According To Mendel's Law Of Segregation
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
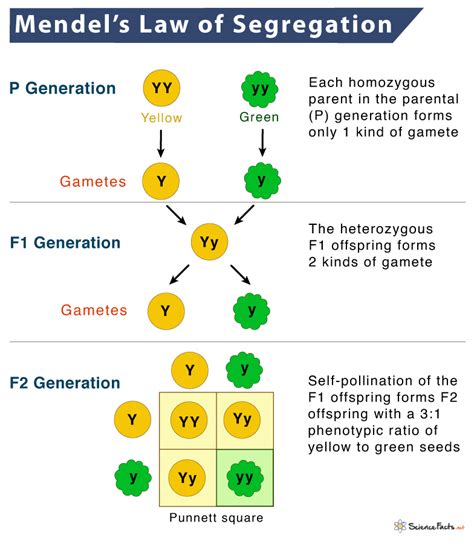
Table of Contents
According to Mendel's Law of Segregation: A Deep Dive into Inheritance
Gregor Mendel's groundbreaking work in the mid-1800s revolutionized our understanding of heredity. His meticulous experiments with pea plants led to the formulation of two fundamental laws of inheritance: the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment. This article will delve deep into Mendel's Law of Segregation, exploring its principles, mechanisms, and significance in modern genetics. We'll examine how this law explains the transmission of traits from one generation to the next, and its implications for understanding genetic diversity and predicting offspring phenotypes.
Understanding the Core Principle: Alleles and Their Separation
At the heart of Mendel's Law of Segregation lies the concept of alleles. Alleles are different versions of a gene that occupy the same locus (position) on homologous chromosomes. Each individual inherits two alleles for each gene – one from each parent. These alleles can be identical (homozygous) or different (heterozygous). The law states that during gamete (sperm and egg) formation, these paired alleles segregate (separate) randomly so that each gamete receives only one allele for each gene.
The Significance of Gamete Formation
The process of meiosis, which produces gametes, is crucial to understanding the Law of Segregation. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and then separate, ensuring that each daughter cell (gamete) receives only one chromosome from each homologous pair. Since alleles are located on these chromosomes, this separation of homologous chromosomes leads to the segregation of alleles. This random separation is what drives the variation seen in offspring.
Illustrating Segregation with a Monohybrid Cross
Let's illustrate this with a classic example: Mendel's pea plant experiment focusing on flower color. Let's assume that 'P' represents the dominant allele for purple flowers, and 'p' represents the recessive allele for white flowers. A homozygous dominant plant (PP) will have purple flowers, a homozygous recessive plant (pp) will have white flowers, and a heterozygous plant (Pp) will also have purple flowers (due to the dominance of 'P').
If we cross a homozygous purple-flowered plant (PP) with a homozygous white-flowered plant (pp), all the offspring (F1 generation) will be heterozygous (Pp) and have purple flowers. This is because each parent contributes one allele, and the dominant 'P' allele masks the recessive 'p' allele.
However, if we then cross two heterozygous plants (Pp x Pp), the Law of Segregation comes into play. During gamete formation, the 'P' and 'p' alleles in each parent separate. This leads to the following possible combinations in the offspring (F2 generation):
- PP: Homozygous dominant (purple flowers) – 25% probability
- Pp: Heterozygous (purple flowers) – 50% probability
- pp: Homozygous recessive (white flowers) – 25% probability
This 3:1 phenotypic ratio (purple:white) is a classic demonstration of Mendel's Law of Segregation. The reappearance of the white flower phenotype in the F2 generation confirms the segregation of alleles during gamete formation.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Scenarios
While the monohybrid cross provides a clear illustration of the Law of Segregation, the principles extend to more complex scenarios involving multiple genes and different inheritance patterns.
