A Firm Earns A Normal Profit When Its
News Leon
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
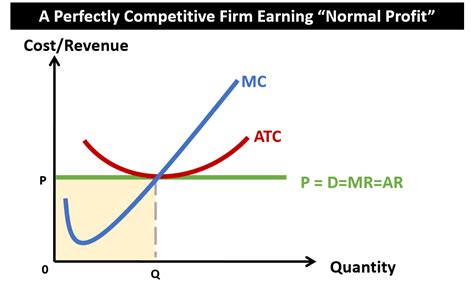
Table of Contents
A Firm Earns a Normal Profit When Its… Total Revenue Equals Total Cost
Understanding profit is fundamental to comprehending how firms operate within a market economy. While the pursuit of maximizing profits is a common business objective, the concept of "normal profit" often causes confusion. This article delves into the intricacies of normal profit, explaining when a firm achieves it and the crucial role it plays in market equilibrium and firm decision-making. We'll explore various market structures and analyze how normal profit functions within each.
What is Normal Profit?
Normal profit isn't the absence of profit; instead, it represents the minimum level of profit required to keep a firm in its current market. It's the return a firm needs to cover all its explicit and implicit costs. Let's break down those cost components:
-
Explicit Costs: These are the direct, out-of-pocket payments a firm makes, such as wages, rent, raw materials, and utilities. These are easily quantifiable and appear on a firm's accounting statements.
-
Implicit Costs: These are the opportunity costs of using resources the firm already owns. For example, if a firm uses its own building instead of renting it out, the forgone rental income represents an implicit cost. Similarly, the owner's time and effort invested in the business represent an implicit cost, often measured as the salary they could earn elsewhere.
A firm earns a normal profit when its total revenue (TR) exactly equals its total cost (TC), where TC includes both explicit and implicit costs. In simpler terms: TR = TC. This means the firm is covering all its costs, including the opportunity cost of using its resources. It's earning just enough to stay in business; there's no economic profit, but neither is there a loss.
Normal Profit vs. Economic Profit
It's crucial to differentiate between normal profit and economic profit:
-
Normal Profit: As discussed, this is the minimum profit needed to stay in business. It's included in the total cost calculation.
-
Economic Profit: This is the profit above and beyond normal profit. It's the difference between total revenue and total economic cost (explicit and implicit costs). A firm earns economic profit when TR > TC. This extra profit attracts new firms to the market, increasing competition.
Normal Profit in Different Market Structures
The achievement of normal profit varies significantly depending on the market structure:
1. Perfect Competition
In a perfectly competitive market, characterized by many buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, free entry and exit, and perfect information, firms earn only normal profit in the long run. The free entry and exit mechanism ensures that if firms earn economic profits, new firms will enter the market, increasing supply and driving down prices until economic profits are eliminated. Conversely, if firms incur losses, some firms will exit, reducing supply and increasing prices until normal profit is restored. Therefore, long-run equilibrium in perfect competition is characterized by firms earning zero economic profit, or simply normal profit.
2. Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition features many firms selling differentiated products. Firms have some degree of market power due to product differentiation. In the short run, monopolistically competitive firms might earn economic profits. However, in the long run, similar to perfect competition, new firms enter the market attracted by these profits. This increased competition erodes the market share of existing firms, reducing prices and ultimately pushing economic profits down to zero, leaving firms with normal profits. However, unlike perfect competition, monopolistic competition firms have some degree of market power due to product differentiation, which means they can charge a price slightly above their marginal cost, ensuring that they stay in the business with normal profit.
3. Oligopoly
Oligopolies are dominated by a few large firms. The interaction between these firms significantly impacts the market price and output. The profit levels in an oligopoly are less predictable than in perfect or monopolistic competition. Firms might earn economic profits in the long run due to barriers to entry, such as high start-up costs or economies of scale. However, intense competition among existing firms could also lead to lower profit levels, even close to normal profit in some cases. Collusion among firms, albeit illegal in many countries, could also lead to higher than normal profits.
4. Monopoly
A monopoly is characterized by a single seller controlling the entire market. Monopolies can restrict supply to maintain higher prices and earn significant economic profits in the long run. Barriers to entry, such as patents, government regulations, or control over essential resources, prevent new firms from entering the market. Therefore, monopolies can earn sustained economic profits above normal profit.
The Significance of Normal Profit
The concept of normal profit is crucial for several reasons:
-
Market Equilibrium: Normal profit plays a vital role in establishing long-run market equilibrium. It indicates that resources are allocated efficiently; firms are earning just enough to cover their costs, including the opportunity cost of resources.
-
Resource Allocation: When firms earn normal profit, it signals that resources are being used efficiently within the market. Firms are neither exiting nor entering en masse, which would disturb the balance of supply and demand.
-
Firm Decision-Making: Normal profit serves as a benchmark for firms evaluating their performance. If a firm is earning less than normal profit, it might consider restructuring, exiting the market, or seeking more efficient operations.
-
Innovation and Efficiency: While earning normal profit might not be exciting, it promotes efficiency. Firms will constantly seek ways to improve their production processes to reduce costs and increase competitiveness to stay in business.
-
Economic Stability: The presence of normal profit signifies a degree of stability in the market. It prevents excessive entry or exit, which can cause fluctuations in prices and output.
Factors Affecting Normal Profit
Several factors can influence the level of normal profit a firm earns:
-
Market Demand: Strong demand allows firms to charge higher prices and earn higher profits, potentially exceeding normal profit.
-
Production Costs: Efficient production processes and low costs are vital for achieving and exceeding normal profit.
-
Technology: Technological advancements can reduce production costs, enhancing profitability.
-
Competition: Intense competition limits a firm's ability to charge higher prices, potentially reducing profits towards normal profit.
-
Government Regulations: Regulations can impact costs and pricing, affecting profitability.
-
Economic Conditions: The overall state of the economy, like inflation or recession, influences market demand and production costs, affecting the level of normal profit.
Conclusion: Normal Profit - A Foundation of Economic Stability
The concept of normal profit, often overlooked in favor of discussions about economic profits, is fundamental to understanding market dynamics and firm behavior. It represents the minimum return required to maintain operations, signifying efficient resource allocation and long-run market equilibrium. Although often not the ultimate goal of many businesses, achieving normal profit is the essential threshold, reflecting the firm's capacity to compete and thrive within its respective market structure. By grasping the nuances of normal profit, we gain deeper insights into the intricacies of market economies and the essential factors driving firm success and sustainability. Understanding the distinction between normal and economic profit helps businesses make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and navigate the complexities of the competitive landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Reactions Which Do Not Continue To Completion Are Called Reactions
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Is Five Hours
Mar 14, 2025
-
Flowering Plants Are Also Known As
Mar 14, 2025
-
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Proprietary Software
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Has The Shortest Wavelength
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Firm Earns A Normal Profit When Its . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
