An Atom With 3 Protons And 4 Neutrons
News Leon
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
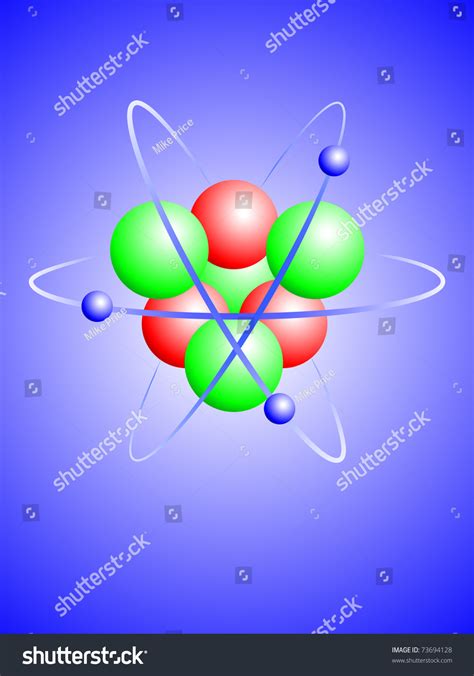
Table of Contents
An Atom with 3 Protons and 4 Neutrons: Delving into Lithium-7
An atom with three protons and four neutrons is an isotope of lithium, specifically Lithium-7 (⁷Li). Understanding this atom requires exploring the fundamental building blocks of matter, the forces that hold them together, and the unique properties that arise from this specific nuclear configuration. This comprehensive article will delve deep into the world of Lithium-7, examining its structure, behavior, and significance in various fields.
The Fundamental Particles: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we dissect Lithium-7, let's refresh our understanding of the fundamental subatomic particles that comprise it.
-
Protons: Positively charged particles residing in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; three protons unequivocally identify the atom as lithium. Protons contribute significantly to the atom's mass and determine its chemical properties.
-
Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also located within the nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but do not directly influence its chemical behavior. The number of neutrons can vary within an element, leading to different isotopes. In Lithium-7, the presence of four neutrons significantly impacts its nuclear stability and properties.
-
Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom, balancing the positive charge of the protons. Electrons determine an atom's chemical reactivity and its interactions with other atoms. Lithium-7, in its neutral state, possesses three electrons.
Isotopes: Variations on a Theme
The term isotope refers to atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. Lithium has two naturally occurring stable isotopes: Lithium-6 (³Li) with three protons and three neutrons, and Lithium-7 (⁷Li) with three protons and four neutrons. The numbers 6 and 7 represent the mass number (protons + neutrons).
The difference in neutron number affects the isotope's mass and, to a lesser extent, its chemical properties. While the chemical behavior is largely governed by the number of electrons (and therefore protons), the nuclear properties and stability are strongly influenced by the neutron-to-proton ratio. The greater stability of Lithium-7 compared to Lithium-6 is a consequence of this ratio.
Nuclear Stability and Binding Energy
The stability of an atomic nucleus depends on the delicate balance between the strong nuclear force (which holds protons and neutrons together) and the electromagnetic force (which causes protons to repel each other). The binding energy is the energy required to separate the nucleons (protons and neutrons) within the nucleus. Higher binding energy implies greater nuclear stability. Lithium-7 has a higher binding energy than Lithium-6, contributing to its greater abundance in nature. This higher binding energy stems from the more optimal neutron-to-proton ratio in Lithium-7, leading to a stronger nuclear force overcoming the electromagnetic repulsion between the protons.
Properties of Lithium-7
Lithium-7, being the more abundant isotope of lithium (approximately 92.4%), exhibits properties characteristic of the element lithium. These properties stem from its electronic structure and its interactions with other atoms.
-
Chemical Properties: Lithium is an alkali metal, characterized by its high reactivity. Its single electron in the outermost shell readily participates in chemical reactions, forming ionic bonds with other elements. This reactivity is driven by the tendency to achieve a stable electron configuration, resembling that of noble gases.
