Find The Lettered Angle In Each Case
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
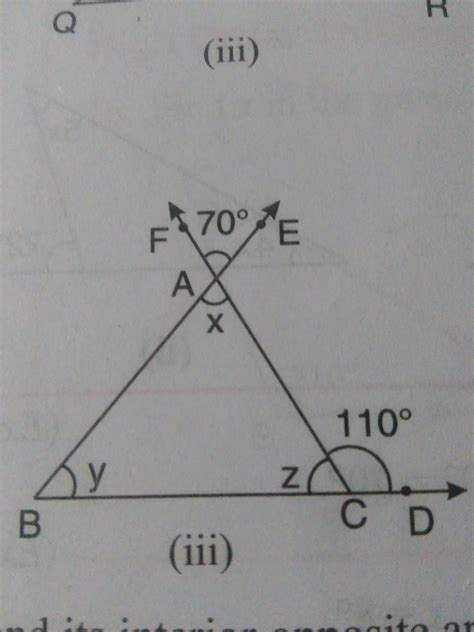
Table of Contents
Find the Lettered Angle in Each Case: A Comprehensive Guide to Geometry
Geometry, the study of shapes, sizes, relative positions of figures, and the properties of space, often presents us with puzzles that require us to find unknown angles. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to confidently solve problems involving finding lettered angles in various geometric figures. We'll cover a range of techniques, from basic angle relationships to more advanced concepts, providing you with a robust understanding of how to tackle these types of problems.
Understanding Basic Angle Relationships
Before delving into complex scenarios, let's solidify our understanding of fundamental angle relationships. These relationships form the bedrock of solving many geometry problems. Mastering these is crucial for success.
1. Complementary Angles:
Complementary angles are two angles whose sum is 90 degrees. If you know one angle in a complementary pair, you can easily find the other. For example, if angle A is 30 degrees and is complementary to angle B, then angle B = 90 - 30 = 60 degrees.
2. Supplementary Angles:
Supplementary angles are two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. Similar to complementary angles, if you know one angle in a supplementary pair, subtracting it from 180 degrees will reveal the measure of the other angle.
3. Vertically Opposite Angles:
When two lines intersect, four angles are formed. Vertically opposite angles are the angles opposite each other, and they are always equal. This is a powerful tool for solving many problems.
4. Angles on a Straight Line:
Angles on a straight line always add up to 180 degrees. This is a direct consequence of supplementary angles. If several angles lie on a straight line, their sum must equal 180 degrees.
5. Angles in a Triangle:
The sum of the angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees. This is a fundamental theorem in geometry and is essential for solving many problems involving triangles.
Finding Lettered Angles in Triangles
Triangles are fundamental shapes in geometry, and understanding their angle relationships is crucial. Let's examine different scenarios where we need to find lettered angles within triangles.
Isosceles Triangles:
An isosceles triangle has two equal sides, and the angles opposite these sides are also equal. If you know one of these equal angles and another angle in the triangle, you can easily find the third angle using the 180-degree rule for triangles.
Equilateral Triangles:
An equilateral triangle has all three sides equal, and consequently, all three angles are equal. Each angle in an equilateral triangle measures 60 degrees.
Right-Angled Triangles:
A right-angled triangle has one angle that is 90 degrees. Knowing this simplifies finding the other angles, as the sum of the other two angles must be 90 degrees (complementary angles).
Solving for Lettered Angles using Triangle Properties:
Many problems involve finding lettered angles within triangles using a combination of the above properties. We often need to use deductive reasoning and apply multiple angle relationships to find the solution. For instance, we might use the exterior angle theorem (discussed below), along with the properties of isosceles or right-angled triangles to find the missing angles.
Advanced Concepts: Beyond Basic Triangles
Let's delve into more complex scenarios and the tools needed to solve them.
1. The Exterior Angle Theorem:
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles. This theorem is extremely useful in solving problems where an exterior angle and one interior angle are known. By subtracting the known interior angle from the exterior angle, you can find the measure of the other opposite interior angle.
