How Do You Balance C2h6 O2 Co2 H2o
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
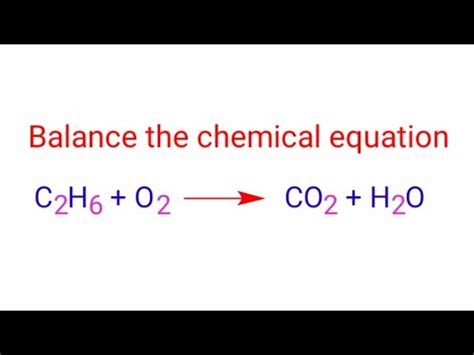
Table of Contents
Balancing the Combustion Equation: C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
The complete combustion of ethane (C₂H₆) in the presence of oxygen (O₂) produces carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O). This seemingly simple chemical reaction is a fundamental concept in chemistry, crucial for understanding combustion processes, energy production, and environmental impact. Balancing this equation, however, requires a systematic approach to ensure the conservation of mass, a cornerstone principle of chemistry. This article will delve into the detailed process of balancing the equation C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O, explaining the underlying principles and providing a step-by-step guide for achieving a balanced chemical equation. We will also explore the practical implications of this reaction and its importance in various fields.
Understanding the Basics of Balancing Chemical Equations
Before diving into the specifics of balancing the ethane combustion equation, let's establish the foundational principles. A balanced chemical equation represents the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The law of conservation of mass dictates that the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products. This translates into the number of atoms of each element remaining constant throughout the reaction. Therefore, balancing an equation involves adjusting the stoichiometric coefficients (the numbers in front of each chemical formula) to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
Key Concepts:
- Reactants: The substances that undergo a chemical change (C₂H₆ and O₂ in this case).
- Products: The substances formed as a result of the chemical reaction (CO₂ and H₂O).
- Stoichiometric Coefficients: The numbers placed in front of the chemical formulas to balance the equation. These coefficients represent the relative number of moles of each substance involved in the reaction.
- Subscripts: The small numbers within a chemical formula indicating the number of atoms of each element in a molecule. These subscripts cannot be changed when balancing an equation.
Balancing the Ethane Combustion Equation: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's now balance the equation for the complete combustion of ethane:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
Step 1: Balancing Carbon (C)
We begin by examining the number of carbon atoms on each side of the equation. The reactant side has two carbon atoms (from C₂H₆), while the product side currently has only one (from CO₂). To balance the carbon atoms, we place a coefficient of 2 in front of CO₂:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → 2CO₂ + H₂O
Step 2: Balancing Hydrogen (H)
Next, we focus on hydrogen. The reactant side has six hydrogen atoms (from C₂H₆), while the product side currently has two (from H₂O). To balance the hydrogen atoms, we place a coefficient of 3 in front of H₂O:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → 2CO₂ + 3H₂O
Step 3: Balancing Oxygen (O)
Finally, we balance the oxygen atoms. The product side now has seven oxygen atoms (four from 2CO₂ and three from 3H₂O). The reactant side has only two oxygen atoms (from O₂). To balance the oxygen atoms, we need a coefficient of 7/2 in front of O₂:
C₂H₆ + (7/2)O₂ → 2CO₂ + 3H₂O
However, it's generally preferred to have whole number coefficients in a balanced chemical equation. To achieve this, we multiply the entire equation by 2:
2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O
The Balanced Equation:
The completely balanced equation for the complete combustion of ethane is:
2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O
This equation now satisfies the law of conservation of mass, with the same number of atoms of each element on both the reactant and product sides.
Practical Implications and Significance
The balanced equation for the combustion of ethane has numerous practical implications across various fields:
-
Energy Production: Ethane is a significant component of natural gas and is used as a fuel source. Understanding the stoichiometry of its combustion is essential for designing efficient combustion engines and power plants. The balanced equation helps determine the optimal fuel-to-air ratio for maximum energy output and minimal pollutant formation.
-
Industrial Processes: Ethane is a key feedstock in the petrochemical industry, used to produce ethylene, a fundamental building block for plastics and other polymers. Precise control of ethane combustion is vital in various industrial processes.
-
Environmental Monitoring: The combustion of ethane produces carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, and its release contributes to climate change. Understanding the stoichiometry of the reaction allows scientists to accurately assess the environmental impact of ethane combustion and develop strategies for mitigation. Incomplete combustion, which can occur under certain conditions, also produces harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO) and soot.
-
Safety and Hazard Assessment: The balanced equation helps in assessing the risks associated with ethane handling and combustion. Knowing the exact amounts of reactants and products involved in the reaction allows for proper safety measures to be implemented in industrial settings and other applications where ethane is utilized.
Beyond Complete Combustion: Incomplete Combustion of Ethane
It's important to note that the equation above represents complete combustion, where sufficient oxygen is available for the complete oxidation of ethane. However, under conditions of limited oxygen supply, incomplete combustion can occur, resulting in the formation of carbon monoxide (CO) and/or elemental carbon (C, soot). The equations for incomplete combustion are more complex and depend on the specific oxygen-to-fuel ratio. Examples of incomplete combustion equations include:
- 2C₂H₆ + 5O₂ → 4CO + 6H₂O (producing carbon monoxide)
- 2C₂H₆ + 3O₂ → 4C + 6H₂O (producing elemental carbon)
These incomplete combustion reactions are less efficient in terms of energy production and generate harmful pollutants.
Conclusion
Balancing the chemical equation for the combustion of ethane (C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O) is a fundamental exercise in chemistry with far-reaching implications. The balanced equation, 2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O, provides crucial information about the quantitative relationships between reactants and products, enabling accurate predictions and control of this important reaction in various applications. Understanding this reaction is essential for optimizing energy production, minimizing environmental impact, and ensuring safe handling of ethane in industrial settings. Furthermore, appreciating the possibility of incomplete combustion highlights the importance of maintaining appropriate oxygen levels to avoid the formation of harmful pollutants. This knowledge is paramount for maintaining a healthy environment and advancing sustainable practices.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Integral Of Sqrt A 2 X 2
Mar 24, 2025
-
X 3 2x 2 X 4
Mar 24, 2025
-
Reproduction Without The Fusion Of Gametes
Mar 24, 2025
-
A Moderate Wind Accelerates A Pebble
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Are Animals Called That Feed On Herbivores
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Balance C2h6 O2 Co2 H2o . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
