Benzoic Acid And Sodium Bicarbonate Reaction
News Leon
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
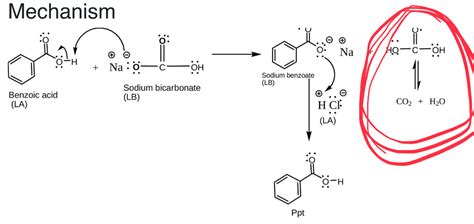
Table of Contents
Benzoic Acid and Sodium Bicarbonate: A Comprehensive Look at the Reaction
The reaction between benzoic acid and sodium bicarbonate is a classic example of an acid-base reaction, frequently encountered in organic chemistry laboratories and relevant to various applications in the chemical industry and beyond. This article delves deep into this reaction, exploring its mechanism, applications, and the underlying principles governing its behavior. We'll examine the stoichiometry, the products formed, and the factors that influence the reaction's rate and efficiency. Furthermore, we will explore the practical implications and applications of this reaction in different fields.
Understanding the Reactants
Before we dive into the reaction itself, let's understand the individual components: benzoic acid and sodium bicarbonate.
Benzoic Acid: A Weak Aromatic Acid
Benzoic acid (C₇H₆O₂), a simple aromatic carboxylic acid, is a white crystalline solid at room temperature. It's a relatively weak acid, meaning it doesn't fully dissociate in water, leading to a relatively low concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺). Its weak acidity is attributed to the electron-withdrawing effect of the benzene ring, which stabilizes the benzoate anion (C₇H₅O₂⁻) formed after proton donation. This weak acidity plays a crucial role in its reaction with sodium bicarbonate. The key characteristic here is its ability to donate a proton (H⁺).
Sodium Bicarbonate: A Weak Base
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃), commonly known as baking soda, is a white crystalline powder. It's an amphoteric compound, meaning it can act as both an acid and a base, depending on the reaction conditions. In the reaction with benzoic acid, it acts as a weak base, accepting a proton (H⁺) to form carbonic acid (H₂CO₃). The crucial property here is its ability to accept a proton.
The Reaction: An Acid-Base Neutralization
The reaction between benzoic acid and sodium bicarbonate is an acid-base neutralization reaction. The acidic proton from benzoic acid is transferred to the bicarbonate ion, resulting in the formation of sodium benzoate, carbon dioxide, and water.
The overall balanced chemical equation is:
C₇H₆O₂ (aq) + NaHCO₃ (aq) → C₇H₅O₂Na (aq) + H₂CO₃ (aq)
Subsequently, carbonic acid decomposes into carbon dioxide and water:
H₂CO₃ (aq) → CO₂ (g) + H₂O (l)
Therefore, the complete reaction can be represented as:
C₇H₆O₂ (aq) + NaHCO₃ (aq) → C₇H₅O₂Na (aq) + CO₂ (g) + H₂O (l)
This equation illustrates the key transformation: benzoic acid, a weak acid, reacts with sodium bicarbonate, a weak base, to produce sodium benzoate, a salt, along with carbon dioxide gas and water. The evolution of carbon dioxide gas is a clear indicator of this reaction.
The Mechanism: Proton Transfer
The reaction mechanism involves a simple proton transfer from the benzoic acid molecule to the bicarbonate ion. The slightly acidic proton attached to the carboxyl group (-COOH) of benzoic acid is attracted to the negatively charged bicarbonate ion (HCO₃⁻). The lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom of the bicarbonate ion facilitates the proton transfer, forming a new bond between the hydrogen and the oxygen of the bicarbonate ion. This results in the formation of carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) and the benzoate anion (C₇H₅O₂⁻). The sodium cation (Na⁺) remains as a spectator ion, meaning it doesn't directly participate in the reaction but balances the charge in the solution.
Step-by-step Mechanism:
-
Proton Transfer: The acidic proton from the carboxyl group of benzoic acid is transferred to the bicarbonate ion, forming carbonic acid and the benzoate ion.
-
Carbonic Acid Decomposition: Carbonic acid is an unstable compound and readily decomposes into carbon dioxide gas and water. This decomposition is a spontaneous process that drives the reaction forward.