2. Angles in Polygons:
The sum of interior angles of a polygon with n sides is given by the formula: (n - 2) * 180 degrees. For example, a quadrilateral (4 sides) has interior angles summing to (4-2) * 180 = 360 degrees. This formula allows you to solve for unknown angles in polygons.
3. Parallel Lines and Transversals:
When a transversal line intersects two parallel lines, several angle relationships are established:
- Alternate Interior Angles: These are equal.
- Alternate Exterior Angles: These are equal.
- Corresponding Angles: These are equal.
- Consecutive Interior Angles: These are supplementary (add up to 180 degrees).
Understanding these relationships is crucial for solving problems involving parallel lines and transversals.
4. Cyclic Quadrilaterals:
A cyclic quadrilateral is a quadrilateral whose vertices all lie on a single circle. In a cyclic quadrilateral, the sum of opposite angles is always 180 degrees. This property is particularly useful for finding unknown angles in cyclic quadrilaterals.
Strategies for Solving Problems: A Step-by-Step Approach
To effectively solve problems involving lettered angles, follow these steps:
-
Identify the Given Information: Carefully examine the diagram and identify all known angles and relationships (e.g., parallel lines, isosceles triangles, etc.).
-
Apply Relevant Theorems and Properties: Use the appropriate theorems and properties (e.g., the exterior angle theorem, properties of parallel lines, etc.) to establish relationships between the known and unknown angles.
-
Formulate Equations: Based on the relationships you've identified, formulate algebraic equations to relate the known and unknown angles.
-
Solve the Equations: Solve the equations to find the value of the lettered angle.
-
Check Your Answer: Once you've found the value of the lettered angle, check your answer to ensure it's consistent with the given information and the relationships you've established.
Examples and Worked Solutions
Let's illustrate the techniques discussed with some examples.
Example 1: A Triangle with an Exterior Angle
Imagine a triangle ABC, where angle A is 50 degrees, angle B is unknown (let's call it 'x'), and the exterior angle at C is 110 degrees.
- Solution: Using the exterior angle theorem, we know that the exterior angle at C (110 degrees) is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles A and B. Therefore, 110 = 50 + x. Solving for x, we find x = 60 degrees. Therefore, angle B is 60 degrees.
Example 2: Parallel Lines and a Transversal
Consider two parallel lines intersected by a transversal. Let's say one of the alternate interior angles is 70 degrees. What is the measure of the other alternate interior angle?
- Solution: Since alternate interior angles are equal when two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, the other alternate interior angle is also 70 degrees.
Example 3: A Cyclic Quadrilateral
Suppose we have a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD. Angle A is 100 degrees and angle C is unknown (let's denote it as 'y').
- Solution: In a cyclic quadrilateral, opposite angles sum to 180 degrees. Therefore, A + C = 180. Substituting the value of angle A, we get 100 + y = 180. Solving for y, we find y = 80 degrees. Therefore, angle C is 80 degrees.
Conclusion: Mastering Angle Calculations in Geometry
Finding lettered angles in various geometric figures is a fundamental skill in geometry. By understanding basic angle relationships, applying relevant theorems, and following a systematic approach, you can confidently solve a wide range of problems. Remember to always carefully analyze the given information, utilize the appropriate theorems and properties, and thoroughly check your solutions. With practice, you'll develop the skills and confidence to tackle even the most challenging geometry problems. This guide provides a solid foundation; continue exploring geometric concepts to further enhance your problem-solving abilities. Keep practicing, and you will master the art of finding those lettered angles!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Function Of Neurons
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Does Positive Delta H Mean
Mar 24, 2025
-
State Whether The Following Statements Are True Or False
Mar 24, 2025
-
In Which Stage Of Meiosis Crossing Over Takes Place
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Major Nutrient
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Find The Lettered Angle In Each Case . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
