Factors Of X 3 Y 3
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
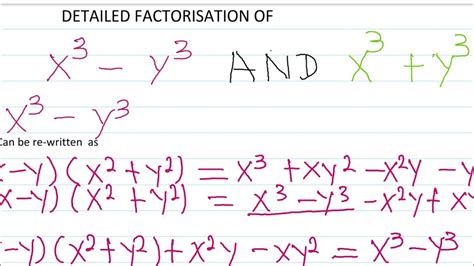
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Factors of x³ + y³: A Deep Dive into Sum of Cubes
The expression x³ + y³ represents the sum of two cubes, a fundamental concept in algebra with significant applications in various mathematical fields. Understanding its factors is crucial for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and tackling more complex problems in calculus, geometry, and beyond. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of factoring x³ + y³, exploring its underlying principles, derivation, and practical applications. We'll also examine related concepts and address common misconceptions.
Understanding the Sum of Cubes Formula
The cornerstone of factoring x³ + y³ lies in its factorization formula:
x³ + y³ = (x + y)(x² - xy + y²)
This formula reveals that the sum of two cubes can be factored into a binomial (x + y) and a trinomial (x² - xy + y²). This seemingly simple equation unlocks a powerful tool for manipulating algebraic expressions.
Deriving the Sum of Cubes Formula
While the formula itself is readily available, understanding its derivation provides deeper insight into its structure and application. We can derive the formula through polynomial long division or synthetic division, but a more intuitive approach involves expanding the product (x + y)(x² - xy + y²):
-
Distribute (x + y) over (x² - xy + y²):
x(x² - xy + y²) + y(x² - xy + y²)
-
Expand each term:
x³ - x²y + xy² + x²y - xy² + y³
-
Combine like terms:
x³ + y³
Notice how the -x²y and +x²y terms, and the +xy² and -xy² terms, cancel each other out, leaving us with the original expression, x³ + y³. This confirms the validity of the factorization formula.
Practical Applications of the Sum of Cubes Factorization
The ability to factor x³ + y³ has far-reaching applications across various mathematical domains:
-
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions: The formula allows for the simplification of complex expressions involving sums of cubes. By factoring, you can reduce the complexity and make the expression more manageable for further calculations or analysis.
-
Solving Cubic Equations: Cubic equations, which involve terms with x³, can sometimes be solved by factoring using the sum of cubes formula. This technique can reduce the cubic equation to a simpler quadratic equation or even linear equations, making the solutions easier to find.
-
Calculus: In calculus, the sum of cubes factorization can be instrumental in simplifying integrands during integration. This simplification often makes integration significantly easier and less prone to error. For instance, it can aid in partial fraction decomposition.
-
Geometry and Volume Calculations: The formula can be applied to geometrical problems involving volumes of solids. Consider, for example, the volume of a composite solid formed by combining two cubes. Understanding factorization can help in efficiently calculating such volumes.
-
Number Theory: The factorization of x³ + y³ has connections to number theory and the study of integers. It can be used in certain proofs and analyses related to properties of integers and their relationships.
Examples of Factoring x³ + y³
Let's illustrate the application of the sum of cubes formula with some examples:
Example 1: Factor 8a³ + 27b³
Here, x = 2a and y = 3b. Applying the formula:
8a³ + 27b³ = (2a + 3b)((2a)² - (2a)(3b) + (3b)²) = (2a + 3b)(4a² - 6ab + 9b²)
Example 2: Factor x³ + 1
This example involves factoring a sum of cubes where y = 1:
x³ + 1 = (x + 1)(x² - x + 1)
Example 3: Factor 64x³ + 125y⁶
In this case, we have x = 4x and y = 5y²:
64x³ + 125y⁶ = (4x + 5y²)((4x)² - (4x)(5y²) + (5y²)²) = (4x + 5y²)(16x² - 20xy² + 25y⁴)
Example 4: A more complex scenario involving substitution:
Factor 8(a + b)³ + 27c³. Let's substitute: u = (a+b) and v=c.
8(a+b)³ + 27c³ = 8u³ + 27v³ = (2u + 3v)(4u² - 6uv + 9v²)
Now, substituting back:
= (2(a+b) + 3c)(4(a+b)² - 6(a+b)c + 9c²)
= (2a + 2b + 3c)(4(a² + 2ab + b²) - 6ac - 6bc + 9c²)
= (2a + 2b + 3c)(4a² + 8ab + 4b² - 6ac - 6bc + 9c²)
These examples showcase the versatility of the sum of cubes formula in tackling various types of expressions.
Distinguishing the Sum of Cubes from Other Factorizations
It's crucial to differentiate the sum of cubes factorization from other similar factorization techniques, such as the difference of cubes and the perfect square trinomial.
-
Difference of Cubes (x³ - y³): The difference of cubes has a different factorization: x³ - y³ = (x - y)(x² + xy + y²). Note the change in signs within the binomial and trinomial factors.
-
Perfect Square Trinomial (x² + 2xy + y²): This represents a perfect square and factors as (x + y)². It's a quadratic expression, unlike the cubic sum of cubes.
Carefully examining the terms and exponents is essential to select the appropriate factorization method.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common errors can occur when factoring the sum of cubes:
-
Incorrect Signs: The most frequent mistake is misplacing the signs within the trinomial factor (x² - xy + y²). Remember the pattern of signs (+, -, +).
-
Confusing with Difference of Cubes: Failing to differentiate between the sum and difference of cubes leads to incorrect factorization.
-
Incomplete Factoring: Sometimes, the trinomial factor (x² - xy + y²) might be further factorable, depending on the values of x and y. Always check for complete factorization.
-
Incorrect application of other factoring rules: Attempting to apply other factoring techniques inappropriately will lead to incorrect results.
Advanced Applications and Extensions
The concept of the sum of cubes extends beyond its basic application. It can be utilized in:
-
Complex Numbers: The sum of cubes formula can be extended to factor expressions involving complex numbers.
-
Higher-Order Polynomials: While the formula directly applies to cubic expressions, its principles can be adapted and understood in the context of higher-order polynomials.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concepts underlying the sum of cubes are explored in abstract algebra, providing a deeper mathematical perspective.
Conclusion
The sum of cubes factorization, represented by x³ + y³ = (x + y)(x² - xy + y²), is a powerful tool in algebra and beyond. Understanding its derivation, applications, and potential pitfalls is crucial for anyone working with algebraic expressions and equations. By mastering this fundamental concept and its variations, you can significantly enhance your problem-solving skills in various mathematical contexts. This thorough exploration provides a solid foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges and deepening your understanding of algebraic principles. Remember to practice regularly and carefully review the common errors to build a strong and error-free grasp of the subject matter.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Two Same Words With Different Meanings
Mar 18, 2025
-
Select The Correct Statement About Equilibrium
Mar 18, 2025
-
Draw The Major Product Of The Following Reaction
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Wire Loop Of Radius 10 Cm And Resistance
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Water Molecules In A Drop Of Water
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factors Of X 3 Y 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
