Explain Incomplete Dominance Using Snapdragon Flowers As An Example
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
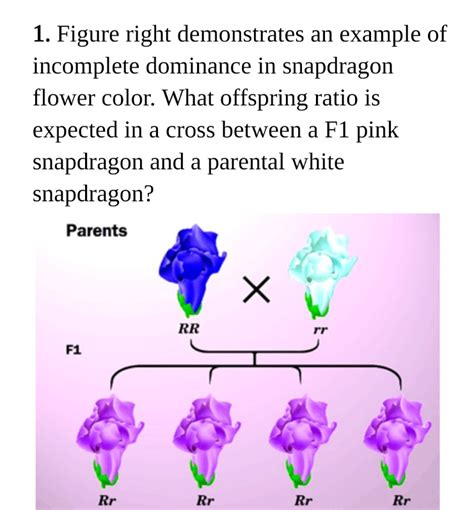
Table of Contents
Incomplete Dominance: A Colorful Explanation Using Snapdragon Flowers
Incomplete dominance, a fascinating concept in genetics, describes a scenario where neither allele for a particular gene completely masks the other. This results in a heterozygous phenotype that's an intermediate blend of the two homozygous phenotypes. Unlike complete dominance, where one allele reigns supreme, incomplete dominance showcases a more nuanced interaction between alleles, leading to a unique expression. This article will delve deep into the concept of incomplete dominance, using the vibrant and visually appealing snapdragon flower as a prime example to illustrate its principles.
Understanding the Basics of Incomplete Dominance
Before diving into the intricacies of incomplete dominance with snapdragons, let's solidify our understanding of the fundamental principles. In simple terms, incomplete dominance occurs when a heterozygote displays a phenotype that is a mixture of the phenotypes of both homozygotes. This differs from complete dominance, where the heterozygote exhibits the phenotype of the dominant allele completely masking the recessive one.
Key characteristics of incomplete dominance:
- Intermediate phenotype: The heterozygote exhibits a phenotype that's a blend of the two homozygous phenotypes.
- No recessive allele: Neither allele is truly "dominant" or "recessive"; instead, both contribute to the heterozygote's phenotype.
- Predictable ratios: While the phenotypes appear blended, the underlying genotypes follow predictable Mendelian inheritance patterns, making them easily analysable.
Snapdragon Flowers: A Perfect Case Study
Snapdragons ( Antirrhinum majus) offer a visually stunning and easily understandable example of incomplete dominance. Let's consider the flower color:
- Homozygous Red (RR): Plants with two copies of the red allele (RR) produce red flowers.
- Homozygous White (rr): Plants with two copies of the white allele (rr) produce white flowers.
- Heterozygous Pink (Rr): Plants with one red allele and one white allele (Rr) produce pink flowers. This pink color is the intermediate phenotype resulting from incomplete dominance.
This demonstrates the key characteristic of incomplete dominance – the heterozygote displays a phenotype that is different from either homozygous parent. Instead of one color dominating the other, the resulting flower color is a pink blend, a visual representation of the incomplete dominance of the alleles.
Punnett Squares and Incomplete Dominance in Snapdragons
The principles of incomplete dominance in snapdragons can be clearly illustrated using Punnett squares. Let's examine the cross between a homozygous red snapdragon (RR) and a homozygous white snapdragon (rr):
| R | R | |
|---|---|---|
| r | Rr | Rr |
| r | Rr | Rr |
All the offspring (F1 generation) from this cross will have the genotype Rr and display pink flowers. This confirms that neither red nor white is completely dominant; instead, their interaction leads to a pink intermediate.
Now, let's consider a cross between two of these pink F1 generation snapdragons (Rr x Rr):
| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | Rr | rr |
This cross results in the following genotypic and phenotypic ratios in the F2 generation:
- Genotypic Ratio: 1 RR : 2 Rr : 1 rr
- Phenotypic Ratio: 1 Red : 2 Pink : 1 White
This ratio clearly demonstrates the intermediate nature of incomplete dominance. The pink flowers are the result of the heterozygous genotype Rr.
Beyond Flower Color: Exploring Other Traits in Snapdragons
While flower color provides the most readily observable example of incomplete dominance in snapdragons, other traits might also exhibit this inheritance pattern. Although less visually striking, traits such as leaf shape, plant height, or even the intensity of certain pigments could potentially demonstrate incomplete dominance under specific genetic conditions. Further research and observation are needed to confirm these possibilities within the diverse genetic background of snapdragons.
Distinguishing Incomplete Dominance from Other Genetic Interactions
It's crucial to differentiate incomplete dominance from other genetic interactions that might produce similar results. Here's a comparison:
1. Incomplete Dominance vs. Codominance:
While both incomplete dominance and codominance involve heterozygotes exhibiting phenotypes different from the homozygotes, they differ in how the alleles interact. In incomplete dominance, the heterozygote shows a blend of the two homozygous phenotypes (e.g., pink snapdragons). In codominance, both alleles are fully expressed simultaneously in the heterozygote, leading to a distinct phenotype showing characteristics of both alleles (e.g., a roan cow with both red and white hairs).
2. Incomplete Dominance vs. Blending Inheritance:
The term "blending inheritance" was once used to describe the appearance of intermediate phenotypes. However, modern genetics shows that incomplete dominance is a specific type of non-Mendelian inheritance where distinct alleles contribute to the blended phenotype, with predictable Mendelian ratios observed in subsequent generations. Blending inheritance, on the other hand, suggested a permanent blending of parental traits, which is not the case with incomplete dominance.
The Significance of Incomplete Dominance
Understanding incomplete dominance has broader implications beyond simply explaining the color of snapdragon flowers. It highlights the complexity of gene interactions and emphasizes that gene expression isn't always a straightforward case of dominance and recessiveness. This concept has implications for:
- Agricultural breeding: Breeders can utilize knowledge of incomplete dominance to develop new varieties with desirable intermediate traits.
- Medical genetics: Incomplete dominance can play a role in certain human genetic conditions, where heterozygotes may exhibit milder symptoms than homozygous individuals.
- Evolutionary biology: Incomplete dominance can influence the evolution of populations by affecting the selection pressures acting on different genotypes.
Further Exploration and Research Opportunities
The study of incomplete dominance in snapdragons offers a fertile ground for further research. Investigating other traits within the species could reveal additional instances of incomplete dominance. Analyzing the molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction of red and white alleles in snapdragon flower color could provide insights into gene regulation and the intricacies of phenotype determination. Advanced techniques such as genomic sequencing and gene editing could further illuminate the genetic architecture behind incomplete dominance in this model organism.
Conclusion: The Beauty and Importance of Incomplete Dominance
Incomplete dominance, as beautifully illustrated by the diverse colors of snapdragon flowers, is a testament to the complexity and elegance of genetic inheritance. It demonstrates that gene interaction is not always a simple case of one allele overpowering another. The study of incomplete dominance, particularly in easily observable systems like snapdragons, provides valuable insights into the mechanisms of gene expression and its implications across various fields of biology, agriculture, and medicine. Its captivating visual demonstration makes it a fundamental concept to grasp for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of the fascinating world of genetics. The seemingly simple pink flower holds within it a complex tale of genetic interplay, offering continuous opportunities for scientific inquiry and exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Oxygen Molecules Can One Hemoglobin Carry
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Form Of Precipitation
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Statement About Natural Selection Is True
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Chamber Of Heart Has Thickest Wall
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 1 2 Miles
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Explain Incomplete Dominance Using Snapdragon Flowers As An Example . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