-
Physical Properties: Lithium-7, like other lithium isotopes, is a soft, silvery-white metal with a relatively low density and melting point. These physical properties are linked to the weak metallic bonding within the lithium crystal structure.
-
Nuclear Properties: As mentioned earlier, the key nuclear property of Lithium-7 is its higher stability compared to Lithium-6 due to its neutron-to-proton ratio and consequently, higher binding energy. This greater stability influences its abundance in nature and its potential applications in various scientific and technological fields.
Applications of Lithium-7
The unique properties of Lithium-7 make it a valuable element in diverse applications. Its abundance and stability contribute to its widespread use.
-
Nuclear Fusion: Lithium-6 and Lithium-7 are potential fuels for future nuclear fusion reactors. The fusion of Lithium-7 with deuterium (an isotope of hydrogen) offers a promising pathway for clean and abundant energy production. The reaction releases significant energy, making it an attractive prospect for sustainable energy generation. The higher abundance of Lithium-7 makes it a more readily available fuel source.
-
Nuclear Medicine: Lithium isotopes, particularly Lithium-6, find application in neutron capture therapy, a form of cancer treatment. Lithium-6 has a high cross-section for neutron absorption, leading to the release of alpha particles that can destroy cancer cells.
-
Batteries: Lithium is widely used in rechargeable batteries, including those found in portable electronics and electric vehicles. While the isotope isn't specifically chosen, the overall lithium content is crucial for these applications, and Lithium-7's abundance contributes to the availability of this vital metal.
-
Lubricants: Lithium-based greases are common lubricants due to their high thermal stability and resistance to water washout. The properties of Lithium contribute to the functionality of these greases, regardless of the specific isotope ratio.
-
Ceramics and Glass: Lithium compounds are added to ceramics and glasses to improve their properties, such as strength, durability, and thermal shock resistance. The specific lithium isotope has less of an effect here than the overall lithium content.
Lithium-7 in Nature
Lithium-7's abundance in the Earth's crust is a testament to its nuclear stability. It is found in various minerals, including spodumene, lepidolite, and petalite. The extraction of lithium from these minerals is a crucial step in providing the element for various industrial applications. The isotopic ratio of Lithium-7 to Lithium-6 varies slightly depending on the source material but Lithium-7 consistently makes up the vast majority.
Future Research and Potential
Ongoing research continues to explore the potential applications of Lithium-7 and its role in various scientific and technological advancements. Further investigation into nuclear fusion reactions utilizing Lithium-7 is critical for the development of clean and sustainable energy sources. Advances in nuclear medicine may also leverage the unique properties of Lithium isotopes for targeted cancer therapies.
The investigation into Lithium-7, its properties, and its applications, has been an ongoing and vital field of research. As technologies advance, new possibilities will likely emerge. Understanding the structure and behavior of Lithium-7 is fundamental to unlocking its full potential and contributing to progress in various technological and scientific sectors.
Conclusion
In summary, an atom with three protons and four neutrons is Lithium-7, a stable isotope of lithium with significant importance in various fields. Its unique nuclear properties, stemming from the optimal neutron-to-proton ratio, contribute to its stability and abundance in nature. This abundance, coupled with its chemical reactivity and resulting physical properties, makes Lithium-7 a crucial element in diverse applications, ranging from energy production to medical treatments and industrial processes. Further research into its properties and applications promises even more significant advancements in the future. The continued exploration and understanding of this element will undoubtedly contribute to technological and scientific breakthroughs in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is True Of Muscle Contraction
Apr 03, 2025
-
Elements That Are Liquids At Room Temperature
Apr 03, 2025
-
Direction Of Propagation Of Electromagnetic Waves
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Protons Neutrons And Electrons In Iron
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Rule For Assigning Oxidation Numbers Is Correct
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about An Atom With 3 Protons And 4 Neutrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
