A Deuterium Nucleus Contains Which Of The Following
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
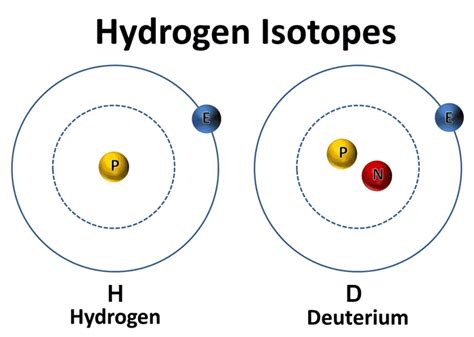
Table of Contents
A Deuterium Nucleus Contains Which of the Following? Understanding Isotopes and Nuclear Composition
The question, "A deuterium nucleus contains which of the following?" probes our understanding of atomic structure, isotopes, and nuclear physics. While seemingly simple, it opens the door to exploring fundamental concepts crucial in various scientific fields. This in-depth article will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the broader implications of deuterium's unique composition and its significance in science and technology.
Understanding the Basics: Protons, Neutrons, and Atomic Nuclei
Before we address deuterium specifically, let's establish a foundation in basic atomic structure. Every atom consists of a nucleus, containing positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The number of protons defines the element – for example, an atom with one proton is hydrogen, an atom with two is helium, and so on. This number is known as the atomic number.
The number of neutrons in an atom can vary, even within the same element. These variations are called isotopes. Isotopes have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties significantly. Isotopes are often represented by the element's symbol with a superscript indicating the mass number (the total number of protons and neutrons).
Deuterium: The Heavy Hydrogen Isotope
Now, let's focus on deuterium. Deuterium, often denoted as ²H or D, is a stable isotope of hydrogen. Remember, hydrogen's atomic number is 1, meaning it has one proton. So, what distinguishes deuterium?
The answer to the question "A deuterium nucleus contains which of the following?" is: one proton and one neutron.
Unlike the most common isotope of hydrogen, protium (¹H), which only has one proton and no neutrons, deuterium possesses an extra neutron in its nucleus. This extra neutron significantly increases its mass, hence the term "heavy hydrogen."
The Significance of the Extra Neutron
This seemingly small difference – a single neutron – has profound implications:
-
Mass: Deuterium is approximately twice as massive as protium because of the additional neutron. This mass difference has significant consequences in various chemical and physical processes.
-
Nuclear Stability: While both protium and deuterium are stable, the presence of the neutron in deuterium contributes to its stability. The strong nuclear force holding the nucleus together is stronger in deuterium due to the extra neutron mediating between the proton and itself.
-
Nuclear Reactions: Deuterium's unique nuclear composition makes it a crucial player in nuclear reactions, including nuclear fusion. It is a key component in nuclear fusion reactions, such as those occurring in the sun and considered for future energy generation.
Isotopes Beyond Deuterium: Tritium and Others
Hydrogen has another isotope, tritium (³H or T), which has one proton and two neutrons. Unlike deuterium, tritium is radioactive, undergoing beta decay with a half-life of approximately 12.3 years. This radioactivity arises from the instability of the nucleus with two neutrons.
Other elements also possess multiple isotopes, some stable and others radioactive. The study of isotopes provides valuable insights into various aspects of:
-
Geology: Isotope ratios in rocks and minerals can be used to date geological formations and understand Earth's history.
-
Archaeology: Radioactive isotopes like carbon-14 are used in radiocarbon dating to determine the age of ancient artifacts.
-
Medicine: Radioactive isotopes are used in medical imaging and treatment, such as PET scans and radiotherapy.
-
Environmental Science: Isotope analysis helps track pollution sources and monitor environmental changes.
Applications of Deuterium: From Nuclear Fusion to MRI
The unique properties of deuterium have led to its diverse applications across various fields:
Nuclear Fusion: The Power of the Future?
Deuterium is a crucial fuel for nuclear fusion reactions. Fusion reactions involve combining light atomic nuclei to form heavier ones, releasing enormous amounts of energy in the process. Deuterium-tritium fusion is a promising avenue for clean and sustainable energy production. While achieving controlled fusion remains a significant technological challenge, the potential benefits are immense.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Seeing Inside
Deuterium's nuclear magnetic properties are exploited in NMR and MRI technologies. These techniques utilize the interaction of atomic nuclei with magnetic fields to generate images of internal structures. Deuterium's distinct magnetic properties allow for specific targeting and enhanced image contrast in certain applications.
Scientific Research: A Versatile Tool
Deuterium's unique properties make it a valuable tool in various scientific research areas. It's used as a tracer in chemical reactions and biological processes, providing insights into molecular mechanisms and dynamics. The difference in mass between protium and deuterium can cause kinetic isotope effects, allowing scientists to study reaction mechanisms and enzyme kinetics.
Other Applications: A Broad Spectrum
Deuterium also finds application in other areas, including:
-
Neutron sources: Deuterium-based targets are used in neutron generators for various applications, including material analysis and industrial processes.
-
Heavy water reactors: Heavy water (D₂O), which contains deuterium instead of protium, is used as a moderator in some nuclear reactors.
-
Chemical synthesis: Deuterium-labeled compounds are used in chemistry to study reaction mechanisms and molecular properties.
Conclusion: Beyond a Simple Answer
The simple answer to the question, "A deuterium nucleus contains which of the following?" is one proton and one neutron. However, this seemingly straightforward response unveils a rich and fascinating world of isotopic variations, nuclear physics, and technological advancements. Understanding the unique composition and properties of deuterium offers crucial insights into fundamental scientific principles and fosters technological innovation across diverse fields, from energy production to medical imaging and beyond. The study of deuterium serves as a microcosm of the broader understanding of atomic structure, isotopes, and the profound implications of subtle changes in nuclear composition.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Moderate Wind Accelerates A Pebble
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Are Animals Called That Feed On Herbivores
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Changes Are Chemical Changes
Mar 24, 2025
-
Molar Mass Of Helium In Kg
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is Meant By Regional Political Party
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Deuterium Nucleus Contains Which Of The Following . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
