All Of The Following Characteristics Are Associated With Epithelium Except
News Leon
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
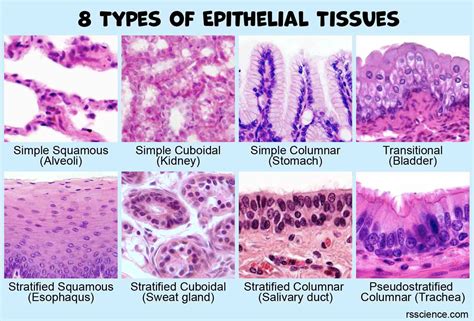
Table of Contents
All of the Following Characteristics are Associated with Epithelium Except…
Epithelial tissue, or epithelium, is one of the four fundamental tissue types in animals. Its defining characteristics make it easily distinguishable from connective, muscle, and nervous tissues. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for grasping its diverse functions throughout the body. This article will delve into the key features of epithelium, highlighting the exceptions to the typical rule and explaining the importance of these variations.
Defining Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue is characterized by several key features:
1. Cellularity: A Tight-Knit Community
Epithelial tissues are composed almost entirely of cells with minimal extracellular matrix. The cells are closely packed together, forming continuous sheets that cover body surfaces, line body cavities, and form glands. This close packing is essential for their barrier function. The tight junctions, adherens junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions connecting these cells further contribute to this cohesive nature.
2. Specialized Cell Junctions: The Glue that Holds it Together
The connections between epithelial cells are not just random; they're highly specialized. These cell junctions provide structural support and regulate the passage of molecules between cells. This controlled permeability is vital for maintaining homeostasis.
- Tight junctions: Prevent the passage of substances between cells, creating a selective barrier.
- Adherens junctions: Provide strong adhesion between cells, contributing to tissue integrity.
- Desmosomes: Similar to adherens junctions but provide even stronger adhesion, particularly important in tissues subjected to mechanical stress.
- Gap junctions: Allow direct communication between cells via channels that connect their cytoplasm, facilitating rapid intercellular signaling.
3. Polarity: A Top and a Bottom
Epithelial cells exhibit apical-basal polarity. This means that the cell has a distinct top (apical) surface and a bottom (basal) surface. The apical surface often faces a lumen (internal space of an organ) or the external environment, while the basal surface rests on a basement membrane. This polarity is reflected in the distribution of organelles and membrane proteins within the cell.
4. Supported by a Basement Membrane: The Foundation
The basal surface of epithelium rests on a specialized extracellular layer called the basement membrane. This membrane provides structural support, anchors the epithelium to underlying connective tissue, and acts as a selective filter regulating the passage of molecules between the epithelium and the connective tissue. It's composed of basal lamina (secreted by epithelial cells) and reticular lamina (secreted by connective tissue cells).
5. Avascular: Relying on Diffusion
Epithelial tissue is generally avascular, meaning it lacks its own blood vessels. Instead, it receives nutrients and oxygen via diffusion from the underlying connective tissue through the basement membrane. This avascular nature has implications for its thickness and regeneration capabilities.
6. Regeneration: A Capacity for Renewal
Epithelial cells have a remarkable capacity for regeneration. This is crucial for replacing cells that are constantly lost due to abrasion, injury, or normal cell turnover. The high rate of cell division contributes to the tissue's ability to repair itself quickly.
Exceptions to the Rule: Characteristics NOT Always Associated with Epithelium
While the above characteristics largely define epithelial tissue, it's important to acknowledge exceptions and variations that highlight the adaptability and complexity of this tissue type. The statement "All of the following characteristics are associated with epithelium except..." could refer to any characteristic not consistently found across all types of epithelium. This can include:
1. Extensive Extracellular Matrix: A Notable Exception
While minimal extracellular matrix is a hallmark of epithelium, some specialized epithelia, particularly those involved in secretion or protection, might contain a more substantial amount of extracellular material. This isn't the norm, however, and the amount is still significantly less than that found in connective tissue.
