Draw The Product Of The Given Reaction Sequence
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
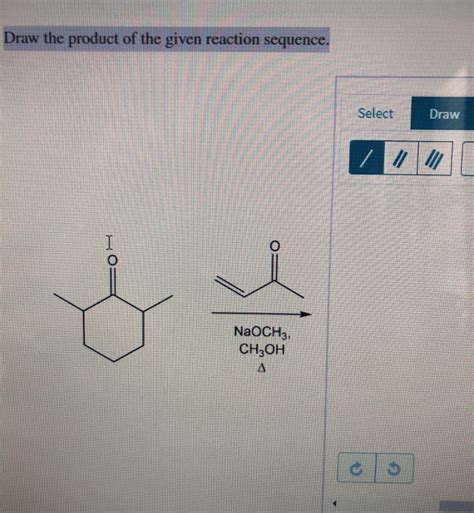
Table of Contents
Drawing the Product of a Given Reaction Sequence: A Comprehensive Guide
Predicting the outcome of a reaction sequence is a cornerstone of organic chemistry. This skill requires a deep understanding of reaction mechanisms, functional group transformations, and the interplay of various reagents. This article provides a comprehensive guide to drawing the product of a given reaction sequence, covering various reaction types, common reagents, and strategies for problem-solving. We'll delve into both simple and complex sequences, equipping you with the tools to confidently tackle any reaction scheme.
Understanding Reaction Mechanisms: The Foundation of Prediction
Before we dive into specific examples, it's crucial to grasp the underlying principles of reaction mechanisms. A reaction mechanism details the step-by-step process by which reactants are transformed into products. Understanding this process allows us to predict the structure of the final product accurately. Key aspects to consider include:
1. Identifying Functional Groups:
The first step is accurately identifying the functional groups present in the starting material. These groups dictate the reactivity and the types of reactions the molecule can undergo. Common functional groups include alcohols (-OH), alkenes (C=C), ketones (C=O), carboxylic acids (-COOH), and amines (-NH2). Knowing their characteristic reactions is paramount.
2. Recognizing Reagent Functionality:
Reagents are the chemical species that initiate or facilitate the reaction. Their functionality determines the type of transformation that will occur. For example, strong acids promote protonation, oxidizing agents facilitate oxidation, and reducing agents lead to reduction. Recognizing the function of the reagent is crucial in predicting the product.
3. Understanding Reaction Conditions:
Reaction conditions such as temperature, solvent, and pressure significantly impact the outcome. For instance, a reaction might favor a specific product at high temperature but a different product at low temperature. Paying close attention to reaction conditions is critical for accurate predictions.
4. Analyzing Reaction Steps:
Complex reaction sequences involve multiple steps. Each step needs careful consideration, as the product of one step often becomes the starting material for the next. Tracking the transformations at each stage is essential for correctly drawing the final product.
Common Reaction Types and Their Products
Let's explore several common reaction types and how they influence the final product:
1. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions (SN1 and SN2):
These reactions involve the substitution of a leaving group by a nucleophile. SN1 reactions proceed through a carbocation intermediate, leading to racemization if the starting material is chiral. SN2 reactions proceed through a concerted mechanism, leading to inversion of stereochemistry if the starting material is chiral.
Example: The reaction of 2-bromobutane with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) via SN2 will yield 2-butanol with inverted stereochemistry.
2. Elimination Reactions (E1 and E2):
These reactions involve the removal of a leaving group and a proton from adjacent carbon atoms, leading to the formation of a double bond (alkene). E1 reactions proceed through a carbocation intermediate, while E2 reactions are concerted. The regioselectivity (position of the double bond) is influenced by Zaitsev's rule (more substituted alkene is favored).
Example: The reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium tert-butoxide (t-BuOK) via E2 will yield 2-butene as the major product (Zaitsev's rule).
3. Addition Reactions:
These reactions involve the addition of a reagent across a double or triple bond. The regioselectivity and stereochemistry are governed by Markovnikov's rule (electrophile adds to the more substituted carbon) and anti-addition (addition from opposite sides of the double bond).
Example: The addition of HBr to propene will yield 2-bromopropane (Markovnikov's rule).
4. Oxidation and Reduction Reactions:
Oxidation reactions involve the loss of electrons, often accompanied by an increase in the number of oxygen atoms or a decrease in the number of hydrogen atoms. Reduction reactions involve the gain of electrons, often accompanied by a decrease in the number of oxygen atoms or an increase in the number of hydrogen atoms.
Example: The oxidation of a primary alcohol using PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate) yields an aldehyde. The reduction of a ketone using LiAlH4 (lithium aluminum hydride) yields a secondary alcohol.
5. Grignard Reactions:
Grignard reagents (RMgX) are powerful nucleophiles that react with carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) to form new carbon-carbon bonds.
Example: The reaction of a Grignard reagent (e.g., CH3MgBr) with formaldehyde (HCHO) yields a primary alcohol.
Strategies for Drawing the Product of a Reaction Sequence
Here are some strategies to approach complex reaction sequences systematically:
1. Step-by-Step Approach:
Tackle each step individually. Draw the product of the first step, then use that product as the starting material for the second step, and so on. This prevents errors and ensures accuracy.
2. Utilizing Reaction Maps and Charts:
Refer to reaction maps or charts that summarize common reactions and their products. These resources provide a quick overview of possible transformations and can guide your analysis.
3. Considering Stereochemistry:
Pay close attention to the stereochemistry of reactants and reagents. Some reactions preserve stereochemistry, while others invert or create new stereocenters. Accurate depiction of stereochemistry is essential.
4. Employing Online Resources and Databases:
Several online resources, including databases of chemical reactions, can aid in predicting reaction outcomes. These resources can provide detailed information on reaction mechanisms, conditions, and products. However, always critically evaluate information found online.
5. Practice, Practice, Practice!
The best way to master this skill is through practice. Work through numerous examples, starting with simple sequences and gradually progressing to more complex ones.
Example: A Multi-Step Reaction Sequence
Let's analyze a more complex example:
Starting Material: 1-butene
Reagents and Conditions:
- HBr (addition)
- NaOH (SN2)
- PCC (oxidation)
Solution:
-
Step 1 (Addition): HBr adds to 1-butene according to Markovnikov's rule, yielding 2-bromobutane.
-
Step 2 (SN2): NaOH acts as a nucleophile, replacing the bromine atom in 2-bromobutane with a hydroxyl group via an SN2 mechanism, leading to 2-butanol with inverted stereochemistry if the 2-bromobutane had a chiral center.
-
Step 3 (Oxidation): PCC oxidizes the secondary alcohol (2-butanol) to a ketone, yielding 2-butanone.
Therefore, the final product of this reaction sequence is 2-butanone.
Conclusion
Drawing the product of a given reaction sequence requires a strong grasp of organic chemistry principles, reaction mechanisms, and the behavior of various reagents. By systematically analyzing each step, understanding the nuances of reaction types, and employing effective problem-solving strategies, you can confidently predict the outcome of even complex reaction sequences. Remember that practice is key to developing this skill, so work through numerous examples and consult reliable resources as needed. With dedication and persistence, you will become proficient in drawing the products of any given reaction sequence.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Moles Of Water Are In 1 Liter
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which One Of The Following Is Not A Strong Electrolyte
Mar 25, 2025
-
In The Figure A Small Nonconducting Ball Of Mass
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Does Rstrip Do In Python
Mar 25, 2025
-
Figure A Shows An Element Of Length Ds
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Draw The Product Of The Given Reaction Sequence . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
