Gravitational Force Between Earth And Sun
News Leon
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
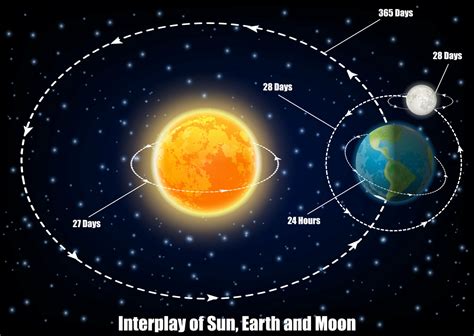
Table of Contents
The Unseen Hand: Exploring the Gravitational Force Between the Earth and the Sun
The Earth, our vibrant home, gracefully orbits the Sun, a celestial dance that has captivated humanity for millennia. This seemingly effortless ballet is orchestrated by an invisible force: gravity. Understanding the gravitational force between the Earth and the Sun is key to comprehending not just our planet's existence, but the very structure and dynamics of our solar system. This article delves deep into this fundamental interaction, exploring its nature, consequences, and implications for our understanding of the cosmos.
Understanding Gravity: Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
The foundation of our understanding of gravity lies in Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation. This pivotal law, formulated by Sir Isaac Newton in the late 17th century, postulates that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. Mathematically, this is expressed as:
F = G * (m1 * m2) / r²
Where:
- F represents the gravitational force
- G is the gravitational constant (a fundamental constant of nature)
- m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects
- r is the distance between the centers of the two objects
This simple yet profound equation reveals several crucial aspects of gravity:
- Mass Matters: The greater the mass of the objects, the stronger the gravitational force between them. The Sun, being vastly more massive than the Earth, exerts a dominant gravitational pull.
- Distance is Key: The force weakens rapidly with increasing distance. The inverse square relationship means that doubling the distance reduces the gravitational force to one-quarter its original strength. This explains why the Sun's gravitational influence diminishes significantly as you move further away from it.
- Mutual Attraction: Gravity is a mutual force; the Earth pulls on the Sun with the same force that the Sun pulls on the Earth, although the Sun's immense mass means its acceleration is negligible compared to the Earth's.
The Earth's Orbit: A Dance of Gravity and Inertia
The Earth's orbit around the Sun isn't a simple fall towards the Sun. Instead, it's a delicate balance between the Sun's gravitational pull and the Earth's inertia. Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion. The Earth, traveling at an immense speed (approximately 67,000 miles per hour), possesses significant inertia, which constantly tries to propel it in a straight line.
The Sun's gravity, however, continuously pulls the Earth towards its center. This combination of inertia and gravitational pull results in a curved path – the Earth's elliptical orbit. Imagine throwing a ball horizontally; gravity pulls it down, while its initial velocity keeps it moving forward. The result is a parabolic arc. Earth's orbit is similar, except that the Sun's gravity is strong enough to keep the Earth perpetually falling around it instead of directly into it.
Factors Influencing the Earth's Orbit:
While the Sun's gravity is the dominant force shaping Earth's orbit, other factors play subtle yet significant roles:
- Other Planets: The gravitational influence of other planets, particularly Jupiter, introduces minor perturbations in Earth's orbit. These perturbations are cyclical and relatively small, but they are measurable and important for long-term orbital predictions.
- Solar System's Evolution: Over millions of years, subtle changes in the distribution of mass within the solar system can slightly alter the Earth's orbit.
- Non-Newtonian Effects: At extremely high precision, Einstein's theory of General Relativity provides a more accurate description of gravity, incorporating effects such as the bending of spacetime around massive objects. These effects subtly influence Earth's orbit but are usually negligible for most practical purposes.
The Consequences of Sun-Earth Gravitational Interaction
The gravitational force between the Earth and the Sun has profound consequences, impacting various aspects of our planet and life as we know it:
- Seasons: The Earth's tilted axis (approximately 23.5 degrees) and its orbit around the Sun create the changing seasons. As the Earth revolves around the Sun, different hemispheres receive varying amounts of sunlight, leading to warmer temperatures in summer and colder temperatures in winter.
- Tides: While the Moon plays a significant role in Earth's tides, the Sun's gravity also contributes. The Sun's gravitational pull causes slight bulges in the Earth's oceans, creating subtle tidal effects. These effects are most noticeable when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are aligned (during new and full moons), resulting in stronger tides.
- Day and Night: The Earth's rotation on its axis, combined with its orbit around the Sun, determines the cycle of day and night. The duration of daylight varies throughout the year due to the Earth's tilt and orbital position.
- Stability of the Solar System: The precise balance of gravitational forces within the solar system maintains its overall stability. This delicate equilibrium ensures that the planets continue their orbits without significant disruptions.
Beyond Newton: General Relativity and Gravitational Waves
While Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation provides an excellent approximation for many situations, Einstein's theory of General Relativity offers a more comprehensive understanding of gravity. General Relativity describes gravity not as a force, but as a curvature of spacetime caused by the presence of mass and energy. Massive objects like the Sun warp the fabric of spacetime, and other objects, like the Earth, follow the curves in this warped spacetime.
General Relativity predicts the existence of gravitational waves, ripples in spacetime caused by accelerating massive objects. These waves, though incredibly weak, have been directly detected, providing further evidence for the accuracy of Einstein's theory. The interaction between the Earth and the Sun, while not a significant source of gravitational waves, contributes infinitesimally to the overall gravitational wave background of the universe.
The Future of Earth's Orbit
While the Earth's orbit remains remarkably stable over human timescales, subtle changes do occur over geological timescales. The long-term evolution of the Sun-Earth system is a complex topic of ongoing research. Factors like the Sun's gradual increase in luminosity and the gravitational interactions with other celestial bodies could influence the Earth's orbit over millions or billions of years. These changes, however, are gradual and do not pose an immediate threat to the Earth's habitability.
Conclusion: A Cosmic Dance of Gravity
The gravitational force between the Earth and the Sun is a fundamental force that shapes our world and influences life as we know it. From the changing seasons and the rhythmic ebb and flow of tides to the very stability of our solar system, this unseen force is essential to our existence. By continuing to explore the complexities of gravity, we gain deeper insights into the universe's workings and our place within it. The dance of gravity between the Earth and the Sun is a testament to the elegant and powerful forces that govern the cosmos. It's a cosmic ballet that has played out for billions of years and will continue to do so for billions more, a constant reminder of the interconnectedness and intricate balance of the universe. The study of this interaction continues to drive scientific advancements, leading to a more profound understanding of celestial mechanics, gravity, and the evolution of our solar system. The intricate details of this gravitational dance are a source of endless fascination and a testament to the beauty and wonder of the universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Best Describes Mitochondrial Dna Mtdna
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Largest Lymphoid Organ
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is A Non Permanent Magnet
Mar 16, 2025
-
3 Cards Same From 52 Probability
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Cell Organelle Is Found Only In Plant Cell
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Gravitational Force Between Earth And Sun . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
