Distance From Earth To Sun Scientific Notation
News Leon
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
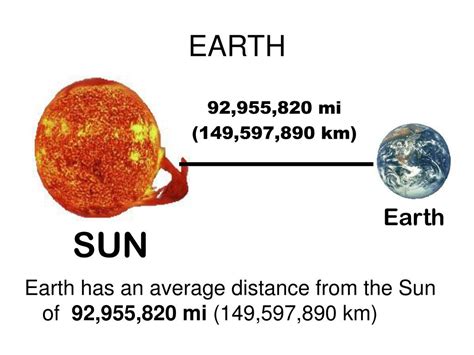
Table of Contents
The Sun's Distance from Earth: A Deep Dive into Scientific Notation
The Sun, our life-giving star, sits at the heart of our solar system. Understanding its distance from Earth is fundamental to comprehending our place in the cosmos and is a cornerstone of astronomical calculations. This distance, however, is vast, defying easy comprehension using standard numerical notation. This is where scientific notation, a powerful tool for expressing extremely large or small numbers, comes into play. This article explores the Earth-Sun distance, delves deep into the mechanics of scientific notation, and explains why it's essential for expressing astronomical distances.
Understanding the Astronomical Unit (AU)
Before we dive into scientific notation, it's crucial to introduce the Astronomical Unit (AU). The AU is a unit of length roughly equal to the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. While not a perfectly consistent distance due to the Earth's elliptical orbit, it provides a convenient and readily understood scale for measuring distances within our solar system. One AU is approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). This seemingly large number highlights the need for a more concise and manageable way to represent it – enter scientific notation.
Scientific Notation: A Concise Representation of Vast Distances
Scientific notation expresses numbers as a product of a number between 1 and 10, and a power of 10. This method dramatically simplifies the handling of extremely large or small numbers. The general form is:
a x 10<sup>b</sup>
where:
- a is a number between 1 and 10 (but not including 10)
- b is an integer (whole number) representing the power of 10.
For instance, the number 3,000,000 can be written in scientific notation as 3 x 10<sup>6</sup>. The exponent (6) tells us to move the decimal point six places to the right. Conversely, a small number like 0.000005 can be expressed as 5 x 10<sup>-6</sup>, indicating moving the decimal point six places to the left.
Expressing the Earth-Sun Distance in Scientific Notation
Using the approximate value of 149.6 million kilometers for one AU, we can express this distance in scientific notation as follows:
1.496 x 10<sup>8</sup> kilometers
This compact representation clearly conveys the magnitude of the Earth-Sun distance. The exponent, 8, indicates that we have a very large number, with eight zeros following the 149.6. This simplification is critical in astronomical calculations, where dealing with such large numbers directly would be cumbersome and prone to errors.
The Importance of Precision in Astronomical Measurements
While 1.496 x 10<sup>8</sup> kilometers provides a good approximation, more precise measurements are essential for many scientific applications. Highly accurate calculations are required for:
-
Spacecraft navigation: Precise knowledge of the Earth-Sun distance is crucial for planning and executing interplanetary missions. Even small errors in distance calculations can lead to significant deviations in trajectory.
-
Understanding planetary orbits: The Earth's orbit around the Sun is not perfectly circular; it's slightly elliptical. Precise measurements of the distance at various points in the orbit are needed to fully understand the dynamics of the Earth's movement.
-
Celestial mechanics: Calculating the gravitational interactions between celestial bodies requires highly accurate measurements of distances. Such calculations are used to predict eclipses, planetary alignments, and other celestial events.
-
Solar energy studies: Understanding the intensity of solar radiation reaching Earth necessitates precise knowledge of the Earth-Sun distance. This is critical for modeling climate change and for optimizing solar energy technologies.
Therefore, instead of the simpler approximation, astronomers often use a more precise value for the AU, which is defined to a higher degree of accuracy within the international astronomical system.
Beyond the AU: Measuring Distances to Other Stars
While the AU is useful within our solar system, it becomes impractical when measuring distances to stars beyond our solar system. For interstellar distances, astronomers employ other units, such as:
-
Light-year: The distance light travels in one year, approximately 9.461 x 10<sup>12</sup> kilometers (5.878 x 10<sup>12</sup> miles). This is a convenient unit for measuring vast interstellar distances. Expressed in scientific notation, it demonstrates the enormous scale of space.
-
Parsec: A unit of distance approximately equal to 3.26 light-years, or 3.086 x 10<sup>13</sup> kilometers (1.917 x 10<sup>13</sup> miles). This is commonly used in professional astronomy for its convenience in parallax calculations.
The Evolution of Measuring the Earth-Sun Distance
Determining the Earth-Sun distance has been a historical challenge that pushed the boundaries of scientific understanding. Early attempts relied on geometric methods, with a notable contribution from Aristarchus of Samos in the 3rd century BC. However, these early calculations were significantly less precise. Over centuries, improvements in observational techniques, including the use of telescopes and more sophisticated mathematical tools, led to progressively more accurate measurements.
Today, highly sophisticated methods, such as radar ranging and spacecraft tracking, offer extraordinarily precise measurements of the Earth-Sun distance. These techniques harness advanced technologies to determine the distance with remarkable accuracy, essential for various scientific endeavors.
Practical Applications of Scientific Notation in Astronomy
The use of scientific notation extends beyond simply expressing distances. It's fundamental in:
-
Calculating orbital velocities: The speeds of planets around the sun are immense, requiring scientific notation to represent them concisely and accurately.
-
Analyzing stellar luminosities: The energy output of stars is expressed in enormous numbers, making scientific notation a necessity for managing and comparing these values.
-
Modeling galactic structures: The scale of galaxies demands scientific notation for handling the distances between stars, their masses, and the overall dimensions of the galactic structures.
-
Cosmology: Studying the universe's structure and evolution involves dealing with immense distances and incredibly large time scales, all of which rely heavily on scientific notation for efficient calculations and representation.
Beyond the Numbers: The Significance of the Earth-Sun Distance
The distance between the Earth and the Sun isn't just a numerical value; it's a crucial factor shaping life on Earth. This distance determines:
-
The Earth's temperature: The distance affects the intensity of solar radiation received, influencing the Earth's average temperature and making it habitable.
-
Climate patterns: Slight variations in the Earth-Sun distance throughout the year contribute to seasonal changes and have long-term effects on climate.
-
The existence of liquid water: The distance from the Sun maintains liquid water on the surface of Earth, crucial for all known forms of life.
Conclusion: A Continuing Quest for Precision
The Earth-Sun distance, expressed elegantly through scientific notation, remains a cornerstone of astronomy and space exploration. Continuous refinement of measurement techniques and increasing precision are driving further advancements in our understanding of the solar system, our galaxy, and the universe beyond. While 1.496 x 10<sup>8</sup> kilometers provides a useful approximation, the ongoing quest for greater accuracy ensures that our knowledge of this fundamental constant continues to evolve, powering groundbreaking discoveries and innovative applications. The concise power of scientific notation remains an indispensable tool in this ongoing exploration of the cosmos.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Companies Is A Manufacturer Of Cpus
Apr 02, 2025
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 8 And 36
Apr 02, 2025
-
In Rna Adenine Always Pairs With
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Diaphragm Separates The Thoracic Cavity From The
Apr 02, 2025
-
Where Does The Majority Of Fat Digestion Take Place
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Distance From Earth To Sun Scientific Notation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
