Do Annelids Have An Open Or Closed Circulatory System
News Leon
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
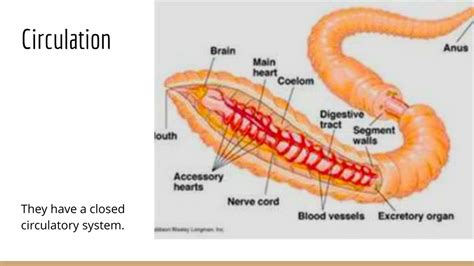
Table of Contents
Do Annelids Have an Open or Closed Circulatory System? A Comprehensive Look at Annelid Hemodynamics
Annelids, a diverse phylum encompassing earthworms, leeches, and marine polychaetes, exhibit a fascinating array of physiological adaptations. Understanding their circulatory systems is crucial to grasping their evolutionary success and ecological roles. A common question arising in the study of annelids is whether they possess an open or closed circulatory system. The short answer is: most annelids have a closed circulatory system, but with notable variations and exceptions. This article delves into the complexities of annelid hemodynamics, exploring the structures, functions, and evolutionary significance of their circulatory systems.
The Closed Circulatory System: A Defining Characteristic of Many Annelids
Unlike insects and many mollusks which possess open circulatory systems, the majority of annelids boast a closed circulatory system. This means that blood is always confined within vessels – arteries, capillaries, and veins – and never directly bathes the tissues. This highly efficient system allows for precise control of blood flow and pressure, enabling rapid transport of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body.
Key Features of the Closed Annelid Circulatory System:
-
Dorsal and Ventral Blood Vessels: A prominent dorsal blood vessel runs along the length of the body, acting as the main artery. This vessel pulsates rhythmically, propelling blood anteriorly. A ventral blood vessel, running parallel to the dorsal vessel, carries blood posteriorly.
-
Lateral Vessels: Connecting the dorsal and ventral vessels are a network of lateral vessels, often paired segmentally. These vessels serve as a crucial link for circulation within individual segments.
-
Capillaries: Fine capillaries permeate the tissues, facilitating the exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and the surrounding cells.
-
Hearts (or Hearts-like structures): While not always present in the same form as in vertebrates, some annelids have specialized regions within the dorsal blood vessel that function as hearts, contracting rhythmically to pump blood. These regions are often referred to as "hearts" or "metameric hearts". In other annelids, the pulsating dorsal vessel itself acts as the primary pump.
-
Efficient Oxygen and Nutrient Delivery: The closed system ensures efficient oxygen delivery to tissues, particularly crucial for larger, more active annelids. It also facilitates rapid waste removal, aiding in maintaining homeostasis.
Exceptions and Variations: Open-like Features in Certain Annelids
While a closed circulatory system is the norm for most annelids, some species exhibit modifications or features that blur the lines between strictly closed and open systems.
1. Reduced Vessels and Lacunar Systems:
Certain annelids, particularly some smaller or less active species, may exhibit less developed capillary networks. In these cases, blood may sometimes leak out of the vessels into tissue spaces, creating lacunae. While the blood remains largely contained within the vessels, these lacunae introduce a degree of openness to the system. This is not a true open system, but rather a modified closed system with elements of interstitial fluid exchange.
2. The Case of Leeches: A Unique Circulatory Adaptation
Leeches present a particularly interesting case. They possess a unique circulatory system which shows characteristics of both open and closed systems. They have a closed circulatory system in their main vessels; however, they also possess a system of lacunae. This lacunae system surrounds and interacts with the main vessels and allows for fluid exchange, creating what has been termed as a "modified closed" or sometimes "open-like" system.
Evolutionary Significance of Annelid Circulatory Systems
The evolution of the closed circulatory system in annelids represents a significant advance in the efficiency of internal transport. This adaptation has been pivotal to their ecological diversification and their ability to occupy a wide range of habitats, from terrestrial soils to deep-sea environments. The closed system allows for the support of larger body sizes and higher metabolic rates compared to organisms with open systems. The segmented body plan of annelids also played a role; the segmental arrangement of vessels and hearts facilitated the efficient distribution of blood throughout the entire body.
Studying Annelid Circulatory Systems: Methods and Techniques
Several methods are employed to study annelid circulatory systems. These include:
-
Microscopy: Microscopic examination of dissected specimens allows for detailed visualization of the vessels and hearts.
-
Imaging Techniques: Advanced imaging techniques, such as X-ray micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) and confocal microscopy, are being increasingly used to study the three-dimensional structure of circulatory systems non-destructively.
-
Physiological Measurements: Measurements of blood pressure and flow rates provide insights into the function of the circulatory system.
-
Molecular Biology: Genetic analysis and molecular techniques are aiding in the identification of genes and proteins involved in heart development and function in annelids.
Ecological Implications and Future Research
Understanding the intricacies of annelid circulatory systems has far-reaching ecological implications. The efficiency of oxygen transport affects an organism's metabolic rate, activity levels, and tolerance to environmental conditions. For example, the robust closed system of some earthworm species contributes to their ability to thrive in diverse soil environments. Studies of annelid circulatory systems are not only crucial for understanding annelid biology itself but also contribute to broader understanding of evolutionary physiology, comparative biology and the development of organ systems.
Future research should focus on:
-
Comparative studies: More comparative studies of circulatory systems across diverse annelid taxa are needed to further elucidate the evolutionary trajectory of this system and how it has adapted to specific environmental pressures.
-
Functional studies: Detailed functional studies examining blood flow dynamics, oxygen transport, and regulation of blood pressure in various annelid species are crucial.
-
Evolutionary developmental biology (Evo-Devo): Studying the genetic and developmental mechanisms underlying circulatory system formation and evolution can reveal further insights into the diversity seen within annelids.
-
Environmental Impacts: Investigating how environmental factors, such as temperature and oxygen levels, influence the function of annelid circulatory systems can shed light on their responses to environmental change.
In conclusion, the statement that annelids have a closed circulatory system is broadly accurate but requires nuance. Most annelids possess a closed system, a key adaptation for their evolutionary success. However, variations exist, with certain species showing modifications or features that might appear open-like in some respects. Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of annelid hemodynamics, providing valuable insights into their biology and their significance in various ecosystems. The efficiency and adaptation of the annelid circulatory system stand as a testament to the remarkable evolutionary plasticity within this diverse phylum. Further studies employing advanced techniques are essential for a fuller understanding of this crucial physiological system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Final Product Of Gene Expression Is
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Main Function Of Trna Is To
Apr 04, 2025
-
Give The Iupac Name Of The Carboxylic Acid Below
Apr 04, 2025
-
An Interior Angle Of A Regular Polygon Measures 170
Apr 04, 2025
-
A Fluids Resistance To Flow Is Called
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Do Annelids Have An Open Or Closed Circulatory System . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
