1 K W H Is Equal To
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
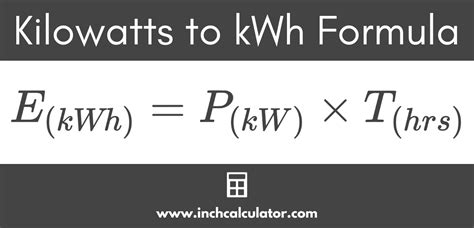
Table of Contents
1 kWh is Equal To: Understanding Kilowatt-Hours and Energy Consumption
Understanding energy consumption is crucial in today's world. Whether you're trying to reduce your carbon footprint, lower your energy bills, or simply grasp the fundamentals of electricity, comprehending the unit of measurement – the kilowatt-hour (kWh) – is essential. This comprehensive guide delves deep into what 1 kWh is equal to, exploring its various interpretations and practical applications.
What is a Kilowatt-Hour (kWh)?
At its core, a kilowatt-hour (kWh) represents a unit of energy. It's not a measure of power, but rather a measure of energy consumed over time. To understand this, let's break down the components:
-
Kilowatt (kW): This refers to the rate at which energy is used or generated. Think of it like the speed of a car. A 1 kW device consumes energy at a rate of 1,000 watts.
-
Hour (h): This represents the duration over which the energy is consumed. Think of it like the time the car is driving.
Therefore, 1 kWh signifies the energy consumed by a 1 kW device operating for one hour. This seemingly simple definition opens doors to a vast array of practical applications and interpretations.
1 kWh: Different Interpretations and Analogies
Understanding 1 kWh can be made easier through relatable analogies and different perspectives:
1. The Household Appliance Perspective
Imagine a 100-watt light bulb. To consume 1 kWh of energy, this bulb would need to remain lit for 10 hours (100 watts x 10 hours = 1000 watt-hours = 1 kWh). A 1 kW appliance, such as a microwave, would consume 1 kWh in just one hour of continuous use.
This perspective helps us visualize the energy consumption of everyday devices. By knowing the wattage of your appliances, you can estimate their energy usage over time.
2. The Heating and Cooling Perspective
Heating and cooling systems often consume significant amounts of energy. A 1 kWh energy consumption might represent a small portion of the energy used to heat a room for a short period, depending on the system's efficiency and the room's size. Similarly, it might only cool a small area for a limited time.
This perspective highlights the energy intensity of climate control systems and the importance of energy-efficient solutions.
3. The Transportation Perspective
Electric vehicles (EVs) commonly use kWh as a measure of energy consumption. The range of an EV depends on its battery capacity (measured in kWh) and its energy efficiency. A 1 kWh charge might only add a few kilometers to the vehicle's driving range, depending on the vehicle's efficiency and factors such as terrain and driving style.
This perspective emphasizes the growing role of kWh in the transportation sector and the ongoing development of energy-efficient vehicles.
4. The Industrial Perspective
In industrial settings, 1 kWh might represent a tiny fraction of the energy used by heavy machinery or large-scale manufacturing processes. Large factories often consume hundreds or thousands of kWh daily.
This perspective demonstrates the scale of energy consumption in industrial applications and the need for energy-efficient industrial processes.
Calculating Energy Consumption: Beyond 1 kWh
While understanding 1 kWh provides a fundamental grasp of energy consumption, calculating the energy usage of various devices and systems requires more extensive calculations. Here's a breakdown:
Formula: Energy (kWh) = Power (kW) x Time (hours)
Example: A 2 kW electric heater running for 30 minutes consumes:
Energy (kWh) = 2 kW x (30 minutes / 60 minutes/hour) = 1 kWh
This formula allows you to calculate the energy consumption of any device given its power rating and operating time.
The Environmental Impact of 1 kWh
The environmental impact of 1 kWh varies significantly depending on the source of the electricity. Electricity generated from renewable sources, such as solar or wind power, has a much smaller carbon footprint than electricity generated from fossil fuels, like coal or natural gas.
Understanding the source of your electricity is crucial for assessing the environmental impact of your energy consumption. Choosing energy-efficient appliances and reducing overall energy consumption are key steps towards minimizing your carbon footprint.
Reducing Energy Consumption: Practical Tips
Saving energy is not only environmentally responsible but also economically beneficial. Here are some practical tips for reducing your energy consumption:
- Switch to LED lighting: LED bulbs consume significantly less energy than incandescent bulbs.
- Unplug electronics when not in use: Many devices continue to consume energy even when turned off.
- Use energy-efficient appliances: Look for appliances with high energy efficiency ratings.
- Improve home insulation: Better insulation reduces the energy needed for heating and cooling.
- Utilize natural light: Open curtains and blinds to take advantage of natural light during the day.
- Programmable thermostats: Set your thermostat to automatically adjust temperatures when you're away or asleep.
- Conserve water: Heating water consumes significant energy. Take shorter showers and fix leaky faucets.
- Monitor energy usage: Use smart meters or energy monitoring tools to track your energy consumption.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts Related to kWh
For those interested in delving deeper, here are some advanced concepts related to kWh:
- Energy efficiency: This refers to the ratio of useful energy output to total energy input. Higher energy efficiency means less energy wasted.
- Peak demand: This is the highest rate of energy consumption over a specific period. Managing peak demand can help reduce energy costs.
- Renewable energy sources: These include solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy, offering cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels.
- Net metering: This allows homeowners with solar panels to sell excess energy back to the grid.
- Time-of-use pricing: This pricing structure charges different rates for electricity depending on the time of day.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding 1 kWh
Understanding the meaning and implications of 1 kWh empowers you to make informed decisions about your energy consumption. From household appliances to large-scale industrial processes, the concept of kWh is fundamental to comprehending energy use and its environmental impact. By actively seeking ways to reduce your energy consumption and choosing renewable energy sources where possible, you can contribute to a more sustainable future. The seemingly simple unit of 1 kWh holds significant weight in shaping our energy landscape and promoting responsible energy practices. Remember that continuous learning and adaptation are essential to staying informed and making the most of available energy-saving technologies and strategies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Two Same Words With Different Meanings
Mar 18, 2025
-
Select The Correct Statement About Equilibrium
Mar 18, 2025
-
Draw The Major Product Of The Following Reaction
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Wire Loop Of Radius 10 Cm And Resistance
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Water Molecules In A Drop Of Water
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 K W H Is Equal To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
