All Of The Following Are Granulocytes Except
News Leon
Mar 18, 2025 · 7 min read
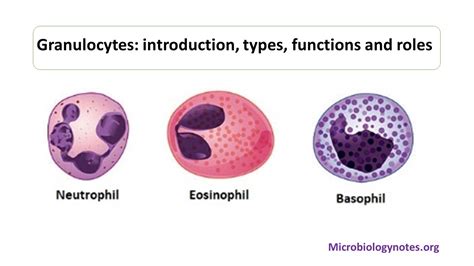
Table of Contents
All of the Following Are Granulocytes Except: Understanding the Types of White Blood Cells
The human body is a complex ecosystem, constantly battling invaders and maintaining internal balance. A crucial part of this defense system is the immune system, and within it, a critical component is the white blood cell (WBC), or leukocyte. These cells are responsible for identifying and eliminating pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and fungi. White blood cells are broadly classified into two main categories: granulocytes and agranulocytes. This article will delve deep into these categories, focusing on granulocytes and specifically addressing the question: "All of the following are granulocytes except...?" We'll explore the characteristics, functions, and clinical significance of each type of white blood cell to fully understand the nuances of this complex system.
Granulocytes: The Defenders with Granules
Granulocytes are named for the presence of prominent granules within their cytoplasm. These granules contain various enzymes and other substances that are crucial for their defensive functions. The granules are visible under a light microscope, a key characteristic distinguishing them from agranulocytes. There are three main types of granulocytes:
1. Neutrophils: The First Responders
Neutrophils are the most abundant type of white blood cell, making up 50-70% of the total WBC count. These are often called the "first responders" of the immune system, rapidly migrating to sites of infection or inflammation. Their granules contain a variety of enzymes, including lysozyme, myeloperoxidase, and elastase, which are crucial for destroying bacteria and other pathogens through phagocytosis – the process of engulfing and digesting foreign particles.
Key Features of Neutrophils:
- Multi-lobed nucleus: Their nucleus is characteristically segmented into 2-5 lobes, giving them a distinctive appearance under the microscope.
- Neutral staining granules: The granules stain a pale lilac color with standard hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stains, hence the name "neutrophil."
- Phagocytic activity: Their primary function is phagocytosis, actively engulfing and destroying bacteria, fungi, and other pathogens.
- Release of antimicrobial substances: They release a range of antimicrobial substances, including reactive oxygen species (ROS), to kill pathogens.
- Important in acute inflammation: They play a central role in acute inflammatory responses, helping to contain and eliminate infections.
2. Eosinophils: The Parasite Fighters
Eosinophils represent a smaller percentage of the total WBC count (1-6%). While they also participate in phagocytosis, their primary role is in combating parasitic infections. Their granules contain major basic protein (MBP) and eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), highly effective against parasites. They are also involved in allergic reactions and inflammatory processes.
Key Features of Eosinophils:
- Bilobed nucleus: Their nucleus is usually bilobed.
- Bright red-orange granules: Their granules stain bright red-orange with eosin, hence the name "eosinophil."
- Parasite defense: They are crucial in defending against parasitic infections, releasing cytotoxic granules to kill parasites.
- Allergic reactions: They play a role in allergic reactions and asthma, releasing mediators that can contribute to inflammation.
- Modulation of immune responses: Eosinophils can modulate both innate and adaptive immune responses.
3. Basophils: The Histamine and Heparin Producers
Basophils are the least abundant type of granulocyte, constituting less than 1% of the total WBC count. These cells are involved in allergic reactions and inflammatory responses. Their granules contain histamine, heparin, and other mediators that contribute to inflammation and vasodilation.
Key Features of Basophils:
- Bilobed or irregular nucleus: Their nucleus is often obscured by large, dark-staining granules.
- Dark purple-blue granules: Their granules stain a dark purple-blue with basic dyes.
- Histamine release: They release histamine, a potent vasodilator that contributes to inflammation and allergic symptoms.
- Heparin release: They release heparin, an anticoagulant that prevents blood clotting.
- Role in allergic and inflammatory responses: They play a significant role in immediate hypersensitivity reactions (allergies) and inflammatory processes.
Agranulocytes: The Lymphocytes and Monocytes
In contrast to granulocytes, agranulocytes lack prominent granules in their cytoplasm. They are also crucial for immune function, but their roles and mechanisms differ significantly. The two major types of agranulocytes are lymphocytes and monocytes.
