Does A Flatworm Have A Coelom
News Leon
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
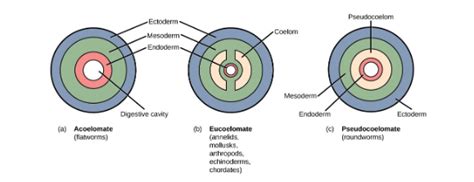
Table of Contents
Does a Flatworm Have a Coelom? A Deep Dive into Acoelomate Anatomy
The question of whether a flatworm possesses a coelom is fundamental to understanding its body plan and evolutionary position within the animal kingdom. The short answer is no, flatworms, or Platyhelminthes, are acoelomates, meaning they lack a true coelom, a fluid-filled body cavity that is completely lined with mesoderm. This absence significantly impacts their physiology, reproduction, and overall lifestyle. This article delves into the details of flatworm anatomy, exploring the reasons behind their acoelomate nature, contrasting them with coelomate animals, and examining the implications of this characteristic.
Understanding the Coelom: A Crucial Body Cavity
Before we delve into the specifics of flatworms, it's crucial to grasp the significance of the coelom. A coelom is a body cavity that develops entirely within the mesoderm, the middle germ layer of an embryo. This internal space serves several vital functions:
- Hydrostatic Skeleton: The fluid within the coelom acts as a hydrostatic skeleton, providing support and enabling movement in many invertebrates. Muscles contract against this fluid, facilitating locomotion.
- Organ Protection: The coelom cushions internal organs, protecting them from damage and providing a space for their development and growth.
- Transport System: The coelom facilitates the transport of nutrients, gases, and waste products throughout the body.
- Space for Organ Development: The coelom provides space for the development and expansion of internal organs, allowing for greater complexity and specialization.
Flatworms: Masters of Acoelomate Adaptation
Flatworms, belonging to the phylum Platyhelminthes, are characterized by their dorsoventrally flattened bodies, hence their common name. This flat body plan is directly related to their lack of a coelom. Their simple body structure, lacking a body cavity, has its advantages and disadvantages.
The Anatomy of an Acoelomate:
Flatworms possess three distinct germ layers during embryonic development: ectoderm (outer layer), mesoderm (middle layer), and endoderm (inner layer). However, unlike coelomates, their mesoderm is not fully developed into a body cavity. Instead, the mesoderm forms a solid mass of tissue between the ectoderm and endoderm, a characteristic of acoelomates. This solid tissue, parenchyma, fills the space between the body wall and the internal organs.
Implications of the Absence of a Coelom:
The lack of a coelom in flatworms directly impacts several aspects of their biology:
- Limited Size and Complexity: The absence of a coelom restricts the size and complexity that flatworms can achieve. The solid parenchyma limits the space available for organ development and the efficiency of nutrient and waste transport.
- Diffusion-Based Transport: Due to their thin, flattened bodies, flatworms rely heavily on diffusion for the transport of gases, nutrients, and waste products. This limits their size and metabolic rate.
- Simple Body Systems: Flatworms possess simple, often incomplete, body systems. Their nervous system is a decentralized network of nerve cells, their excretory system consists of flame cells, and their circulatory and respiratory systems are absent. These simple systems are sufficient for their lifestyle but prevent them from achieving the complexity of coelomate animals.
- Surface Area to Volume Ratio: The flat body plan maximizes surface area relative to volume. This enhances diffusion, compensating to some extent for the lack of a circulatory system. This is crucial for gas exchange and nutrient uptake.
Comparing Coelomates and Acoelomates: A Tale of Two Body Plans
The difference between coelomate and acoelomate body plans is profound, influencing various aspects of animal biology. Here's a comparison highlighting the key distinctions:
| Feature | Coelomates | Acoelomates (like Flatworms) |
|---|---|---|
| Body Cavity | True coelom, lined with mesoderm | No coelom; mesoderm forms a solid mass (parenchyma) |
| Body Support | Hydrostatic skeleton | Muscle layers against the body wall |
| Organ Protection | Coelom provides cushioning and support | Organs embedded in parenchyma |
| Transport System | Efficient circulatory system (often) | Diffusion; limited transport |
| Size and Complexity | Can be larger and more complex | Generally smaller and less complex |
| Example Animals | Annelids, mollusks, arthropods, vertebrates | Flatworms, some cnidarians |
Evolutionary Significance of the Acoelomate Body Plan
The acoelomate body plan of flatworms is a crucial feature in understanding their evolutionary history. While it may seem like a primitive trait, it's important to note that the absence of a coelom isn't necessarily indicative of a less evolved organism. Flatworms are highly successful animals, thriving in diverse habitats. Their simple body plan is well-suited to their specific niches.
The evolutionary relationships among acoelomates and other animal phyla are still debated. Some evolutionary hypotheses propose that acoelomates represent an early branching group in animal evolution. Others suggest that the acoelomate condition may be a secondary simplification, derived from coelomate ancestors. Further research, particularly in molecular phylogenetics, is needed to clarify these complex evolutionary relationships.
Flatworm Diversity: Acoelomates in Various Habitats
Despite their simple body plan, flatworms exhibit remarkable diversity, occupying a wide range of habitats. We can find them in:
- Marine environments: Many flatworm species are found in the oceans, inhabiting diverse habitats from shallow coastal waters to deep-sea trenches.
- Freshwater environments: Flatworms are also common inhabitants of lakes, rivers, and ponds.
- Terrestrial environments: Some species have adapted to terrestrial life, inhabiting moist environments like leaf litter and soil.
- Parasitic lifestyles: Many flatworms are parasitic, living within or on other organisms. These parasites can infect a variety of animals, including humans.
Specialized Structures in Flatworms: Compensating for the Lack of a Coelom
While flatworms lack a coelom, they've evolved specialized structures to compensate for the absence of a body cavity. These include:
- Flame Cells (Protonephridia): These specialized excretory cells filter waste products from the parenchyma, maintaining osmotic balance.
- Highly Branched Gut: The branched gut enhances the absorption of nutrients, compensating for the lack of a circulatory system.
- Efficient Diffusion: The flattened body shape maximizes surface area for gas exchange and nutrient absorption through diffusion.
- Muscular System: A well-developed muscular system allows for locomotion through a variety of methods, including gliding and swimming.
Conclusion: Acoelomate Success Story
In conclusion, flatworms are indeed acoelomates, lacking a true coelom. This characteristic significantly influences their body plan, physiology, and lifestyle. While the absence of a coelom might seem like a limitation, it's crucial to remember that this simple body plan has enabled flatworms to thrive in diverse habitats and adopt diverse ecological roles. Their adaptations, such as efficient diffusion and specialized excretory structures, compensate effectively for the lack of a coelom. The study of flatworms continues to be vital for understanding the evolutionary relationships among animals and the diverse ways in which organisms adapt to their environments. Further research will undoubtedly reveal more about their fascinating biology and evolutionary history. The continuing investigation into the evolutionary origins and diversification of the acoelomates remains an exciting area of biological research. The flatworm's adaptation to its acoelomate condition is a testament to the remarkable versatility and evolutionary success possible within the constraints of a seemingly simple body plan.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Bill Is To Law As Larva Is To
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Organelle Is Responsible For Cellular Respiration
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Ph For A Neutral Solution
Mar 29, 2025
-
Is Black Hair A Dominant Trait
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Joules Is A Calorie
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Does A Flatworm Have A Coelom . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
