An Instrument Used To Measure Atmospheric Pressure Is Called A
News Leon
Apr 02, 2025 · 7 min read
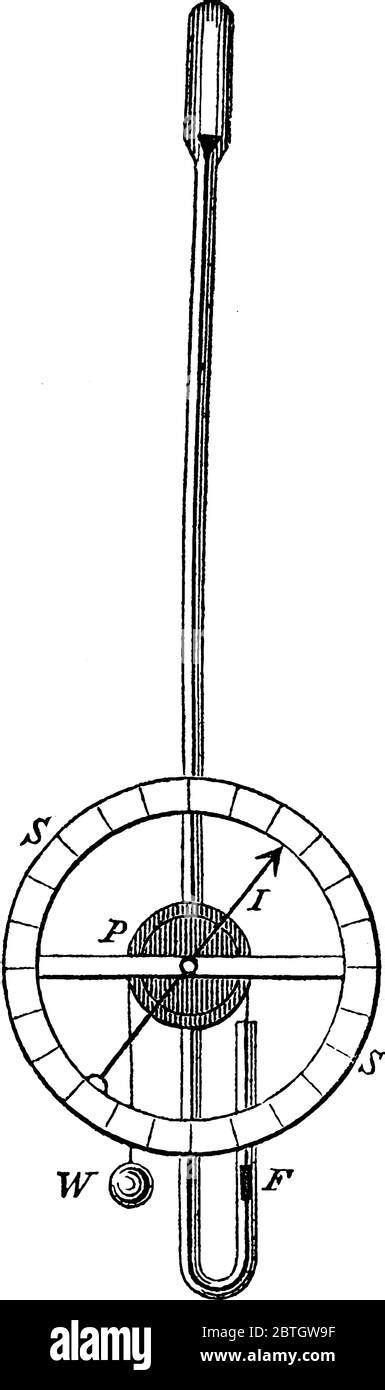
Table of Contents
An Instrument Used to Measure Atmospheric Pressure is Called a Barometer: A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Pressure Measurement
An instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure is called a barometer. Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure, is the force exerted by the weight of air in the atmosphere on the Earth's surface and everything on it. Understanding atmospheric pressure is crucial in various fields, from meteorology and aviation to medicine and even cooking. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of barometers, exploring their history, different types, working principles, applications, and the significance of accurate atmospheric pressure measurement.
A Brief History of Barometers
The invention of the barometer is attributed to Evangelista Torricelli, an Italian physicist and mathematician, in 1643. Before Torricelli's invention, the concept of atmospheric pressure wasn't well understood. Torricelli's experiment, which involved filling a glass tube with mercury and inverting it into a dish of mercury, demonstrated conclusively that air exerted pressure. The height of the mercury column in the tube directly corresponded to the atmospheric pressure. This groundbreaking experiment laid the foundation for the development of various types of barometers.
Following Torricelli's invention, numerous improvements and variations of the barometer emerged. Scientists and inventors continually refined the design and accuracy of these instruments, leading to the sophisticated barometers we use today.
Types of Barometers: Exploring the Diverse Range
There are several types of barometers, each with its own unique design and mechanism for measuring atmospheric pressure. The most common types include:
1. Mercury Barometer: The Classic Standard
The mercury barometer, also known as a Torricellian barometer, is the original type of barometer and remains a standard for accurate pressure measurement. It consists of a vertical glass tube filled with mercury, sealed at one end and inverted into a reservoir of mercury. The height of the mercury column in the tube is directly proportional to the atmospheric pressure. A scale alongside the tube allows for reading the pressure in various units, such as millimeters of mercury (mmHg) or inches of mercury (inHg). While highly accurate, mercury barometers are less common now due to the toxicity of mercury.
2. Aneroid Barometer: The Portable Choice
The aneroid barometer is a more portable and convenient alternative to the mercury barometer. It doesn't use mercury but instead relies on a small, flexible metallic capsule called an aneroid cell. This cell is partially evacuated of air, and its shape changes in response to variations in atmospheric pressure. These shape changes are mechanically amplified and transmitted to a needle that moves across a calibrated dial, indicating the atmospheric pressure. Aneroid barometers are widely used in weather forecasting, aviation, and various other applications due to their portability and ease of use.
3. Fortin Barometer: Precision and Adjustability
The Fortin barometer is a type of mercury barometer known for its high precision and adjustability. It features a reservoir of mercury with a screw-adjustable bottom, allowing for precise setting of the mercury level to zero before taking a reading. This feature improves the accuracy of pressure measurements compared to simpler mercury barometers. Fortin barometers are often used in laboratories and scientific research settings where high accuracy is paramount.
4. Altimeter: Measuring Pressure and Altitude
An altimeter is a specialized barometer primarily used for measuring altitude. While it measures atmospheric pressure, it's calibrated to display the corresponding altitude instead. The principle is that atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude. Altimeters are essential instruments in aviation, mountaineering, and surveying. They are often found in aircraft, providing pilots with crucial information about their altitude.