1. Lymphocytes: The Adaptive Immunity Specialists
Lymphocytes are a major component of the adaptive immune system, responsible for targeted and long-lasting immunity. They are further subdivided into several types, including B cells, T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
- B cells: Produce antibodies that specifically target and neutralize pathogens.
- T cells: Coordinate immune responses, directly attacking infected cells, and regulating other immune cells. Different subtypes of T cells, such as helper T cells (Th cells) and cytotoxic T cells (Tc cells), play distinct roles.
- NK cells: Identify and destroy infected or cancerous cells without prior sensitization.
Key Features of Lymphocytes:
- Large, round nucleus: They have a large, round nucleus that occupies most of the cell volume.
- Scanty cytoplasm: They have a relatively small amount of cytoplasm.
- Adaptive immunity: They are central to the adaptive immune response, providing specific and long-lasting immunity.
- Memory cells: Some lymphocytes, particularly B and T cells, form memory cells, providing long-term protection against re-infection.
2. Monocytes: The Phagocytic Giants
Monocytes are the largest type of white blood cell. They circulate in the blood and then migrate to tissues, differentiating into macrophages and dendritic cells.
- Macrophages: Large phagocytic cells that engulf and destroy pathogens, cellular debris, and other foreign materials. They also present antigens to lymphocytes, bridging the innate and adaptive immune systems.
- Dendritic cells: Antigen-presenting cells that play a critical role in initiating adaptive immune responses. They capture antigens from pathogens and then present them to lymphocytes, activating them to mount an immune response.
Key Features of Monocytes:
- Kidney-shaped or horseshoe-shaped nucleus: Monocytes have a characteristic kidney-shaped or horseshoe-shaped nucleus.
- Abundant cytoplasm: They have a relatively large amount of cytoplasm.
- Phagocytosis: They are potent phagocytes, engulfing and destroying pathogens and cellular debris.
- Antigen presentation: They act as antigen-presenting cells (APCs), initiating adaptive immune responses.
Answering the Question: All of the Following Are Granulocytes Except...
Now, we can finally address the core question: "All of the following are granulocytes except...?" The answer will always be an agranulocyte. A typical question might list neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and lymphocytes (or monocytes). Lymphocytes and monocytes are agranulocytes, lacking the prominent cytoplasmic granules characteristic of neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.
Clinical Significance: Understanding Abnormal White Blood Cell Counts
Analyzing the different types of white blood cells, particularly their relative proportions, is a crucial aspect of diagnosing various medical conditions. A complete blood count (CBC) with a differential is a common blood test that provides information on the number and types of white blood cells. Abnormalities in white blood cell counts can indicate various conditions:
- Neutrophilia: An elevated neutrophil count can suggest bacterial infection, inflammation, or stress.
- Neutropenia: A low neutrophil count can increase susceptibility to infections.
- Eosinophilia: Elevated eosinophil counts can indicate parasitic infections, allergic reactions, or certain types of cancer.
- Eosinopenia: Low eosinophil counts can be associated with certain conditions, such as Cushing's syndrome.
- Basophilia: Elevated basophil counts can be associated with allergic reactions, certain cancers, or hypothyroidism.
- Lymphocytosis: Elevated lymphocyte counts can suggest viral infections, certain types of leukemia, or other immune disorders.
- Lymphocytopenia: Low lymphocyte counts can indicate severe infections, autoimmune diseases, or immunosuppression.
- Monocytosis: Elevated monocyte counts can suggest chronic infections, autoimmune diseases, or certain types of leukemia.
Conclusion: The Intricate World of White Blood Cells
Understanding the different types of white blood cells, their characteristics, and their functions is essential for comprehending the complexities of the immune system. Granulocytes, with their distinct granules and roles in innate immunity, play a crucial first-line defense against pathogens. Agranulocytes, including lymphocytes and monocytes, are fundamental to both innate and adaptive immunity, providing targeted and long-lasting protection. By understanding the distinctions between these cell types and recognizing abnormalities in their counts, healthcare professionals can diagnose and manage a wide range of medical conditions. The immune system, with its intricate network of cells and processes, remains a fascinating and vital area of ongoing research and discovery. The continuing study of white blood cells and their interactions offers promising avenues for developing new treatments and therapies for infectious diseases, cancers, and autoimmune disorders.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Chamber Of Heart Has Thickest Wall
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 1 2 Miles
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lines Of Symmetry On A Trapezoid
Mar 18, 2025
-
Two Same Words With Different Meanings
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about All Of The Following Are Granulocytes Except . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