2. Presence of Blood Vessels: Variations in Vascularity
The avascular nature of epithelium is generally true, but some exceptions exist. Certain thicker epithelia, particularly those found in some glands, may contain blood vessels penetrating into the tissue to support their metabolic demands. These cases are relatively rare compared to the norm.
3. Lack of Cell Junctions in Some Specialized Cells: The Case of Certain Glandular Epithelia
While cell junctions are vital in maintaining epithelial integrity, some specialized glandular epithelia, particularly those secreting substances into ducts, may show a less pronounced degree of cell-to-cell adhesion. These cells might rely more on other mechanisms to maintain their organization.
4. Variations in Cell Shape and Arrangement: Stratified vs. Simple
Epithelial tissues exhibit remarkable diversity in cell shape (squamous, cuboidal, columnar) and arrangement (simple, stratified, pseudostratified). These variations reflect their functional specialization. Simple epithelium consists of a single cell layer, while stratified epithelium has multiple layers. Pseudostratified epithelium appears stratified but is actually a single layer of cells with varying heights. These variations can obscure the "typical" epithelial characteristics when examined in isolation.
5. Lack of Apical-Basal Polarity in Some Cases: An Unusual Circumstance
Though apical-basal polarity is a defining feature, some specialized epithelial cells, particularly those in developing tissues or undergoing significant transformation, may exhibit a less distinct polarity than others. This is often transient and part of a larger developmental process.
6. Limited Regeneration Capacity in Certain Situations: Age and Pathology
The high regenerative capacity of epithelium is generally observed, but factors like age and disease can significantly impact this ability. Older individuals might experience slower epithelial regeneration, while chronic diseases can further compromise this capacity.
7. Presence of Specialized Structures: Cilia and Microvilli
The presence of specialized structures like cilia (for movement) and microvilli (for absorption) is common in specific epithelial types but isn't a universal characteristic of all epithelial tissues. These structures add to the functional diversity of epithelium but are not present in every type.
The Importance of Understanding Epithelial Characteristics
The ability to distinguish between different types of epithelium and recognize their unique features is essential in various fields:
-
Histology: Understanding epithelial characteristics is fundamental in microscopic analysis of tissues for diagnosis and research.
-
Pathology: Recognizing deviations from normal epithelial structure is crucial in identifying various diseases, such as cancers.
-
Developmental Biology: Epithelial development is a complex process, and understanding its characteristics is key to understanding organogenesis and tissue formation.
-
Pharmacology: Many drugs target epithelial cells, so knowing the specific properties of different epithelial types is critical for drug development and delivery.
-
Clinical Practice: Understanding epithelial characteristics is paramount for diagnosis and treatment of various conditions affecting epithelial tissues, including skin lesions, ulcers, and respiratory diseases.
Conclusion: Epithelium's Versatile Nature
Epithelial tissue is a remarkably diverse and adaptable tissue type. While certain characteristics like cellularity, specialized cell junctions, and apical-basal polarity are consistently observed, variations exist. The "exception" in the statement "All of the following characteristics are associated with epithelium except..." depends entirely on the specific characteristic in question and the type of epithelium being considered. A comprehensive understanding of epithelial tissue and its exceptions is crucial for professionals in various biological and medical fields. It is the intricacies of these variations that contribute to the immense functional diversity observed throughout the body. Remember, exceptions prove the rule, and in the case of epithelium, these exceptions broaden our comprehension of its dynamic nature and remarkable adaptability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is True Of Muscle Contraction
Apr 03, 2025
-
Elements That Are Liquids At Room Temperature
Apr 03, 2025
-
Direction Of Propagation Of Electromagnetic Waves
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Protons Neutrons And Electrons In Iron
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Rule For Assigning Oxidation Numbers Is Correct
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about All Of The Following Characteristics Are Associated With Epithelium Except . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