5. Digital Barometer: Modern Convenience and Precision
Digital barometers utilize electronic sensors to measure atmospheric pressure and display the reading on a digital screen. These barometers offer several advantages, including high accuracy, ease of use, and additional features such as data logging and wireless connectivity. Digital barometers are becoming increasingly popular due to their convenience and sophisticated capabilities.
Working Principles of Barometers: Understanding the Physics
The fundamental principle behind all barometers is the relationship between atmospheric pressure and the height or deformation of a sensing element.
-
Mercury Barometer: The weight of the atmospheric air exerts pressure on the mercury in the reservoir. This pressure pushes the mercury up the glass tube until the weight of the mercury column balances the atmospheric pressure. The height of the mercury column is directly proportional to the atmospheric pressure.
-
Aneroid Barometer: Changes in atmospheric pressure cause the aneroid cell to expand or contract. This movement is amplified through a system of levers and gears, resulting in the movement of the needle on the dial.
-
Digital Barometer: Digital barometers use electronic pressure sensors, typically based on piezoresistive or capacitive principles. These sensors convert changes in atmospheric pressure into electrical signals that are then processed to display the pressure reading.
Applications of Barometers: A Wide Range of Uses
Barometers are used extensively in a wide range of applications across various fields:
1. Meteorology: Weather Forecasting and Prediction
Barometers play a critical role in weather forecasting. Changes in atmospheric pressure are indicators of approaching weather systems. A falling barometer typically signals the approach of a low-pressure system, which can bring stormy weather. Conversely, a rising barometer often suggests fair weather. Meteorologists use barometers, along with other weather instruments, to analyze atmospheric conditions and predict weather patterns.
2. Aviation: Altitude Measurement and Flight Safety
Barometers, particularly altimeters, are indispensable in aviation. Pilots rely on altimeters to determine their altitude, ensuring safe flight operations. Accurate altitude measurement is crucial for navigation, avoiding obstacles, and ensuring proper flight procedures.
3. Medicine: Monitoring Pressure in Healthcare
Barometers can be used in specialized medical applications for monitoring pressure in various situations. For example, barometric pressure can influence the body and might affect certain medical conditions.
4. Industry: Calibration and Process Control
Barometers are employed in various industrial processes to monitor and control pressure levels. Accurate pressure measurement is vital in many manufacturing processes, ensuring quality control and efficiency.
5. Scientific Research: Atmospheric Studies and Experimentation
Barometers are essential tools in atmospheric science research. They provide precise measurements of atmospheric pressure, which are crucial for understanding atmospheric dynamics, climate change, and other environmental phenomena.
The Significance of Accurate Atmospheric Pressure Measurement
Accurate atmospheric pressure measurement is crucial for various reasons:
-
Improved Weather Forecasting: Accurate pressure readings enhance the accuracy and reliability of weather forecasts, enabling better preparedness for extreme weather events.
-
Enhanced Flight Safety: Precise altitude measurement via altimeters is critical for safe aviation operations, preventing accidents caused by altitude misjudgment.
-
Reliable Scientific Research: Accurate atmospheric pressure data are fundamental to scientific studies of atmospheric processes and climate change.
-
Effective Industrial Processes: Precise pressure control is essential for many industrial processes, ensuring product quality and operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Barometer: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right barometer depends on specific requirements:
-
Accuracy: The level of precision needed influences the type of barometer suitable for the task. High-precision applications require mercury or high-quality aneroid or digital barometers.
-
Portability: Portability is a major factor if the barometer is frequently moved. Aneroid and digital barometers are more portable than mercury barometers.
-
Features: Additional features such as data logging, wireless connectivity, and altitude display may be crucial depending on the application.
-
Cost: The price varies significantly among different barometer types, influencing the choice based on the budget.
Conclusion: The Barometer's Enduring Legacy
The barometer, a seemingly simple instrument, has profoundly impacted our understanding of the atmosphere and its influence on our lives. From its humble beginnings as a groundbreaking scientific invention to its widespread applications across diverse fields, the barometer remains an indispensable tool for accurate atmospheric pressure measurement. As technology advances, we can expect even more sophisticated and accurate barometers to emerge, further enhancing our ability to monitor and understand atmospheric conditions and their impact on our world. The continued evolution of the barometer reflects its enduring importance in scientific discovery, practical applications, and our quest to comprehend the complexities of our planet's atmosphere.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Delta H Positive For Endothermic
Apr 03, 2025
-
Cytoplasm Of The Cell Is Being Divided
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Elements Has Only One Valence Electron
Apr 03, 2025
-
Co2 Enters The Inner Spaces Of The Leaf Through The
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Alcohol
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about An Instrument Used To Measure Atmospheric Pressure Is Called A . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