Dihybrid Crosses and Independent Assortment
Mendel also explored dihybrid crosses, involving two different genes. His findings led to the formulation of the Law of Independent Assortment, which states that during gamete formation, the segregation of alleles for one gene is independent of the segregation of alleles for another gene, assuming the genes are located on different chromosomes.
For example, considering two traits – flower color (P/p) and seed shape (R/r), where R represents round seeds and r represents wrinkled seeds – a dihybrid cross between two heterozygous plants (PpRr x PpRr) will result in a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation, demonstrating both segregation and independent assortment. This ratio reflects the various combinations of alleles inherited for both traits.
Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
Mendel's Law of Segregation also holds true for inheritance patterns beyond simple dominance. In incomplete dominance, the heterozygote exhibits an intermediate phenotype. For example, if 'R' represents red flowers and 'r' represents white flowers, an 'Rr' heterozygote might show pink flowers. Even with this blending of phenotypes, the alleles still segregate independently during gamete formation.
Codominance occurs when both alleles are fully expressed in the heterozygote. For instance, in certain flower types, an 'Rr' heterozygote might show both red and white patches on the petals. Again, the segregation of alleles remains consistent with Mendel's law.
Epistasis and Other Gene Interactions
The Law of Segregation provides a foundational understanding of inheritance, but it doesn't encompass all the complexities of gene interactions. Epistasis, for example, occurs when one gene affects the expression of another. In such cases, the phenotypic ratios observed may deviate from those predicted by simple Mendelian principles.
Nevertheless, the underlying principle of allele segregation during gamete formation remains crucial, even in the context of gene interactions. Understanding the complexities of these interactions requires a deeper understanding of gene regulation and expression.
The Significance of Mendel's Law of Segregation in Modern Genetics
Mendel's Law of Segregation laid the groundwork for modern genetics. Its implications extend far beyond the simple inheritance patterns observed in pea plants.
Understanding Genetic Disorders
The law is crucial for understanding the inheritance of genetic disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles. Individuals who are heterozygous (carrying one copy of the recessive allele) are usually unaffected (carriers), but they can transmit the recessive allele to their offspring. Knowing the segregation patterns helps predict the probability of affected offspring in families with a history of such disorders.
Genetic Counseling and Predictive Testing
Genetic counselors utilize Mendel's principles to advise families about the risks of inherited conditions. They can help couples estimate the probability of having children with certain genetic diseases based on their family history and the inheritance pattern of the disorder. Predictive genetic testing also relies on these principles to assess individual risk.
Plant and Animal Breeding
The Law of Segregation is fundamental to plant and animal breeding. Breeders use Mendel's principles to select and cross individuals with desired traits, increasing the frequency of those traits in subsequent generations. Understanding how alleles segregate helps breeders make informed decisions about which individuals to breed.
Understanding Evolution
Mendel's work, including the Law of Segregation, is a cornerstone of evolutionary biology. The variation generated by the segregation of alleles is the raw material upon which natural selection acts. The random shuffling of alleles during sexual reproduction ensures that each individual is genetically unique, contributing to the diversity of life and the ongoing process of evolution.
Conclusion: A Lasting Legacy
Mendel's Law of Segregation remains a fundamental principle in genetics. Although its initial application was limited to observable traits in pea plants, its principles have broad implications across various fields of biology, including medicine, agriculture, and evolutionary biology. Understanding this law is essential for comprehending the mechanisms of inheritance, predicting offspring phenotypes, and interpreting complex genetic phenomena. Its lasting legacy continues to shape our understanding of life itself, driving ongoing research and advancements in genetics and related fields. The simplicity and elegance of Mendel's work, combined with its profound impact, solidifies its place as a cornerstone of modern biological science.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Mn Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lines Of Symmetry On A Trapezoid
Mar 18, 2025
-
Two Same Words With Different Meanings
Mar 18, 2025
-
Select The Correct Statement About Equilibrium
Mar 18, 2025
-
Draw The Major Product Of The Following Reaction
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about According To Mendel's Law Of Segregation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
