Double Displacement Reaction Examples In Real Life
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
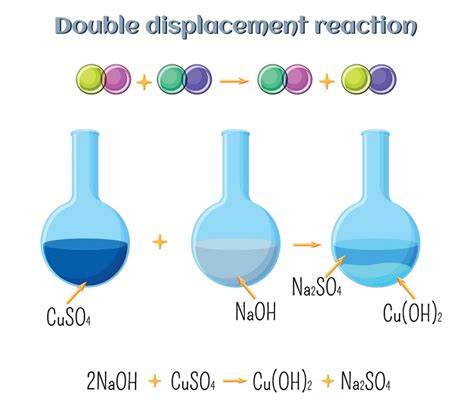
Table of Contents
Double Displacement Reactions: Everyday Encounters in the Real World
Double displacement reactions, also known as metathesis reactions, are a fundamental type of chemical reaction where two compounds exchange ions or elements to form two new compounds. These reactions are surprisingly prevalent in our daily lives, often occurring without us even realizing it. From the mundane to the extraordinary, double displacement reactions play a significant role in various processes, impacting our health, environment, and technology. This comprehensive article will explore numerous examples of double displacement reactions encountered in everyday life, explaining the underlying chemistry and their real-world applications.
Understanding the Mechanism of Double Displacement Reactions
Before diving into real-life examples, let's briefly review the core mechanism of a double displacement reaction. The general form is:
AB + CD → AD + CB
Where A and C are cations (positively charged ions) and B and D are anions (negatively charged ions). For the reaction to proceed, one of the products (AD or CB) must be insoluble (precipitate), a gas, or a weak electrolyte (such as water). This driving force ensures the reaction proceeds to completion, shifting the equilibrium away from the reactants.
Real-Life Examples of Double Displacement Reactions
The applications of double displacement reactions are incredibly diverse. Here are some examples categorized for better understanding:
1. Everyday Occurrences in the Home
-
Formation of Soap Scum: Hard water contains dissolved calcium and magnesium ions. When soap (containing sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids) is added, a double displacement reaction occurs, forming insoluble calcium and magnesium salts of fatty acids. This is the soap scum that accumulates in bathtubs and sinks.
Example: 2C₁₇H₃₅COONa(aq) + Ca²⁺(aq) → (C₁₇H₃₅COO)₂Ca(s) + 2Na⁺(aq)
-
Antacids and Acid Reflux: Antacids, used to relieve heartburn and indigestion, neutralize stomach acid (HCl) through double displacement reactions. Ingredients like calcium carbonate react with HCl, producing soluble calcium chloride, water, and carbon dioxide gas.
Example: CaCO₃(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl₂(aq) + H₂O(l) + CO₂(g)
-
Baking Soda and Vinegar: The classic science experiment of mixing baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and vinegar (acetic acid) showcases a double displacement reaction. The products are sodium acetate, water, and carbon dioxide gas, resulting in fizzing.
Example: NaHCO₃(s) + CH₃COOH(aq) → CH₃COONa(aq) + H₂O(l) + CO₂(g)
2. Applications in Industry and Manufacturing
-
Production of Precipitates in Pigment Manufacturing: Many pigments used in paints and dyes are produced through double displacement reactions. Insoluble compounds, often metal oxides or sulfides, are generated by reacting soluble metal salts with appropriate anions.
Example: Pb(NO₃)₂(aq) + H₂S(aq) → PbS(s) + 2HNO₃(aq) (Lead sulfide, a black pigment)
-
Water Treatment: In water softening, double displacement reactions are employed to remove unwanted calcium and magnesium ions. These ions are precipitated out by reacting water with substances like sodium carbonate or phosphate.
Example: Ca²⁺(aq) + Na₂CO₃(aq) → CaCO₃(s) + 2Na⁺(aq)
-
Production of Fertilizers: Certain fertilizers are synthesized using double displacement reactions. For instance, ammonium phosphate fertilizers are made by reacting phosphoric acid with ammonia.
Example: 3NH₃(aq) + H₃PO₄(aq) → (NH₄)₃PO₄(aq)
3. Processes in the Environment
-
Formation of Limestone and Other Minerals: The formation of many minerals, including limestone (calcium carbonate), involves double displacement reactions. These reactions occur over geological timescales, often involving the interaction of dissolved ions in groundwater with other substances.
Example: Ca²⁺(aq) + 2HCO₃⁻(aq) → CaCO₃(s) + H₂O(l) + CO₂(g)
-
Acid Rain Effects: Acid rain, containing sulfuric and nitric acids, reacts with various minerals in soil and water, causing their dissolution through double displacement reactions. This leads to soil acidification and water pollution.
Example: CaCO₃(s) + H₂SO₄(aq) → CaSO₄(aq) + H₂O(l) + CO₂(g)
4. Biological Processes
-
Blood Clotting: The complex process of blood clotting involves several reactions, including some double displacement reactions where ions participate in the cascade of events leading to fibrin formation.
-
Enzyme Catalysis: Some enzymatic reactions can involve the exchange of ions or functional groups, which can be conceptually represented as a type of double displacement. However, this is a simplification, as enzyme-catalyzed reactions are typically much more complex.
5. Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications
-
Radioactive Tracer Studies: Radioactive isotopes are often used as tracers in medical imaging. Double displacement reactions might be used to incorporate the radioactive isotope into a compound which the body can absorb or interact with, allowing doctors to monitor specific processes or organs.
-
Drug Delivery Systems: Certain drug delivery systems rely on the principles of double displacement reactions for the controlled release of medication.
Advanced Aspects and Considerations
Solubility Rules and Predicting Reactions
Predicting whether a double displacement reaction will occur requires understanding solubility rules. These rules predict the solubility of various ionic compounds in water. If a product is insoluble, a precipitate will form, driving the reaction forward.
Driving Forces of Double Displacement Reactions
As mentioned earlier, the formation of a precipitate, gas evolution, or the formation of a weak electrolyte (like water) are the driving forces behind double displacement reactions. These factors influence the equilibrium of the reaction.
Limitations and Exceptions
While the general scheme of AB + CD → AD + CB is helpful, there are exceptions. Some reactions might not proceed to completion, or the actual products might be different than anticipated due to complex equilibrium shifts and other reaction pathways.
Conclusion: The Ubiquitous Nature of Double Displacement Reactions
Double displacement reactions are far from abstract concepts; they are deeply intertwined with our everyday experiences. From the simple act of using antacids to the complex processes of industrial manufacturing and environmental chemistry, these reactions play a crucial, often unnoticed role. Understanding their mechanisms and applications helps us appreciate the fundamental principles of chemistry and its profound influence on our world. Further research into specific double displacement reactions within their various contexts can lead to innovations in numerous fields, from medicine and materials science to environmental remediation and agricultural practices. By continuing to study these reactions, we can unlock even more possibilities for their practical use.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Lines Are Parallel Justify Your Answer
Mar 23, 2025
-
Anything That Is Not Matter Is A Form Of
Mar 23, 2025
-
Plants That Make Their Own Food Are Called
Mar 23, 2025
-
Value Of K In Coulombs Law
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Part Of The Cell Cycle Is The Longest
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Double Displacement Reaction Examples In Real Life . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
