A Wheelbarrow Is An Example Of Which Class Of Lever
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
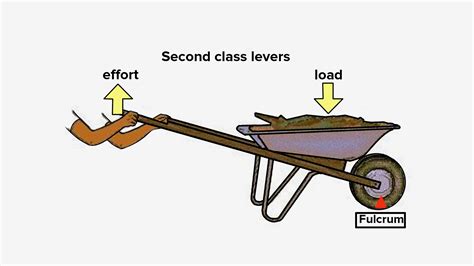
Table of Contents
A Wheelbarrow: A Class 2 Lever Explained
A wheelbarrow, that seemingly simple tool found in gardens and construction sites worldwide, provides a fascinating example of a fundamental physics principle: the lever. Understanding its classification as a Class 2 lever is key to appreciating its efficiency and the broader concept of mechanical advantage. This article will delve deep into the mechanics of a wheelbarrow, explaining its lever classification, exploring its components, and examining its application in various contexts. We'll also explore the broader implications of understanding lever systems and their role in everyday life.
Understanding the Three Classes of Levers
Before we pinpoint the wheelbarrow's lever class, let's briefly review the three types:
1. Class 1 Lever: In a Class 1 lever, the fulcrum (the pivot point) is located between the effort (the force applied) and the load (the weight being moved). Think of a seesaw—the fulcrum is the center, the effort is your pushing down on one side, and the load is your friend on the other.
2. Class 2 Lever: Here, the load is positioned between the fulcrum and the effort. A wheelbarrow perfectly embodies this type. The wheel acts as the fulcrum, the load (e.g., bricks, soil) is in the middle, and the effort is the force applied to the handles.
3. Class 3 Lever: In a Class 3 lever, the effort is applied between the fulcrum and the load. Think of your forearm—your elbow is the fulcrum, your bicep's contraction is the effort, and the weight in your hand is the load. Most levers in the human body fall into this category.
The Wheelbarrow as a Class 2 Lever: A Detailed Analysis
The wheelbarrow's design brilliantly utilizes the principles of a Class 2 lever to amplify the user's force, making it easier to move heavy loads. Let's dissect its components and their roles within this lever system:
-
Fulcrum: The wheel itself acts as the fulcrum, providing the pivot point around which the entire system rotates. Its position is crucial; it must be stable and able to withstand the forces involved.
-
Load: This is the material being transported—dirt, rocks, bricks, concrete, etc. The load's weight is the resistance that must be overcome. The further the load is positioned from the wheel (within limits), the greater the mechanical advantage. However, a very far load will require more force on the handles to lift. There is an optimum distance.
-
Effort: This is the force applied by the user to the handles of the wheelbarrow. The closer the effort is applied to the wheel (the shorter the handle), the less mechanical advantage is available. The longer the handle, the less effort required. This is why manufacturers use a design that provides enough leverage for the effort but doesn't make the wheelbarrow unwieldy.
Mechanical Advantage and Efficiency
The wheelbarrow's efficiency is directly linked to its mechanical advantage. Mechanical advantage refers to the ratio of the output force (the force overcoming the load) to the input force (the effort applied). In a Class 2 lever, the mechanical advantage is always greater than 1, meaning the wheelbarrow multiplies the user's effort. This magnification of force is what allows a person to move significantly heavier loads than they could lift directly.
The mechanical advantage of a Class 2 lever, including a wheelbarrow, is calculated as follows:
Mechanical Advantage = Distance from Fulcrum to Effort / Distance from Fulcrum to Load
By increasing the distance from the wheel to the handles (effort), and decreasing the distance from the wheel to the load, the mechanical advantage of the wheelbarrow increases. However, it's essential to maintain stability and balance. Increasing the handle distance too far will affect balance, rendering it difficult to control the wheelbarrow. Similarly, a weight placed too far forward risks tipping the wheelbarrow. The design optimizes this balance.
Components and Design Optimizations
Understanding the efficiency of a wheelbarrow requires considering its key components:
-
The Wheel: This is the fulcrum, and its design significantly impacts the wheelbarrow's maneuverability and overall performance. Pneumatic tires provide a smoother ride over uneven surfaces, while solid rubber tires offer more durability. The wheel bearings are also crucial for minimizing friction.
-
The Handles: The length and design of the handles directly affect the mechanical advantage. Longer handles provide greater leverage, requiring less effort, but also make it more challenging to control. The handles' grip and overall ergonomics also significantly influence user comfort and efficiency.
-
The Tray (or Tub): The tray's design should be suited for the type of load being carried. It needs to be strong enough to hold the load, and the shape may be optimized to prevent spillage, particularly in the case of loose materials such as sand or soil.
-
The Frame: The frame connects the wheel, handles, and tray, and its strength is essential for overall stability and longevity. The frame’s material and construction affect the weight of the wheelbarrow itself.
Applications and Everyday Relevance
The wheelbarrow's applications are vast, extending far beyond the home garden:
-
Construction: Moving bricks, cement, gravel, and other building materials is a fundamental task in construction, and the wheelbarrow is indispensable for efficient transport.
-
Agriculture: In farming, wheelbarrows are used to transport harvested crops, fertilizers, and other agricultural supplies.
-
Landscaping: From moving soil and mulch to transporting plants, wheelbarrows are essential for landscaping projects of all sizes.
-
Material Handling: In many industries, wheelbarrows assist in short-distance material transportation, offering a simple and efficient solution.
-
Disaster Relief: In emergency situations, wheelbarrows can be crucial for moving supplies and equipment.
The wheelbarrow's ubiquitous presence highlights its enduring utility and effectiveness as a simple yet powerful application of the Class 2 lever principle.
Beyond the Wheelbarrow: Class 2 Levers in Everyday Life
Numerous everyday objects utilize the Class 2 lever principle:
-
Nutcrackers: The nut is the load, the hinge is the fulcrum, and your hand applies the effort.
-
Bottle Openers: The cap is the load, the bottle opener's pivot is the fulcrum, and your hand applies the effort.
-
Oar of a Rowboat: The water is the fulcrum, the resistance of the water is the load and the effort is from the rower.
-
Wheelchair: The wheels are the fulcrum, the user's body is the load, and the hands are used for the effort to propel.
Understanding the Class 2 lever principle is not just about understanding the mechanics of a wheelbarrow; it provides a broader understanding of how simple machines enhance human effort.
Conclusion: Leveraging Knowledge for Greater Efficiency
The seemingly simple wheelbarrow serves as a compelling illustration of the Class 2 lever system. Its design, employing the principles of mechanical advantage, demonstrates the power of physics in everyday tools. By understanding the mechanics of levers, we gain insights into efficiency, design, and the amplification of human effort. The wheelbarrow's widespread adoption across various sectors underscores its enduring relevance and the enduring value of simple yet effective mechanical solutions. From the garden to the construction site, the wheelbarrow remains a testament to the enduring power of leveraging the principles of physics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
18 Quarts Equals How Many Gallons
Mar 23, 2025
-
Pertaining To Destruction Of Worn Out Red Blood Cells
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Was A Main Benefit Of Industrialization
Mar 23, 2025
-
The Major Product Of The Following Reaction Is
Mar 23, 2025
-
1 5 To The Power Of 3
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Wheelbarrow Is An Example Of Which Class Of Lever . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