-
Salt Formation: The benzoate ion (C₇H₅O₂⁻) combines with the sodium ion (Na⁺) from the sodium bicarbonate to form sodium benzoate (C₇H₅O₂Na), a water-soluble salt.
Factors Affecting the Reaction
Several factors can influence the rate and extent of the reaction between benzoic acid and sodium bicarbonate:
-
Concentration of Reactants: Higher concentrations of both benzoic acid and sodium bicarbonate lead to a faster reaction rate due to increased collision frequency between reactant molecules.
-
Temperature: Increasing the temperature generally accelerates the reaction, but the effect might be less pronounced than in other reactions due to the relatively low activation energy of this acid-base neutralization.
-
Solubility: The solubility of benzoic acid in the aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution plays a role. If benzoic acid is poorly soluble, the reaction rate will be affected, as the interaction between the reactants will be limited.
-
Presence of Catalysts: While not typically necessary, the presence of certain catalysts could potentially enhance the reaction rate. However, this is not a common practice for this particular reaction.
-
pH of the Solution: The pH of the solution will significantly affect the reaction. A more acidic environment will slow down the reaction, while a more basic environment might speed it up, although sodium bicarbonate itself will buffer against significant changes in pH.
Applications and Significance
The reaction between benzoic acid and sodium bicarbonate, seemingly simple, has several valuable applications in various fields:
1. Pharmaceutical Industry:
-
Preparation of Sodium Benzoate: Sodium benzoate, a common food preservative, is often prepared using this reaction. It's effective against many types of bacteria, yeasts, and molds and has a broad range of applications in food preservation.
-
Drug Formulation: Understanding this reaction is crucial in pharmaceutical formulation, particularly when dealing with drugs containing acidic functional groups. The reaction can be used to control pH and improve drug stability and solubility.
2. Food Industry:
-
Food Preservation: As mentioned, sodium benzoate is a widely used food preservative, often found in acidic foods like soft drinks, fruit juices, and pickles.
-
Baking: While less direct, the principles involved in this reaction are relevant to understanding the leavening process in baking, where acids and bases react to produce carbon dioxide.
3. Chemical Synthesis:
-
Synthesis of Benzoate Derivatives: The reaction can be used as a step in the synthesis of other benzoate derivatives, which have various applications in the chemical industry.
-
Organic Chemistry Experiments: This reaction is often used as a simple demonstration of acid-base reactions in organic chemistry labs, providing a straightforward way to illustrate the principles of proton transfer and neutralization.
4. Environmental Applications:
- Wastewater Treatment: Understanding acid-base neutralization reactions, including this one, is essential in designing wastewater treatment processes to neutralize acidic or basic effluents before discharge.
Safety Precautions
When conducting this reaction, it's essential to follow standard laboratory safety procedures:
-
Eye protection: Always wear safety goggles to protect your eyes from splashes.
-
Gloves: Use chemical-resistant gloves to prevent skin contact with the reactants.
-
Ventilation: The reaction produces carbon dioxide gas, so it should be conducted in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to prevent inhalation hazards.
-
Disposal: Properly dispose of the reaction mixture according to local regulations.
Conclusion
The reaction between benzoic acid and sodium bicarbonate is a fundamental acid-base neutralization reaction with significant practical implications across several industries. Understanding the mechanism, stoichiometry, and the factors affecting the reaction's rate and efficiency is crucial for optimizing its use in diverse applications, ranging from pharmaceutical drug development and food preservation to chemical synthesis and environmental remediation. While seemingly simple, this reaction serves as a foundational concept in chemistry with far-reaching consequences. Further research and exploration of this reaction continue to uncover new applications and improve our understanding of its underlying principles. Careful consideration of safety precautions is crucial when working with these chemicals in any context.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Most Important Parts Of The Control System
Mar 31, 2025
-
Difference Between Convex And Concave Polygon
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Structure Is Found Only In Animal Cells
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Is Not A Function Of The Cerebrospinal Fluid
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Vector Has Magnitude And Direction
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Benzoic Acid And Sodium Bicarbonate Reaction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
