careful control of particle size distribution ensures uniform reaction kinetics throughout the furnace.
-
Blending and Mixing: The prepared quicklime and carbon are carefully weighed and thoroughly mixed in a precise ratio to ensure uniform reaction throughout the furnace. The mixing process is crucial for achieving high yield and product consistency.
Furnace Operation: A Controlled High-Temperature Environment
The mixed raw materials are then fed into the electric arc furnace. The electric arc generates temperatures exceeding 2000°C, initiating and sustaining the reaction. The furnace's operation is closely monitored and controlled to ensure:
-
Temperature Regulation: Maintaining a stable and consistent temperature is essential for optimal reaction kinetics and product quality. Sophisticated control systems monitor and adjust the electric power input to maintain the desired temperature.
-
Feed Rate Control: The rate at which the raw materials are fed into the furnace is precisely controlled to prevent clogging or uneven reaction. The feed rate is often optimized to maintain a constant level of molten calcium carbide in the furnace.
-
Product Tapping: Once the reaction is complete, the molten calcium carbide is tapped from the furnace. This tapping process needs careful control to avoid accidents and ensure the smooth flow of the molten product.
Post-Processing: Purification and Handling
The molten calcium carbide is then cooled and solidified. The process of cooling needs care to avoid cracks or internal stresses that may compromise the quality of the final product. Sometimes, a further purification step might be included to remove any residual impurities that might have survived the furnace reaction. The solidified calcium carbide is then crushed, graded, and packaged for distribution to various industries.
Variations in Calcium Carbide Production: Technological Advancements
While the electric arc furnace remains the dominant technology, various innovations have aimed to improve efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and enhance product quality. These include:
-
Improved Furnace Designs: Modern furnaces incorporate advanced technologies such as improved electrode designs, more efficient cooling systems, and better raw material feeding mechanisms to enhance the overall efficiency of the process.
-
Alternative Energy Sources: Research is ongoing into exploring alternative energy sources, such as plasma arc furnaces, to reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environmental footprint of calcium carbide production.
-
Process Optimization through Modeling and Simulation: Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and other modeling techniques are employed to simulate and optimize the reaction conditions within the furnace, leading to higher yield and reduced energy consumption.
-
Waste Minimization and Environmental Considerations: Modern manufacturing facilities emphasize waste minimization and environmental protection. Efforts are focused on recycling waste materials and reducing emissions.
Applications of Calcium Carbide: A Versatile Industrial Chemical
Calcium carbide's widespread utility stems from its ability to react with water to produce acetylene gas (C₂H₂). This reaction forms the basis of many of its applications:
-
Acetylene Gas Production: This is arguably calcium carbide's most significant application. Acetylene, a highly reactive gas, is widely used in welding and cutting torches, providing a high-temperature flame.
-
Chemical Synthesis: Calcium carbide serves as a raw material in the synthesis of various organic and inorganic chemicals, including polyvinyl chloride (PVC), plastics, and other valuable compounds.
-
Other Applications: It finds niche applications in the production of certain fertilizers, in the desulfurization of iron, and in other specialized industrial processes.
Future Trends in Calcium Carbide Manufacturing
The future of calcium carbide production is likely to be shaped by:
-
Sustainability: Greater emphasis will be placed on minimizing the environmental footprint of the process, reducing energy consumption, and exploring alternative energy sources.
-
Automation and Process Control: Further automation and advanced process control technologies will improve efficiency, reduce operational costs, and enhance product quality.
-
Research and Development: Continuous research and development efforts will aim to enhance the efficiency of the process, explore alternative raw materials, and develop new applications for calcium carbide.
This detailed exploration of calcium carbide production underscores its crucial role in modern industry. From the high-temperature chemistry within the electric arc furnace to the versatility of its applications, calcium carbide remains a cornerstone of many industrial processes. Continued advancements in technology and a growing focus on sustainability will undoubtedly shape the future of this essential chemical.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Whats Half Of 1 1 2 Tsp
Mar 28, 2025
-
Genes Had Been Absent On The Chromosomes
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Nonrenewable Source Of Energy
Mar 28, 2025
-
An Improvement In Production Technology Will
Mar 28, 2025
-
If 2 X 1 14 Then X
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Make Calcium Carbide . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
