Draw The Structure Of Propanoic Acid
News Leon
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
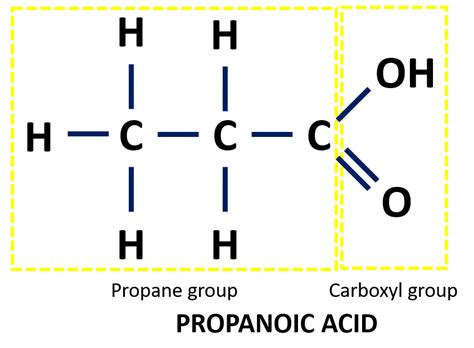
Table of Contents
Draw the Structure of Propanoic Acid: A Comprehensive Guide
Propanoic acid, also known as propionic acid, is a simple carboxylic acid with a wide range of applications. Understanding its structure is fundamental to comprehending its properties and functions. This comprehensive guide will delve into various ways to represent the structure of propanoic acid, exploring its molecular formula, condensed formula, skeletal formula, 3D structure, and even delve into its isomeric forms. We will also explore its properties and applications to provide a holistic understanding of this important chemical compound.
Understanding the Basics: Molecular Formula and IUPAC Nomenclature
Before drawing the structure, let's establish the fundamentals. The molecular formula of propanoic acid is C₃H₆O₂. This tells us the types and numbers of atoms present in a single molecule. However, it doesn't illustrate how these atoms are connected.
According to IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature, propanoic acid gets its name from the three-carbon chain (prop-) followed by the "-anoic acid" suffix, which designates it as a carboxylic acid. This systematic naming system allows chemists worldwide to unambiguously identify the compound.
Representing Propanoic Acid: Different Structural Forms
Several ways exist to represent the structure of propanoic acid, each with its own advantages and disadvantages depending on the context.
1. Condensed Structural Formula
The condensed structural formula offers a more detailed representation than the molecular formula. It shows the connectivity of the atoms, grouping them together to simplify the representation. For propanoic acid, the condensed structural formula is CH₃CH₂COOH. This clearly indicates a three-carbon chain with a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to one end. This is a very common and readily understandable way to depict the molecule.
2. Expanded Structural Formula
The expanded structural formula shows every bond explicitly. This provides the most detailed representation of the molecule's structure, making it visually clear how every atom is connected. For propanoic acid, the expanded structural formula would be:
H H O
| | ||
H-C-C-C-O-H
| |
H H
This clearly shows the single bonds between the carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms, as well as the double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms within the carboxyl group, and the single bond between the oxygen and hydrogen atom in the hydroxyl group of the carboxyl group.
3. Skeletal Formula (Line-Angle Formula)
The skeletal formula, also known as the line-angle formula, is a simplified representation frequently used in organic chemistry. Carbon atoms are implied at the intersections and ends of lines, and hydrogen atoms attached to carbons are omitted for simplicity. Only other atoms (like oxygen) are explicitly shown. The skeletal formula for propanoic acid is:
CH₃CH₂COOH becomes: CH₃CH₂C(=O)OH or even further simplified to: CH₃CH₂CO₂H
This skeletal structure is particularly useful for larger, more complex molecules, as it reduces visual clutter while still conveying the essential structural information.
4. 3D Representation (Ball-and-Stick and Space-Filling Models)
While 2D representations are convenient, they don't fully capture the three-dimensional nature of a molecule. 3D models, such as ball-and-stick models and space-filling models, are crucial for understanding molecular geometry and properties.
-
Ball-and-stick models: These models represent atoms as balls (with different colors for different elements) and bonds as sticks. This provides a clear visualization of the bond angles and overall molecular shape.
-
Space-filling models: These models show the relative sizes of atoms, giving a better representation of the molecule's overall volume and how atoms pack together.
In propanoic acid, the carbon atoms form a chain with approximately tetrahedral geometry (bond angles close to 109.5°), while the carboxyl group exhibits a planar configuration due to the resonance between the carbonyl oxygen and the hydroxyl oxygen. Visualization tools or molecular modeling software can readily create these 3D models.
Isomers of Propanoic Acid
It is crucial to note that propanoic acid does not have structural isomers with the same molecular formula (C₃H₆O₂). Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. While it does not have structural isomers, other functional groups containing the same number of atoms can exist, such as methyl acetate (CH₃COOCH₃).
However, propanoic acid does exhibit stereoisomerism, more specifically, conformational isomerism due to the rotation around the single carbon-carbon bonds. These conformations differ in their energy levels and spatial arrangements but are readily interconverted at room temperature.
Properties and Applications of Propanoic Acid
Understanding the structure of propanoic acid is key to grasping its properties. Propanoic acid is a weak organic acid, meaning it only partially dissociates in water. Its acidic nature is due to the carboxyl group, which can donate a proton (H⁺).
Its properties contribute to its various applications, including:
-
Food preservative: Propanoic acid and its salts (propionates) inhibit the growth of mold and some bacteria, making them valuable preservatives in bread, cheese, and other foods.
-
Chemical intermediate: It serves as a starting material in the synthesis of various other compounds, such as pharmaceuticals and polymers.
-
Herbicide: Some propionic acid derivatives are used as herbicides in agriculture.
-
Animal feed: It can be used as a feed additive to prevent fungal growth.
-
Textile industry: It finds some use in textile processing and dyeing.
Conclusion
Drawing the structure of propanoic acid might seem simple, but it's the foundation for understanding its chemical properties and applications. From the concise molecular formula to detailed 3D representations, several methods allow for visualizing this essential organic molecule. Knowing how to represent this structure, whether through condensed, expanded, or skeletal formulas, is crucial for any student or professional working with organic chemistry. The ability to visualize these structures in 3D enhances the comprehension of the molecule's behavior and interactions. This comprehensive guide has aimed to offer a complete picture, empowering readers with a thorough understanding of propanoic acid and its significance across diverse scientific and industrial domains. The different representations shown illustrate the versatility of structural depiction in chemistry, catering to various levels of understanding and specific applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Rubbing Alcohol Homogeneous Or Heterogeneous
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is Equivalent Fraction Of 4 5
Apr 02, 2025
-
Organelle Where Cellular Respiration Takes Place
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Number Is 45 Of 60
Apr 02, 2025
-
Is Oxygen A Solid Liquid Or A Gas
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Draw The Structure Of Propanoic Acid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
