H2o2 H2o O2 What Type Of Reaction
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
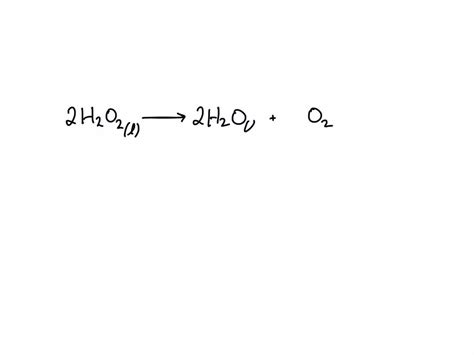
Table of Contents
H₂O₂, H₂O, O₂: Understanding the Reaction Types
The chemical transformations between hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), water (H₂O), and oxygen (O₂) represent a fascinating interplay of redox reactions. Understanding the reaction types involved is crucial in various fields, from industrial applications to biological processes. This article delves deep into the chemistry behind these transformations, explaining the different reaction types and their implications.
Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide: A Classic Redox Reaction
The most common reaction involving these three species is the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. This reaction is a prime example of a redox reaction, where both oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
Understanding Redox Reactions
A redox reaction, short for reduction-oxidation reaction, involves the transfer of electrons between species. One species undergoes oxidation, losing electrons, while another undergoes reduction, gaining electrons. In the decomposition of H₂O₂, the following occurs:
- Oxidation: Oxygen in H₂O₂ goes from a -1 oxidation state to a 0 oxidation state in O₂. This is oxidation because it loses electrons.
- Reduction: Oxygen in H₂O₂ goes from a -1 oxidation state to a -2 oxidation state in H₂O. This is reduction because it gains electrons.
The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2H₂O₂ → 2H₂O + O₂
This reaction is spontaneous but relatively slow under normal conditions. However, its rate can be significantly increased by several factors, including:
-
Catalysts: Certain substances, like manganese dioxide (MnO₂), platinum (Pt), and even biological enzymes like catalase, act as catalysts, speeding up the reaction without being consumed themselves. They provide an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy.
-
Heat: Increasing the temperature provides the molecules with more kinetic energy, leading to more frequent and energetic collisions, thus increasing the reaction rate.
-
Light: Exposure to light can also accelerate the decomposition of H₂O₂.
Implications of Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposition
The decomposition of H₂O₂ has significant implications in various areas:
-
Industrial Applications: The controlled decomposition of H₂O₂ is used in various industrial processes, including bleaching textiles and paper, disinfecting surfaces, and propulsion systems (e.g., some rockets use H₂O₂ as a propellant).
-
Biological Systems: The enzyme catalase plays a vital role in protecting living organisms from the damaging effects of H₂O₂. Catalase efficiently decomposes H₂O₂ into harmless water and oxygen, preventing oxidative stress.
-
Environmental Concerns: While H₂O₂ itself is not particularly harmful to the environment in small quantities, uncontrolled release of large amounts can lead to environmental issues. The produced oxygen can contribute to eutrophication in aquatic systems, and the decomposition process can consume dissolved oxygen, impacting aquatic life.
The Formation of Hydrogen Peroxide: A More Complex Scenario
The formation of H₂O₂ isn't a single straightforward reaction. Multiple pathways exist, depending on the reaction conditions and the reactants involved. Some key methods include:
-
Electrochemical Synthesis: H₂O₂ can be produced by the electrochemical reduction of oxygen in an acidic environment. This process is often used for the industrial production of H₂O₂.
-
Autoxidation of Organic Compounds: Certain organic compounds can react with oxygen to produce H₂O₂ as a byproduct. This is a complex process involving free radicals.
-
Photochemical Reactions: Under certain conditions, light can initiate reactions that produce H₂O₂. This often involves the interaction of water and oxygen with light energy.
The formation of H₂O₂ often involves multiple steps and intermediate species, making it a more complex process than its decomposition. The specific reaction mechanisms are highly dependent on the conditions employed.
The Role of Water: A Solvent and a Reactant
Water (H₂O) acts as more than just a product in these reactions. It plays a crucial role as a solvent, mediating the interactions between H₂O₂ and O₂. Moreover, water itself can participate in reactions involving these species under specific conditions.
Water as a Solvent
Water's polar nature and its high dielectric constant make it an excellent solvent for many ionic and polar compounds. This property is essential for the decomposition of H₂O₂ in aqueous solutions, allowing the reactants and catalysts to interact effectively.
The Significance of Oxygen: An Oxidizing Agent and a Product
Oxygen (O₂) is a key player in the reactions involving H₂O₂ and H₂O. It is a powerful oxidizing agent, meaning it readily accepts electrons from other species. In the decomposition of H₂O₂, oxygen is the product of the reduction of H₂O₂. However, under different conditions, oxygen can react with other substances to produce H₂O₂.
Oxygen in Biological Systems
Oxygen's role in biological systems is paramount. It acts as the final electron acceptor in cellular respiration, a process that provides the energy needed for life. This process, however, also produces reactive oxygen species (ROS), including H₂O₂, which can damage cells if not effectively neutralized by enzymes like catalase.
Industrial Uses of Oxygen
Oxygen finds widespread industrial applications, ranging from combustion processes to the production of various chemicals, including H₂O₂ itself. Understanding its reactivity is essential in controlling and optimizing these processes.
Other Reaction Types and Considerations
While the focus has been primarily on redox reactions, it's important to note that other reaction types might be involved, depending on the specific conditions and presence of other reactants. For instance, the reactions of H₂O₂, H₂O, and O₂ can also involve:
-
Acid-Base Reactions: H₂O₂ can act as a weak acid, donating a proton (H⁺). This can influence the reaction rate and pathway.
-
Nucleophilic Reactions: The peroxide bond in H₂O₂ can be susceptible to nucleophilic attack under specific conditions.
-
Free Radical Reactions: Formation of free radicals can play a significant role in some reactions involving H₂O₂, especially in the presence of catalysts or light.
Understanding these different reaction types and the interplay between them is crucial for a complete picture of the chemistry of H₂O₂, H₂O, and O₂.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Interplay
The reactions between H₂O₂, H₂O, and O₂ represent a dynamic interplay of oxidation, reduction, and other reaction types. The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen is a classic example of a redox reaction with significant implications across various fields. The formation of H₂O₂ is more complex, involving multiple pathways and intermediate species. Water plays a crucial role as a solvent, while oxygen acts as both a reactant and a product, demonstrating its importance as an oxidizing agent in various processes. Furthermore, the inclusion of other reaction types, such as acid-base reactions and free radical reactions, highlights the complexity and versatility of these chemical transformations. By understanding these different aspects, we gain a deeper appreciation for the vital roles these compounds play in both natural and industrial processes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Urinary Bladder Is Composed Of What Epithelium
Mar 26, 2025
-
Sphere Is To Circle As Cube Is To
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Convex Lens Of Focal Length 10cm
Mar 26, 2025
-
Gases Have Indefinite Shape And Volume
Mar 26, 2025
-
Round 64 To The Nearest Ten
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about H2o2 H2o O2 What Type Of Reaction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
