Cos Alpha Beta Cos Alpha Beta
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
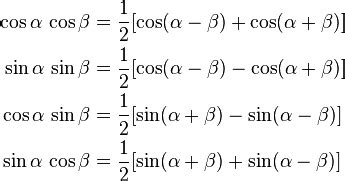
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: A Deep Dive into Cos(α+β) and Cos(α-β)
The trigonometric identities cos(α+β) and cos(α-β) are fundamental building blocks in mathematics, particularly within trigonometry, calculus, and various branches of physics and engineering. Understanding these identities and their derivations is crucial for solving complex problems and grasping deeper mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of cos(α+β) and cos(α-β), exploring their derivations, applications, and connections to other trigonometric identities.
Understanding the Core Identities: Cos(α+β) and Cos(α-β)
The core identities we'll explore are:
- cos(α+β) = cos α cos β - sin α sin β
- cos(α-β) = cos α cos β + sin α sin β
These seemingly simple equations unlock a vast array of possibilities in mathematical problem-solving. They allow us to express the cosine of a sum or difference of two angles in terms of the cosines and sines of the individual angles. This property is invaluable in simplifying complex trigonometric expressions and solving equations.
Geometric Derivation of Cos(α+β) and Cos(α-β)
One powerful way to understand these identities is through a geometric approach. While various proofs exist, the unit circle method provides an elegant visualization. Consider two points on the unit circle:
- Point A: represented by the angle α. Its coordinates are (cos α, sin α).
- Point B: represented by the angle (α + β). Its coordinates are (cos(α+β), sin(α+β)).
Now, consider rotating point A by an angle β. This rotation maps point A to point B. Using the rotation matrix and the properties of vector multiplication, we can establish the relationship between the coordinates of A and B. This leads us to the derivation of cos(α+β). Similarly, by considering the difference in angles, we can derive the formula for cos(α-β). The rigorous mathematical details of these derivations are readily available in various trigonometric textbooks and online resources, often using techniques from linear algebra.
Algebraic Derivation of Cos(α+β) and Cos(α-β) using Rotation Matrices
A more formal approach uses rotation matrices. A rotation by an angle θ in two dimensions is represented by the matrix:
R(θ) = | cos θ -sin θ |
| sin θ cos θ |
Rotating a point (x, y) by angle θ results in the new point (x', y'):
| x' | | cos θ -sin θ | | x |
| y' | = | sin θ cos θ | * | y |
Applying this to the derivation of cos(α+β), we first rotate by α, then by β. The composite rotation is equivalent to a single rotation by (α+β). Equating the resulting coordinates gives us the identity cos(α+β) = cos α cos β - sin α sin β. A similar process, using the appropriate rotation angles, can be used to derive cos(α-β).
Applications Across Diverse Fields
The identities cos(α+β) and cos(α-β) have far-reaching applications beyond pure mathematics:
1. Physics and Engineering:
- Wave Interference: In physics, these identities are crucial for understanding wave interference, where the superposition of waves (e.g., sound waves, light waves) results in constructive or destructive interference. The cosine addition formula is integral to modeling the resulting wave patterns.
- Signal Processing: In signal processing, these identities are essential for analyzing and manipulating signals. They play a key role in techniques like Fourier analysis, which decomposes complex signals into simpler sinusoidal components.
- Robotics and Control Systems: Robotics often involves precise calculations of angles and positions. The cosine addition and subtraction formulas are instrumental in kinematic calculations and path planning for robots.
2. Solving Trigonometric Equations:
These identities are indispensable for simplifying and solving complex trigonometric equations. They allow us to rewrite expressions in a more manageable form, often reducing the equation to a solvable form involving only one trigonometric function.
3. Calculus:
In calculus, these identities are used extensively in:
- Differentiation and Integration: The derivative and integral of trigonometric functions often involve the application of these identities to simplify the expressions before proceeding with the calculation.
- Trigonometric Substitution: In integration, the substitution of trigonometric functions is a powerful technique. The identities cos(α+β) and cos(α-β) are frequently used to simplify the resulting integrals.
4. Other Mathematical Areas:
The identities find applications in areas such as:
- Complex Numbers: The identities have direct connections to Euler's formula, linking trigonometric functions to exponential functions of complex numbers (e^(iθ) = cos θ + i sin θ).
- Geometry: They are utilized in various geometric proofs and calculations involving triangles and other shapes.
Deriving Other Trigonometric Identities: Building Blocks for More Complex Relationships
The identities for cos(α+β) and cos(α-β) serve as fundamental building blocks for deriving many other trigonometric identities. For example:
- Cosine Double Angle Formula: Setting α = β in the cos(α+β) identity yields the double angle formula: cos(2α) = cos²α - sin²α. This formula has numerous applications in calculus and other areas.
- Cosine Half Angle Formula: The double angle formula can be manipulated to derive the half angle formulas for cosine.
- Product-to-Sum Formulas: By combining the identities for cos(α+β) and cos(α-β), we can derive the product-to-sum formulas, which express the product of two cosine functions as a sum of cosine functions. This transformation is highly useful in simplifying expressions and solving equations.
- Sum-to-Product Formulas: Conversely, we can also derive the sum-to-product formulas which transform sums of cosine functions into products.
Illustrative Examples: Practical Application of Cos(α+β) and Cos(α-β)
Let's illustrate the practical application of these identities with a few examples:
Example 1: Simplifying a Trigonometric Expression
Simplify the expression: cos(x + π/3) + cos(x - π/3)
Using the sum and difference formulas, we get:
(cos x cos(π/3) - sin x sin(π/3)) + (cos x cos(π/3) + sin x sin(π/3)) = 2 cos x cos(π/3) = cos x
Example 2: Solving a Trigonometric Equation
Solve the equation: cos(2x + π/4) = 1/√2
Using the sum formula:
cos(2x)cos(π/4) - sin(2x)sin(π/4) = 1/√2
Substituting the values for cos(π/4) and sin(π/4) and simplifying yields an equation that can be solved for x.
Example 3: Calculus Application (Integration)
Consider the integral: ∫cos(3x + 2) dx. While direct integration is possible, applying the sum formula to simplify the argument before integrating often simplifies the process.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals of Cos(α+β) and Cos(α-β)
The trigonometric identities cos(α+β) and cos(α-β) are fundamental tools in mathematics, physics, and engineering. Understanding their derivation, applications, and connections to other trigonometric identities is crucial for success in these fields. Their versatility makes them essential for solving a wide range of problems, from simplifying complex expressions to solving intricate equations and performing advanced calculations in calculus and other advanced mathematical disciplines. By mastering these identities, you are equipping yourself with powerful tools that will continue to be valuable throughout your mathematical journey. Furthermore, understanding the underlying principles and the ability to derive related identities strengthens problem-solving skills and promotes a deeper appreciation of the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The 4 Types Of Possession
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Intellectual Property
Mar 24, 2025
-
Thick Filaments Are Made Of The Protein
Mar 24, 2025
-
The Current Density Inside A Long Solid Cylindrical Wire
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Statement Best Describes The Passage
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cos Alpha Beta Cos Alpha Beta . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
